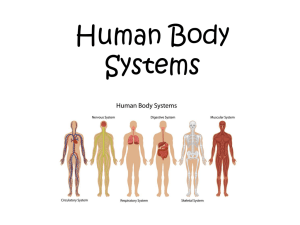
Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to anatomy Prepared by: Ismael zaki Albalishi Master in critical care nursing Anatomy • Gross anatomy: the study of body structures visible to the naked eye (without a microscope) • Microscopic anatomy: • Cytology: Analysis of the internal structures of individual cells • Histology: examination of tissues (groups of specialized cells that work together to perform a specific function. 2 Homeostasis • Homeostasis is the ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment in an ever-changing outside world • The internal environment of the body is in a dynamic state of equilibrium • Chemical, thermal, and neural factors interact to maintain homeostasis Anatomical Position • Anytime you describe structures relative to one another, you must assume this standard position: • Body erect • Feet slightly apart • Palms facing forward • Thumbs point away from body 4 Anterior Landmarks 5 Posterior Landmarks 6 Body Orientation and Direction • These are relative positions • Proximal/distal • Used to describe locations on the arms and legs • GI tract • Medial/lateral • Medial is closer to the midline • Farther away from the midline 7 Body Orientation and Direction • Dorsal: Back • Ventral: Front • Superior or Cephalad is toward the head • Inferior or Caudal is toward the feet • Anterior: most forward • Posterior: toward the backside 8 Orientation and Directional Terms Table 1.1 (1 of 3) Directional Terms Table 1.1 Planes of the Body 11 Dorsal Body Cavity • Dorsal cavity protects the nervous system • Contains Brain and Spinal Cord 12 Cavities • Thoracic Cavity • Heart & Lungs • Subdivided into the mediastinum and plural cavities • Lower border is the diaphragm • Abdominal Cavity • Stomach, Liver, Intestines • Pelvic Cavity • Reproductive organs Bladder, Rectum 13 Serous Membranes of the Heart 14 Quadrants • RUQ • Liver • LUQ • Spleen • RLQ • Appendix • LLQ • Sigmoid colon 15 Abdominopelvic Regions 16 The Integumentary System Forms external body covering Protects deeper tissues from injury Synthesizes vitamin D Site of cutaneous receptors (pain, pressure, etc.) and sweat and oil glands The Skeletal System – Protects and supports body organs – Provides a framework for muscles – Blood cells formed within bones – Stores minerals The Muscular System Allows manipulation of environment Locomotion Facial expression Maintains posture Produces heat The Nervous System Fast-acting control system Responds to internal and external changes The Endocrine System Glands secrete hormones that regulate Growth Reproduction Nutrient use The Cardiovascular System Blood vessels transport blood Carries oxygen and carbon dioxide Also carries nutrients and wastes Heart pumps blood through blood vessels The Lymphatic System Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels Disposes of debris in the lymphatic system Houses white blood cells (lymphocytes) Mounts attack against foreign substances in the body The Respiratory System Keeps blood supplied with oxygen Removes carbon dioxide Gas exchange occurs through walls of air sacs in the lungs The Digestive System Breaks down food into absorbable units Indigestible foodstuffs eliminated as feces The Urinary System Eliminates nitrogenous wastes Regulates water, electrolyte, and acidbase balance Reproductive System Overall function is to produce offspring Testes produce sperm and male sex hormones Ovaries produce eggs and female sex hormones Mammary glands produce milk