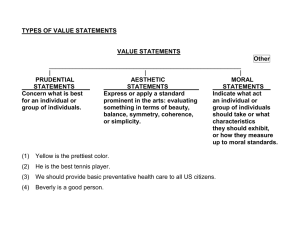
MORAL AGENT AND MORAL DEVELOPMENT Ryan Javier cumbe Instructor MORALITY -principles concerning, the distinction between right and wrong or good and bad behavior se lf a ware ness u n d e rstan din g FRUITS OF KNOWING YOURSELF & s e lf p eop le are th e m ost im portan t o rga n iza tio na l r e s o urce improv ing p re d ictab ility a n d s e lf -co nfide nce b u ild in g r e la tio nship s e ffectiv e u tiliza tio n h u m a n r e s o urces av o id ing c o n flic ts or of ma nag ing im prov ing th e qu a lity o f life a n d w o r k e n vironm ent Metaphysical (level of being), fundamental, radical, substantial, the act of being. What makes us a HUMAN BEING Operational (level of doing), accidental Our being human & even fundamental dignity lies in the level of being (substantial), not in the level of operation (accidental). Operationally (biologically, socially, morally, intellectually, emotionally)< the human person has yet to grow Conception is when human life begins. Metaphysically, the embryo is already a human person, created in the image and likeness of God. MAN IS RATIONAL It means that human being posses the faculty of intellection (knowledge) and volition (will). by knowledge is meant the power of generalization, the conception of abstract ideas, and the possession of intellectual truths. by will is meant that strong desire to acquire an object which after due consideration of its consequences has been pronounces by reason to be good. o Capable of making choice o Ability to make judgement o Capacity to make decisions o Power to determine himself freely in attaining his destiny o an ethical representative for a public person o an irrelevant label discussing ethics when o responsible for his or actions and behaviors her o not responsible for his or her actions By “moral agent” we understand a creature able to act morally. To act morally supposes a creature has the ability to know that its actions have moral consequences. e va lu ative or ie ntat io n th at d isting u ish es go o d a n d ba d an d p r e s c rib es g o o d s ense of obligat ion t ow ards s t a n d ar ds o f a s o c ia l c o lle c tive MORAL CHARACTER s en se of re sp o ns ibilit y f or actin g out of concern for others c onc e rn f or t he right s ot he rs c o mmitmen t to h o n est y in t e r pe rso n al r e la t io n sh ip s in st ate of min d c a us es n eg ative e motional rea ctions to immora l acts ability of moral agents to make moral judgments based on some notion of right and wrong MORAL AGENCY traditionally moral agency is assigned only to those who can be held responsible for their actions FORMS Teleological MORAL AGENCY Deontological Social morality Noble character DIMENSIONS Rational Thoughts MORAL AGENCY Feeling/ Emotions action MORAL DEVELOPMENT - focuses on the emergence, change, and understanding of morality from infancy through adulthood. Morality develops across a lifetime and is influenced by an individual's experiences and their behavior when faced with moral issues through different periods' physical and cognitive development. o Moral development includes characteristics of the honesty, truthfulness, trustworthiness, selfrespect, respect of others, righteousness, self-control, duty consciousness , compassion in the child o According to Zanden (1978), moral development refers to the process by which children adopt principles that lead them to evaluate given behaviours as right and wrong and to govern their own actions in terms of their principles. o Baron (2001) defined moral development as changes in the capacity to reason about rightness or wrong ness of various actions that occurs with age. o Moral development is the process through which children develop proper attitudes and behaviours towards other people in society, based on social and cultural norms, rules and laws. o Thus, we can say that-in moral development a child learns the rules and laws of the society which helps him to differentiate between right and wrong behaviour. Rules and laws learned in moral development determines the behaviour of the person and process of moral development get strengthened with age. o Baron (2001) defined moral development as changes in the capacity to reason about rightness or wrong ness of various actions that occurs with age. STAGES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT 5. Social contract and individual rights 6. Universal Principles 3. Good interpersonal relationships 4. Maintaining social order 1. 2. Obedience and punishment Individualism and exchange FEATURES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT INFANCY At the time of birth child is neither moral or immoral. Moral self is developed as a result of sanctions and punishment provided by the parents. In schools, teachers develop desirable conduct through approval or disapproval of their behaviors and by providing worth experiences. FEATURES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT CHILDHOOD Peer groups plays an important role in developing moral behavior. Moral self is strengthened by the reward and punishment received by parents and teachers. Children follow the social and cultural norms and codes. DIMENSIONS / COMPONENTS OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT Emotional Dimension Behavioural Dimension Cognitive Dimension is one of the important dimension of moral development because it is the emotions or feelings of a person which make him realize the sorrow of others and to feel guilty if he himself is the reason of sorrow of others. second important of moral development is behaviors and its consequences. Consequences of behavior done by the child motivates him to learn moral rules. is another dimension of moral development. If a child has social understanding then he can take correct decision about right and wrong behavior. Cognitive maturity and social experiences helps in the development of moral behavior. THEORIES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT Sigmund Freud believed that moral development of a child on his super ego. He regarded superego as a moral commander which tell the individual about moral values, principles and moral standards. THEORIES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT Kohlberg’s Theory According Lawrence Kohlberg’s theory, moral development proceeds in sequential stages. This theory states that internal or cognitive processes like thinking and reasoning plays a major role in one’s moral developments. The way children make moral judgment depends on their up bringing and learning experiences. Kohlberg in this theory states that there are 3 levels of moral development and movement from one stage to another depends on cognitive abilities rather that acquisition of moral values from parents elders of peers. THEORIES OF MORAL DEVELOPMENT Social Learning Theory Albert Badura believed that just as a child learns other behaviors similarly he learns moral behavior. This theory states that moral behaviors . This theory states that moral behavior is learnt by observation. When a child sees someone doing a behavior and getting a positive response as a result of the behavior then he also learns that behavior. Similarly when a child sees the model doing a moral behavior he also learns to do that moral behavior. Thus, it means that moral development depends on observation of moral behavior and imitation of that moral behavior. Piaget’s view on moral development According to Piaget (1932), there are 4 stages of moral development of a child o Anomy (0-5years) o Hetronomy – Authority (5 – 8 years) o Hetronomy – Reciprocity (9 – 13 years) o Autonomy (13 – 18 years) ANOMY It is a stage without law. At this stage the behavior of the child is neither moral or immoral but no moral. Th behavior of the child is not guided by moral standards but it is regulated by pain and pleasure. The child repeats the behavior which give him pleasure and avoids those that give him pain. HETRONOMY-AUTHORITY It is a stage in which moral development is controlled by external authority. Moral development in this stage is regulated by rewards and punishment. It is also called the stage of discipline of artificial consequences imposed by adults HETRONOMY-RECIPROCITY It this moral behavior / development is regulated by reciprocity which means that whatever is offensive to us, we should not do to others. In this stage conformity with the group becomes imperative. FACTORS INFLUENCING MORAL DEVELOPMENT PHYSICAL & MENTAL HEALTH Health of an individual affects his moral behavior: health of an individual affects his point-of-view and ideal of life. A child with sound health learns desirable behavior very fast. FACTORS INFLUENCING MORAL DEVELOPMENT FAMILY ENVIRONMENT Family environment is a significant factor affecting moral development. Moral views of the family members, parents, moral discipline among family, lack of love and compensation among the family members influence the moral development of the child. FACTORS INFLUENCING MORAL DEVELOPMENT SOCIAL INFLUENCE It included society , friends and group members. Child’s moral behavior is influenced by the moral view point of the groups, child’s view regarding what is right or what is wrong to a great extent is controlled by the views of his group member. FACTORS INFLUENCING MORAL DEVELOPMENT INTELLIGENCE Moral thinking and reasoning depends on intelligence. Higher the level of intellectual development or intelligence of an individual, higher will be moral development. FACTORS INFLUENCING MORAL DEVELOPMENT RELIGION Plays an important role in the moral development. All the religions emphasize on development of moral values. The more the child is committed towards his religion the greater will be his moral development. FACTORS INFLUENCING MORAL DEVELOPMENT AGE Moral development also depends on age of a person. As the age increases moral conduct also increases. GENDER Moral development also depends on gender. Generally it is said that as compared to boys, girls shows better moral conduct. FACTORS INFLUENCING MORAL DEVELOPMENT MOTIVATION Moral behavior also depends on motivation level of the child. If a person has high achievement need but fear or failure then he commits immoral behavior like cheating. OTHER FACTORS INFLUENCING MORAL DEVELOPMENT Culture Socio-economic status Experiences Rules an regulations of the community Sanctions and punishment given by elders Conscious training Moral reasoning intellectual development