Pneumonia: Definition, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
advertisement

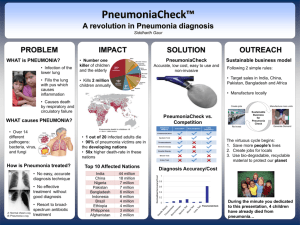
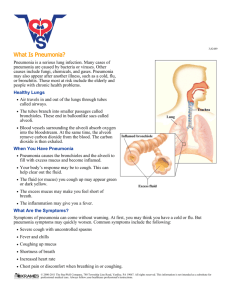
Pneumonia Name: KHOR WEI CHIAN Batch: BTCM19C Lecturer: Dr. Liew Zhi Hao Lung anatomy Lung anatomy Definition Pneumonia defined as an acute infection of pulmonary parenchyma in one or both lungs. Pneumonia causes inflammation in the alveoli. The alveoli are filled with fluid or pus, making it difficult to breath Etiology Bacterial Viruses Streptococcus pneumoniae Adenovirus Haemophilus influenza Influenza A and B Staphylococcus aureus Parainfluenza Mycoplasma pneumoniae Respiratorysyncytial virus Chlamydia species Fungi(Rare) Legionella species Coccidioidomycosis Histoplasmosis Blastomyosis Pathophysiology Infection to the lung(eg. bacteria, virus) Inflammatory response initiated Alveolar edema+ exudate formation Alveoli and respiratory bronchioles fill with serous exudate, blood cells, fibrin, bacteria Consolidation of lung tissues Factors that predispose to pneumonia Classification TYPE OF PNEUMONIA 1. Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Occurs in community & during < 48 hours of hospitalization. Is the most common type of pneumonia. 2. Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia occurring 48 hours or more during a hospital stay for another illness. Higher risk client on a mechanical ventilator eg. Ventilatorassociated pneumonia (VAP). Classification 3. Health Care-associated Pneumonia (HCP) Pneumonia in other health care settings, such as nursing homes, dialysis centers, and outpatient clinics. 4. Aspiration Pneumonia Due to inhale foreign body, food, drink, vomit, or saliva from your mouth into lungs that occur in condition of poor gag reflex eg. Brain injury, dysphagia, or excessive use of alcohol or drugs. Classification 5. Atypical Pneumonia Is most commonly caused by mycoplasma. Legionnaires' disease or chlamydia and usually appears in children and young adults. 6.Hypostatic pneumonia Results from the collection of fluid in the dorsal region of the lungs and occurs especially in those(as the bedridden or elderly, etc). Anatomical classification Bronchopneumonia affects the lungs in patches around bronchi Lobar pneumonia is an infection that only involves a single lobe or section Interstitial pneumonia involves the areas in between the alveoli • Patchy areas • Asymmetrical • Peribronchial cuffing • Fluid localized to a single lobe • Unilateral • Air bronchogram • Ground glass appearance • Bilateral, symmetrical • Concentrated in the perihilar region • Reticular Symptoms Difficulty breathing Chest pain Productive Cough- pus or bloody sputum Nausea Vomit Diarrhea Fever and chills Confusion Headache Muscle pain Fatigue Complications SLAP HER Septicaemia 败血症 Lung abscess Acute respiratory distress syndrome Pleural effusions Hypotension Empyema Respiratory failure / Renal failure Diagnosis 1. History- s/s of suggestive pneumonia 2. Auscultation: Abnormal lung sound. (bubbling or crackling) 3. Palpation: Increased tactile fremitus 4. Percussion: Dullness on percussion 3. Blood test- raised WBC 4. Chest X Ray 5. Sputum test Bacterial Pneumonia: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenza, etc. Purulent (pus-like) sputum, which may be yellow or greenish in color. Viral Pneumonia: Influenza A and B, etc. Sputum may be less purulent compared to bacterial pneumonia. 6. Pulse oximetry 7. Bronchoscopy may reveal inflamed and reddened airway walls may show the presence of excessive mucus, pus, or fluid in the airways 8. CT scan and pleural fluid culture Treatment Antibiotics Analgesics Mucolytic drugs Antihistamines Oxygen therapy TCM Treatment Syndrome Differentiation and Treatment: the practitioner will determine the patient's diagnosis based on the patient's signs, symptoms, tongue and pulse. Common types of pneumonia include: Phlegm-heat congestion of the lungs (痰热壅肺)- 清金化痰汤加减 to clear away heat and resolve phlegm Lung yin deficiency (肺阴虚证)- 养阴清肺汤加减 to nourish Yin and moisten the lungs Wind-cold attacking the lungs (风寒袭肺)- 小青龙汤加减 to relieving exterior cold Acupuncture therapy: regulate the body's qi and blood balance, enhance immunity, and relieve inflammation by stimulating specific points. References Hua-Huat Soo, Lee-Gong Lau, Peng-Hong Chew. Sarawak Handbook of Medical Emergencies. C. E. Publishing First Edition; 1999. Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson J, Loscalzo J. eds. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 18e. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2012. World Health Organization. (2021, November 11). Pneumonia. Who.int; World Health Organization: WHO. https://www.who.int/news-room/factsheets/detail/pneumonia Cunha, B. A. (2001). Pneumonia in the Elderly. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 7(11), 581–588. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1198-743x.2001.00328.x Carden DL, Gibb KA. Pneumonia and lung abscess. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 1983 Aug;1(2):345-70. PMID: 6394291. Thank You!!!