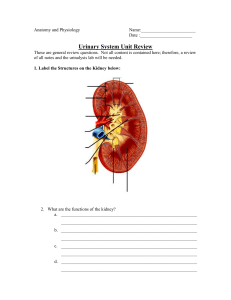
CHAPTER 26 URINARY (QUIZ 1) 1. The function of the urinary system is to *A)* maintain homeostasis *B)* excrete waste products *C)* secrete a hormone that stimulates production of red blood cells *D)* maintain fluid and electrolyte balance and pH *E)* all of the above 2. Which of the following is the smallest unit of the urinary system capable of forming urine? *A)* glomerulus *B)* nephron and collecting duct *C)* peritubular capillaries *D)* loop of Henle 3. The urinary system organ that removes waste products from the body and helps regulate blood pressure is the *A)* liver. *B)* heart. *C)* kidney. *D)* lungs. 4. Blood and the lymphatic vessels and nerves enter and exit the kidney through what structure? *A)* hilus *B)* renal sinus *C)* renal calyces *D)* adrenal glands 5. Of the layers of tissue that surround the kidney, which layer is continuous with the outer layer of the ureter? *A)* adipose capsule *B)* renal capsule *C)* renal fascia *D)* peritoneum 6. The layer of fatty tissue that surrounds the kidney is called the *A)* renal sinus *B)* renal pelvis *C)* adipose capsule *D)* renal capsule 7. The layer that holds the kidney in place within the abdominal cavity is called the *A)* renal sinus *B)* renal fascia *C)* renal capsule *D)* adipose capsule 8. The inner region of the kidney that appears to contain striated triangles (i.e. the renal pyramids) is called the *A)* renal cortex *B)* renal sinus *C)* renal medulla *D)* renal pelvis 9. Nephrons are found running through which two layers of the kidney? *A)* renal sinus, medulla *B)* cortex, medulla *C)* hilus, pyramids *D)* pyramids, renal sinus 10. The apexes of the renal pyramids are called *A)* renal columns *B)* renal papillae *C)* renal pyramid *D)* renal pelvis 11. In addition to the blood vessels, the nephron consists of two other principal parts, the ______ where the fluid is filtered and a______ into which the filtered fluid passes. *A)* glomerulus; renal tubule *B)* renal pelvis; proximal tubule *C)* collecting duct; distal tubule *D)* glomerulus; juxtamedullary nephron 12. The _____ drains blood from the glomerular capillaries. *A)* efferent arteriole *B)* afferent arteriole *C)* Bowman's capsule *D)* peritubular capillary 13. Which of the following descend into the medulla? *A)* Bowman's capsule *B)* distal tubule *C)* proximal tubule *D)* loop of Henle 14. Trace the flow of urine from nephrons to the renal pelvis. *A)* glomerulusglomerular capsuleproximal tubulesloop of Henledistal tubulescollecting ductrenal pelvis *B)* glomerular capsule -glomerulus-loop of Henle-distal tubulesproximal tubules-distal tubular-collecting duct-renal pelvis *C)* loop of Henle-distal tubules-collecting duct-proximal tubulesglomerulus glomerular capsule-renal pelvis *D)* none of the above is correct 15. What are the cells called that wrap pedicels around the glomerular capillaries? *A)* pinocytes *B)* sertoli *C)* podocytes *D)* None of the above. 16. Which of the following does NOT contain a smooth muscle layer? *A)* kidney *B)* urinary bladder *C)* ureters *D)* urethra 17. The kidney lies on the dorsal wall of the ______ cavity. *A)* cranial *B)* abdominal *C)* thoracic *D)* lateral 18. The most superficial covering of the urinary bladder on the posterior and inferior surface is the *A)* adventitia. *B)* serosa. *C)* sphincter. *D)* muscularis. 19. What is the principal function of the ureter? *A)* transport blood to the efferent arterioles *B)* transport urine from the renal pelvis into the urinary bladder *C)* transport glucose and protein into the renal pelvis *D)* none of the above 20. Mucus secreted by the ______prevents the cells lining the ureter from coming in contact with urine. *A)* fibrous capsule *B)* adventitia *C)* muscularis *D)* mucosa 21. Urine moves down the ureter by way of *A)* hydrostatic pressure. *B)* gravity. *C)* peristaltic contractions. *D)* All the above. 22. What structure receives urine flowing down the ureters? *A)* ureter *B)* urinary bladder *C)* urethra *D)* renal pelvis 23. The small tube leading from the floor of the urinary bladder to the exterior of the body is the *A)* renal pelvis *B)* ureter *C)* urethra *D)* calyx 24. What is the terminal portion of the urinary system? *A)* urethra *B)* penis *C)* vagina *D)* ureter 25. The urinary bladder *A)* is bean shaped *B)* varies in size depending on how full it is *C)* is pear shaped when full *D)* Both B and C. 26. In the floor of the urinary bladder is a small triangular muscle called *A)* serosa *B)* mucosa *C)* detrusor *D)* trigone 27. In the urinary bladder which of the following is composed of skeletal muscle and is a modification of the urogenital diaphragm muscle? *A)* external urethra sphincter *B)* internal urethra sphincter *C)* serosa *D)* adventitia 28. In the male what functions does the urethra serve? *A)* discharge of semen only *B)* discharge of sperm only *C)* discharge of urine *D)* discharge of semen and urine 29. Suppose a large stone is blocking a calyx. What effect might this have on NFP (net filtration pressure)? *A)* It would increase NFP by increasing CHP (capsular hydrostatic *B)* It would decrease NFP by increasing CHP. *C)* It would increase NFP by increasing colloid osmotic pressure. *D)* None of the above. pressure). 30. What is the condition called when a patient's output of urine is less than 50 ml? *A)* dysuria *B)* anuria *C)* enuresis *D)* azotemia 31. How much blood enters the renal arteries per minute? *A)* 180 L *B)* 1200 ml *C)* 500 ml *D)* 700 ml 32. Where does the first step in the production of urine occur? *A)* Bowman's capsule *B)* glomerulus *C)* vasa recta *D)* proximal convoluted tubule 33. In the kidneys, the largest volume of of the following? water reabsorption occurs in which *A)* glomerular capillaries *B)* collecting duct *C)* proximal convoluted tubules *D)* distal convoluted tubules 34. In the kidneys, the largest volume of which of the following? glucose reabsorption *A)* glomerular capillaries *B)* collecting duct *C)* proximal tubules *D)* distal tubules occurs in 35. Which of the following determines the rate of chloride reabsorption in the kidney? *A)* rate of water reabsorption *B)* rate of sodium reabsorption *C)* rate of glucose reabsorption *D)* rate of phosphate reabsorption 36. There are three basic renal processes for urine formation. Which of the following is NOT one of these processes? *A)* urine excretion *B)* tubular reabsorption *C)* tubular secretion *D)* glomerular filtration 37. In glomerular filtration, what is the normal value for net filtration pressure? *A)* 55 mmHg *B)* 30 mm Hg *C)* 15 mm Hg *D)* 10 mm Hg 38. Which of the following filtered substances is *A)* sodium *B)* glucose *C)* urea *D)* creatinine NOT present in normal urine? 39. Filtration of blood in the glomeruli is promoted by *A)* blood colloid osmotic pressure *B)* blood hydrostatic pressure *C)* capsular hydrostatic pressure *D)* Both A and B. 40. Small proteins and peptides that pass the glomerular filters are usually reabsorbed by *A)* osmosis *B)* simple diffusion *C)* pinocytosis *D)* phagocytosis 41. The concentration of solutes in tubular fluid is greatest in the *A)* glomerular capsule *B)* proximal tubule *C)* distal tubule *D)* loop of Henle 42. Which of the following would pass through the glomerular filters in the kidney most easily? *A)* albumin *B)* antibodies *C)* glucose *D)* angiotensinogen 43. Normally most filtered bicarbonate ions are reabsorbed in the *A)* proximal tubule *B)* loop of Henle *C)* collecting duct *D)* glomerulus 44. The reabsorption of glucose and amino acids is mediated by *A)* facilitated diffusion *B)* co-transport *C)* antiport *D)* Both A and B. 45. What solutes contribute to the osmotic pressure of interstitial fluid in the renal medulla? *A)* NaCl *B)* urea *C)* uric Acid *D)* both A and B 46. Which of the following is derived from amino acids and can be found in urine? *A)* HCl *B)* Ca2^+ *C)* phosphate *D)* urea 47. Which of the following would be in the highest concentration in normal urine? *A)* urobilinogen *B)* creatinine *C)* bilirubin *D)* albumin 48. The kidney secretes a hormone that triggers a cascade that regulates blood Na+ and blood pressure. It is called *A)* erythropoietin *B)* vasopressin *C)* renin *D)* angiotensin 49. Which hormone most directly affects glomerular filtration? *A)* renin *B)* ADH *C)* Angiotensin II *D)* Atrial natriuretic peptide 50. The kidney has a built-in system to compensate for moderate changes in systemic arterial pressure for a short period of time. What is the name of this system? *A)* renin *B)* hormonal regulation *C)* autoregulation *D)* vaspressin 51. Urine that is hypotonic to blood plasma are produced when *A)* levels of aldosterone are high *B)* levels of antidiuretic hormone are high *C)* levels of antidiuretic hormone are low *D)* plasma concentration of sodium ions is high 52. The sweet odor of diabetic urine is due to the presence of *A)* ketone bodies *B)* glucose *C)* sucrose *D)* albumin 53. Angiotensinogen is produced by the *A)* kidney *B)* liver *C)* lungs *D)* adrenal cortex 54. Vasopressin (ADH) acts at the level of the basolateral membrane in the distal tubules and ____tubules. *A)* collecting *B)* proximal *C)* arterioles *D)* glomerulus 55. How do diuretics affect the urine? *A)* increase the urine flow *B)* decrease the urine flow *C)* increase the cellular composition of the urine *D)* none of the above 56. How can you tell if your patient has diabetes insipidus? *A)* very dilute urine *B)* extreme thirst *C)* decrease in ADH *D)* all the above 57. The most common cause of glucosuria is untreated diabetes mellitus, in which the *A)* rate at which glucose enters the glomerular filtrate is higher than the rate at which the distal tubules and collecting duct can reabsorb it. *B)* sodium plus glucose symports in the distal tubules are defective *C)* are defective sodium plus glucose symports in the proximal convoluted tubule *D)* transport maximum for glucose reabsorption in the proximal tubule is exceeded 58. If the level of aldosterone in the blood increases, then *A)* more potassium is excreted in the urine *B)* more sodium is excreted in the urine *C)* blood pressure will drop *D)* glomerular filtration rate will drop 59. Principal cells in the distal tubules and collecting duct *A)* secrete renin *B)* respond to ADH and aldosterone *C)* respond to ADH only *D)* respond to aldosterone only 60. Urinalysis consists of which of the following? *A)* chemical properties of urine *B)* physical properties of urine *C)* microscopic properties of urine *D)* All the above 61. If a substance is filtered but not reabsorbed or secreted its renal clearance rate *A)* equals the GFR. *B)* is always greater than the GFR. *C)* is less than the GFR. *D)* does not affect the GFR. 62. Renal threshold equals *A)* urine output *B)* *C)* molecule cardiac output plasma concentration at which reabsorption is saturated and the appears in urine *D)* GFR 63. If a substance has exceeded its transport maximum (Tmax) in the kidney tubules, it is likely that *A)* urine volume will increase *B)* urine volume will decrease *C)* unusually high *D)* the concentration of the substance in the blood would become Both A and C 64. The reason insulin is used to determine glomerular filtration rate is because it is *A)* both filtered and efficiently secreted by nephrons *B)* both filtered and completely reabsorbed by nephrons *C)* neither secreted nor reabsorbed *D)* only secreted 65. Which of the following is measure plasma clearance? NOT a characteristic of substances that are used to *A)* It must pass through the filtration membrane as easily as water. *B)* It must not be reabsorbed. *C)* It must be metabolized by the kidney. *D)* It must not be secreted into the nephron. 66. Which of the following may occur in patients with severe diabetes mellitus? *A)* Tubular maximum may exceed tubular load. *B)* Tubular load may exceed tubular maximum. *C)* They have dilute urine. *D)* They have high glucose in the blood without glucose in the urine? 67. A bladder containing _____ml of urine could be close to bursting point in an average-sized human. *A)* 700 *B)* 300 *C)* 1000 *D)* 500 68. What is the term for urine discharge? *A)* azotemia *B)* enuresis *C)* micturition *D)* polyuria 69. What are some common constituents of kidney stones (renal calculi)? *A)* uric acid *B)* calcium *C)* magnesium *D)* all the above 70. Enuresis is which of the following? *A)* bed wetting *B)* difficult in urine *C)* excess urine *D)* kidney stone 71. Which of the following would increase peristaltic contractions in the ureters? *A)* sympathetic nervous system stimulation *B)* central nervous system stimulation *C)* parasympathetic stimulation *D)* none of the above 72. At about what volume of urine does the bladder create strong action potentials to be sent to the spinal cord for micturition? *A)* 100ml of urine *B)* 500ml of urine *C)* 200ml of urine *D)* 300ml of urine 73. Which of the following areas of the brain are involved with conscious urination? *A)* cerebrum *B)* pons *C)* medulla *D)* both A and B 74. Uremia is defined as which of the following? *A)* a kidney stone *B)* accumulation of nitrogenous waste due to tubule malfunction *C)* blood in the urine *D)* a high diastolic and low systolic pressure reading 75. Which of the following is the special branch of medicine that deals with the structure, function, and disease of the kidney? *A)* urology *B)* renalology *C)* nephrology *D)* glomerulus specialist 76. Pyelonephritis relates to which of the following? *A)* an inflammation of the ureter *B)* an inflammation of the renal pelvis *C)* an inflammation of the urethra *D)* an inflammation of the urinary bladder 77. If a surgeon removed one kidney, which of the following would be the outcome? *A)* the other kidney would enlarge *B)* the other kidney would do the job of both *C)* both A and B *D)* None of the above. 78. Urethritis is which of the following? *A)* inflammation of the urethra *B)* painful urination *C)* increase urination *D)* blood in the urine 79. Cystitis relates to which of the following? *A)* protein buildup in the urine *B)* inflammation of the ureter *C)* inflammation of the urinary bladder *D)* inflammation of the urethra