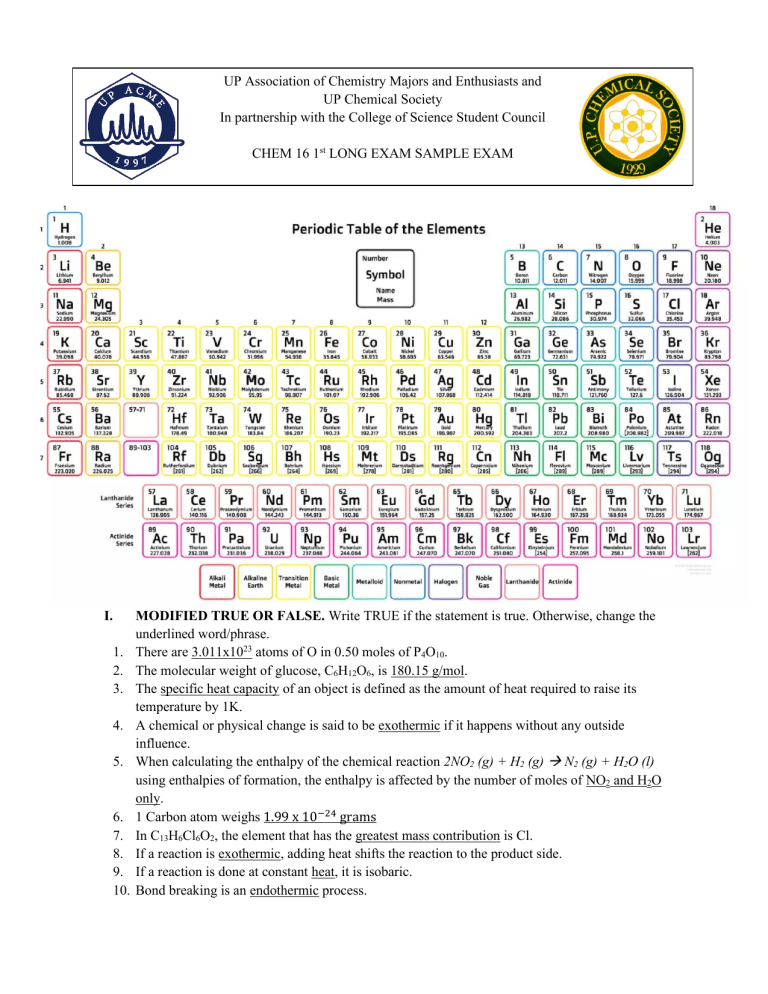
UP Association of Chemistry Majors and Enthusiasts and UP Chemical Society In partnership with the College of Science Student Council CHEM 16 1st LONG EXAM SAMPLE EXAM I. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE. Write TRUE if the statement is true. Otherwise, change the underlined word/phrase. There are 3.011x1023 atoms of O in 0.50 moles of P4O10. The molecular weight of glucose, C6H12O6, is 180.15 g/mol. The specific heat capacity of an object is defined as the amount of heat required to raise its temperature by 1K. A chemical or physical change is said to be exothermic if it happens without any outside influence. When calculating the enthalpy of the chemical reaction 2NO2 (g) + H2 (g) → N2 (g) + H2O (l) using enthalpies of formation, the enthalpy is affected by the number of moles of NO2 and H2O only. 1 Carbon atom weighs 1.99 x 10−24 grams In C13H6Cl6O2, the element that has the greatest mass contribution is Cl. If a reaction is exothermic, adding heat shifts the reaction to the product side. If a reaction is done at constant heat, it is isobaric. Bond breaking is an endothermic process. II. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Which of the following are considered as state functions? I. Internal Energy (U) III. Temperature (T) II. Pressure (P) IV. Entropy (S) a. I only b. I, IV c. I, III, IV d. I, II, III, IV 2. Which of the following is false? a. ΔH<0: ΔS>0: spontaneous at all T’s b. ΔH>0: ΔS>0: spontaneous at low T’s c. ΔH>0: ΔS>0: spontaneous at high T’s d. ΔH<0: ΔS<0: spontaneous at low T’s 3. What mass of O2 is required to completely react with 175 g of carbon disulfide (no excess is produced)? CS2 + O2 → CO2 + SO a. 24.5 g b. 221 g c. 139 g d. 41.8 g 4. Which of the following does not lead to the decrease in entropy? I. Vaporization III. Freezing II. Condensation IV. Melting a. II only b. I, IV c. II, III d. I, II, III, IV 5. Which of the following reactions is incorrectly paired with its type of aqueous reaction? a. Precipitation: 2Na3PO4 + 3MgCl2 → 6NaCl + Mg3(PO4)2 b. Neutralization: H2CO3 + 2KOH → K2CO3 + 2H2O c. Redox: CuSO4 + Pb(NO3)2 → Cu(NO3)2 + PbSO4 d. Precipitation: AlBr3 + 3NaOH → 3NaBr + Al(OH)3 6. Use Hess’s Law to determine ΔHrxn for the reaction: a. b. c. d. -3.7 kJ -289.5 kJ -853.7 kJ -4728 kJ 7. In the titration of acid A with base B (A + B → P + Q), the equivalence point of 0.5 M of acid A was known to be 12 mL of 0.25 M B. How much of acid A should be titrated? a. 0.24 L b. 0.06 L c. 6 mL d. 24 mL 8. Which of the following chemical reactions results in an increase in entropy? a. 2H2O(l) + O2 (g) → 2H2O2 (l) b. C6H12O6 (s)+ 12O2 (g) → 6CO2 (g) + 12H2O(g) c. Fe(s) + 3O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) d. N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) 9. A compound containing only C, H, and O is detected in a lab sample. It contains 75.73% C, 8.74% H, and 15.53% O. Its molecular weight is found to be 206 g/mol. What is the identity of this drug? a. Citric Acid (C6H8O7) b. Glucose (C6H12O6) c. Octylphenol (C14H22O) d. Ibuprofen (C13H18O2) 10. Given C(graphite) → C(diamond), calculate the ΔG of the reaction at 400K. Is the reaction spontaneous at the given temperature? a. 1346 J/mol, nonspontaneous b. -1346 J/ mol, spontaneous c. 3244 J/mol, nonspontaneous d. -3244 J/mol, spontaneous 11. Which of the following compounds has the highest % Oxygen composition? a. P2O5 b. H2O c. CO2 d. COOH 12. One oxide of rubidium has 0.187g Oxygen: 1g Rb. A possible O:Rb mass ratio for a second oxide of Rubidium is: a. 2.000g : 10.695g b. 0.150g : 0.803g c. 1.167g : 6.250g d. 3.145 : 16.888g 13. In a given reaction, the system gained 420 J of heat and -80 J was work done by the system. What is the total heat in the system? a. -500 J b. 500 J c. 340 J d. -340 J 14. How much heat is needed to raise the temperature of 20g of Ice from -5 ˚C to 100 ˚C of water? Given: cice = 2.14 J/g•K ∆Hf = 334 J/g cwater = 4.184 J/g •K ∆Hv = 2260 J/g csteam = 1.996 J/g•K a. 60462 kJ b. 15262 kJ c. 60462 J d. 15262 J 15. Given the phase change diagram below, the current state of the substance is represented by the yellow dot. If the temperature is increased to -50 ˚C while the pressure is held constant, then the state of the substance will be: a. Solid b. Liquid c. Gas d. Super Critical 16. Which of the following is an endothermic process? a. Formation of ice crystals b. Condensation of ethanol in distillation of alcohols c. Combustion of fuel in cars d. Sublimation of moth balls 17. Which of the following substance has a ∆H of zero? a. Ozone gas b. C (diamond) c. Bromine gas d. Au+ in aqueous solution 18. What is the empirical formula of a Cl-containing compound if it’s composed of 21.51 %C, 2.22% H, and 17.64% O? a. C4H7O2Cl4 b. C3H6O2Cl2 c. C5H6O2Cl4 d. C5H6OCl2 19. Given the following reaction and data, calculate total energy and determine whether exothermic or endothermic. a. -184 kJ; exothermic b. +184 kJ; endothermic c. +247 kJ; exothermic d. -247 kJ; endothermic 20. Which of the following compounds has an empirical formula of CH3O? a. Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) b. Acetone (CH3CH3CO) c. Ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH) d. Acetic Acid (CH3COOH) III. PROBLEM SOLVING 1. A 94.5-gram sample of an unknown hydrated magnesium sulfate compound (MgSO4•xH2O) was heated to liberate all water. The resulting weight of anhydrous magnesium sulfate was found to be 54.0 grams. a. What is the molecular formula of the hydrated magnesium sulfate compound? b. What is the hydrate’s molar mass? Report answer until the third decimal place. c. How much of the hydrate will be needed to obtain 94.5 grams of anhydrous magnesium sulfate? 2. Five (5.00) grams of a shiny grey metal is heated to 50°C in a water bath. The metal is then added to 2.21g of water in a coffee cup calorimeter, and the water temperature changed from 19°C to 25°C. a. What is the specific heat of the metal? b. How many grams of water at 19°C must originally be added to the calorimeter for the final temperature to be 20°C? c. If one mole of the metal requires 23.077 J of heat for its temperature to be raised by one degree Celsius, what is the identity of the metal? 3. Gold is present in sea water in small quantities (0.15 mg/ton). If the density of sea water is 1.03g/ml: a. How many g of gold can be extracted in 3.14 L of sea water (1 ton = 907185 grams) If the following redox reaction is observed: +3 − 𝐴𝑢(𝑠) + 𝑁𝑂3(𝑎𝑞) ↔ 𝐴𝑢(𝑎𝑞) + 𝑁𝑂2 (𝑔) b. How many moles of NO3- are needed to fully consume the gold in letter a? c. If the actual yield of NO2 (g) was 7.84 x 10-8 moles of NO2, what is the %error? 4. Glycolysis is a biochemical reaction which involves the conversion of 1 molecule of glucose to 2 lactic acid molecules. The equation is as follows: 𝐶6 𝐻12 𝑂2 (𝑠) + 𝑂2 (𝑔) → 𝐶𝑂2 (𝑔) + 𝐻2 𝑂(𝑙) → 𝐶𝐻3 𝐶𝐻(𝑂𝐻)𝐶𝑂𝑂𝐻(𝑠) The standard molar enthalpy of the reaction is determined from the standard molar enthalpy change for the combustion reactions of glucose and lactic acid using Hess’ Law. On the other hand, the value for these quantities is determine experimentally by carrying out the reaction in a bomb calorimeter. Upon performing, the following data was obtained. Parameter Mass burned Heat capacity of Calorimeter Initial temp. of Calorimeter Final temp. of Calorimeter Glucose 1.18 g Lactic Acid 2.56 g 4.728 kJ/ ˚C 23.8 ˚C 27.7 ˚C 21.4 ˚C 29.5 ˚C a. Write the chemical equation for both combustion of glucose and lactic acid. b. Determine the standard molar enthalpy change (∆H˚) for the combustion of both glucose and lactic acid. c. Using Hess’ Law, what is the standard molar enthalpy change for glycolysis? Determine if exothermic or endothermic. d. Given that the standard molar entropy of glucose and lactic acid is 212 J/mol•K and 34.0 cal/mol•K respectively, find the standard molar entropy change in the glycolysis. e. Determine the molar Gibbs free energy change for the glycolysis. At room temp (298 K) is the reaction spontaneous or not?