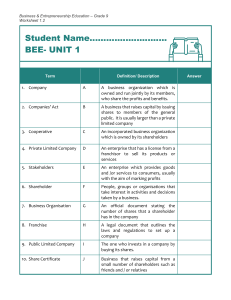
lOMoARcPSD|11824253 Audit of SHE Testbank Accontancy (Tarlac State University) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Shaena Mae (maeshaenaclumidao@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|11824253 AUDIT OF SHAREHOLDERS EQUITY (CPAR OCT 2013 – AP 7401) PROBLEM NO.2 The shareholders equity section of Bahrain corporation’s statement of financial position as of dec 31 2012 is as follows Share capital – ordinary (10 par, 750,000 shares authorized, 412,500 issued and outstanding 4,125,000 share premium 825,000 total paid in capital 4,950,000 unappropriated retained earnings 2,002,500 Appropriated retained earnings 750,000 Total retained earnings 2,752,500 Total shareholders’ equity 7,702,500 Bahrain Corporation had the following shareholders’ equity transaction during 2013 Jan 15 completed the building renovation for which 750,000 of retained earnings had been restricted. Paid the contractor 727,500, all of which is capitalized March 3 issued 150,000 additional ordinary shares for 18 per share May 18 declared a dividend of 1.50 per share to be paid on july 31 2013, to shareholders’ record on june 30 2013 June 19 approved additional building renovation to be funded internally. The estimated cost of the project is 600,000, and retained earnings are to be restricted for that amount July 31 paid dividend Nov 12 declared property dividend to be paid on jan 5 2014. The dividend is to consist of equipment that has a carrying amount of 360,000 and fair value of 472,500 on nov. 12 Dec 31 net income for 2013 (before recognition of impairment loss on the equipment declared as properlt dividend) is 1,327,500. The equipments fair value less cost to distribute on dec 31 is 330,000 1. Share capital – ordinary on dec 31 2013 is A. 5,625,000 b. 4,125,000 c. 4,950,000 d. 7,650,000 2. Share premium on dec 31 2013 is a. 2,625,000 b. 825,000 c. 2,025,000 d. 1,200,000 3. Unappropriated retained earnings on dec 31 2013 is a. 2,163,750 b. 2,246,250 c. 2,133,750 d. 2,276,250 4. The total shareholders’ equity on dec 31 2013. a. 10,376,250 b. 10,526,250 c. 9,926,250 d. 7,650,000 PROBLEM NO.3 You were engaged by City Corporation, a publicly held company whose shares are traded on the Philippine stock exchange, to conduct an audit of its 2013 financial statements. You were told by the company’s controller that there were numerous equity transactions that took place in 2013. The shareholders’ equity accounts at dec 31 2012 had the following balances: Share capital – preference, 100 par value, 6% cumulative; 30,000 shares authorized; 18,000 shares issued and outstanding share capital – ordinary 1 par value, 1,800,000 shares authorized; 1,200,000 shares issued and outstanding share premium Downloaded by Shaena Mae (maeshaenaclumidao@gmail.com) 1,800,000 1,200,000 2,400,000 lOMoARcPSD|11824253 retained earnings total shareholders’ equity 980,000 6,380,000 you summarized the following transactions during 2013 and other information relating to the shareholders’ equity in your working papers as follows: January 6, 2013 – issued 45,000 ordinary shares in exchange for land. On the date issued, the shares had a market price of 16.50 per share. The land had a carrying value of 420,000 and an assessed value for property taxes of 490,000 January 31 2013 – sold 2,400, P1,000 12% bonds due jan 31 2023, at 98 with one detachable share warrant to each bond. Interest is payable annually on jan 31. The fair value of the bond without the share warrant is 95. The detachable share warrants have a fair value of P50 each and expire on jan 31 2014. Each warrant entitles the holder to purchase 10 ordinary shares at P10 per share February 28 2013 – subscriptions for 42,000 ordinary shares were received at P26 per share, payable 50% down and the balance by march 15 March 15 2013 – the balance due on 36,000 ordinary shares was received and those shares issued. The subscriber who defaulted on the 6,000 remaining shares forfeited the down payment in accordance with the subscription agreement September 14 2013 – there were 1,890 warrants detached from the bonds and exercised November 30 – declared a cash dividend of .50 per share to all ordinary shareholders of record dec 15 2013. The dividend was paid on dec 30 2013 December 15 2013 – declared the required annual cash dividends of preference shares for 2013. The dividend was paid on January 15 2014 January 8 2014 – before closing the accounting records for 2013 , city become aware that no depreciation had been recorded for 2012 for a machine purchased on july 1 2012. The machine was properly capitalized at 960,000 and had an estimated useful life of eight years when purchased. The appropriate correcting entries was recorded on the same date. ADJUSTED net income for 2012 was 840,000 Based on the following and the result of your audit, answer the following (ignore tax implications) 1. Share capital – ordinary at dec 31 2013 is a. 1,290,900 b. 1,305,900 c. 1,281,000 d. 1,299,900 2. How much is the total share premium as of dec 31 2013 a. 4,239,600 b. 4,317,600 c. 4,363,200 d. 4,065,100 3. The unappropriated retained earnings on dec 31 2013 is a. 982,550 b. 622,550 c. 766,550 d. 790,550 4. How much is the total shareholders’ equity on dec 31 2013 a. 8,184,050 b. 7,968,050 c. 8,168,750 d. 8,190,050 PROBLEM NO.4 A CPA was engaged by Birdie Company in 2013 to examine its books and records and to make whatever corrections are necessary. An examination of the accounts discloses the following: a.) Devidends had been declared on dec 15 in 2011 and 2012 but not been entered in the books until paid b.) Improvements in buildings and equipment of 32,400 had been debited to expense at the end of april 2012. Improvements were estimated to have 12-year life. The company uses straightline method in recording and computes depreciation to the nearest month. c.) The physical inventory of merchandise had been understated by 9,600 at the end of 2011 and by 14,250 at the end of 2012 Downloaded by Shaena Mae (maeshaenaclumidao@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|11824253 d.) The merchandise inventories at the end of 2012 and 2013 did not include merchandise that was then in transit and to which the company had title. These shipments of 6,300 and 8,700 were recorded as purchases in January 2013 and 2014, respectively. e.) The company had failed to record sales commissions payable of 10,800 and 3,300 at the end of 2012 and 2013 respectively. f.) The company had failed to recognize supplies on hand of 2,550 and 5,160 at the end of 2012 and 2013 respectively The retained earnings account appeared as shown below on the date the CPA began examination Date 2011 Jan 1 Dec 31 2012 Jan 10 Mar 6 Dec 31 2013 Jan 10 Dec 31 item Retained earnings debit balance net income for the year credit balance 84,000 195,000 279,000 dividends paid stock sold – excess over par net loss for year 46,500 53,400 232,500 295,500 242,100 dividends paid net loss for the year 46,500 57,900 195,600 137,700 63,000 1. What is the corrected 2011 net income a. 124,200 b. 90,900 c. 121,500 d. 71,700 2. What is the corrected 2012 net loss a. 53,400 b. 66,000 c. 54,300 d. 59,700 3. What is the corrected 2013 net loss a. 64,740 b. 62,340 c. 56,040 d. 71,040 4. What is the corrected retained earnings on dec 31 2012 a. 226,200 b. 163,800 c. 100,800 d. 183,060 5. What is the corrected retained earnings on dec 31 2013 a. 63,000 b. 99,060 c. 92,760 d. 36,060 PROBLEM NO.5 At the beginning of year 1, entity a grants share option to each of its 100 employees working in the sales department. The share option will vest at the end of year 3, provided that the employees remain in the entity’s employ, and provided that the volume of sales of a particular product increase by at least an average of 5% per year. If the volume of sales of the product increases by an average of 5% and 10% per year, each employee will receive 100 share options. If the volume of sales increases by an average of 11% and 15% each year, each employee will receive 200 share options. If the volume of sales increases by an average of 16% or more, the employee will receive 300 share options On grant date, entity A estimates that the share options have fair value of 20 per option. Entity A also estimates that the volume of sales of the product will increase by an average of between 11% and 15% per year, and therefore expects that, for each employee who remains in service until the end of year 3, 200 share options will vest. The entity also estimates, on the basis of a weighted average probability, that 20% of employees will leave before end of year 3 By the end of year 1, seven employees have left and the entity still expects that a total 20 employees Downloaded by Shaena Mae (maeshaenaclumidao@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|11824253 will leave by the end of year 3. Hence the entity expects that 80 employees will remain in service for the three year period. The product sales have increased by 12% and the entity expects this rate of increase to continue over the next 2 years By the end of year 2, a further 5 employees have left, bringing the total to 12 to date. The entity now expects only three more employees will leave during year 3, and therefore expect a total of 85 employees will remain at the end of year 3. Product sales have increased by 20%, resulting in an average of 16% over the two years to date. The entity now expect that sales will average 16% or more over the three-year period, and hence expects each sales employee to receive 300 share options at the year 3 By the end of year 3, a further two employees have left. Hence 14 employees have left during the three-year period, and 86 employees remain. The entity’s sale have increased by an average of 16% over three years. Based on the following information, answer the following 1. What is the compensation expense for year 1 a. 106,667 b. 53,333 c. 160,000 d. 172,000 2. What is the compensation expense for year 2 a. 286,667 b. 180,000 c. 233,333 d. 168,000 3. What is the compensation expense for year 3 a. 114,667 b. 176,000 c. 282,667 d. 188,000 4. What is the cumulative compensation for year 1 , 2 , 3 a. 320,000 b. 516,000 c. 344,000 d. 172,000 5. At the and of year 2, the entity should report share option outstanding of a. 328,000 b. 226,667 c. 286,667 d. 340,000 PROBLEM NO.7 An entity grants to an employee the right to choose either 1,000 phantom shares (i.e., a right to cash payment equal to the value of 1,000 shares) or 1,200 shares with a par value of 10 per share. The grant is conditional upon the computation of three years’ services. If the employee chooses the share alternative, the shares must be held for three years after vesting date. At grant date, the entity share price is 50 per share. At the end of year 1 2 and 3 the share price is 52 55 and 60 respectively. The entity does not expect to pay dividends in the next three years. After taking into account the effects of the post-vesting transfer restrictions, the entity estimates that the grant date fair value of the share alternative is 48 per share At the end of year 3, the employee chooses Scenario 1: the cash alternative Scenario 2 the equity alternative Base on the preceding information, answer the following: 1. What is the total fair value of equity component as a result of a share-based payment transaction with settlement alternatives a. 7,600 b. 10,000 c. 2,400 d. -02. What is the compensation expense in year 1 a. 17,333 b. 19,886 c. 19,333 d. 23,334 3. What is the compensation expense in year 2 a. 19,866 b. 17,333 c. 21,867 d. 19,333 4. What is the compensation expense in year 3 a. 23,334 b. 25,867 c. 19,333 d. 19,866 Downloaded by Shaena Mae (maeshaenaclumidao@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|11824253 5. If the employee chosen cash alternative, the amount to be paid at end of year 3 should be. a. 55,000 b. 67,600 c. 52,000 d. 60,000 6. Is the employee has chosen the share alternative, the amount of share premium to be recognized is a. 7,600 b. 55,600 c. 60,000 d. 67,600 THEORY 1. In an examination of shareholders equity, the auditor is most concerned that a. Capital stock transactions are properly authorized b. Stock splits are capitalized at par or stated value on the dividend declaration date c. Dividends during the year under audit were approved by the shareholders d. Changes in the accounts are verified by a bank serving as a registrar and stock transfer agent 2. In an audit of medium sized manufacturing concern, which one of the following can be expected to require least amount of audit time a. Owners ‘equity b. Asset c. Revenue d. Liabilities 3. When a corporate client maintains its own stock records, the auditor primarily will rely upon A. Confirmation with the company secretary of shares outstanding at year-end B. Review of the corporate minutes for data as to shares outstanding C. Confirmation of the number of shares outstanding at year-end with the appropriate state official D. Inspection of the stock book at year-end and accounting for all certificate numbers 4. When a client company does not maintain its own stock records , the auditor should obtain written confirmation from the transfer agent and register concerning a. Restriction on the payment of dividends b. The number of shares issued and outstanding c. Guarantees of preferred stock liquidation value d. The number of shares subject to agreement to repurchase 5. The auditor is concerned with establishing that dividends are paid to client corporation shareholders owning stock as of the a. Issue date b. Declaration date c. Record date d. Payment date 6. The audit program for the retained earnings account should include a step that requires verification of the a. Fair value used to change retained earnings to account for a two-for-one stock split. b. Approval of the adjustment to the beginning balance as a result of a write-down of an account receivable c. Authorization for both cash and stock dividends d. Gain or loss arising from disposition of treasury shares 7. During an audit of an entity’s shareholders’ equity accounts, the auditor determines whether there are restrictions of retained earnings resulting from loans, agreements, or law. This audit procedure most likely is intended to verify management assertion of a. Existence b. Completeness c. Valuation Downloaded by Shaena Mae (maeshaenaclumidao@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|11824253 d. Presentation and disclosure 8. If the auditee has a material amount of treasury stock on hand at year-end, the auditor should a. Count the certificates at the same time other securities are counted b. Count the certificate only if the company had treasury stock transaction during the year c. Not count certificates of treasury stock is a deduction from shareholders’ equity d. Count the certificates only if the company classifies treasury stock with other asset 9. In performing test concerning the granting of stock options, an auditor should a. Confirm the transaction with the securities and exchange commission b. Verify the existence of option holders in the entity’s payroll records or stock ledgers c. Determine that sufficient treasury stock is available to cover any new stock issued d. Trace the authorization for the transaction to vote of the board of directors 10. The auditor would not expect the client 세 debit retained earnings for which of the following transaction a. A 4-for-a stock split b. Loss arising from disposition of treasury shares c. A 1-for-10 stock dividend d. Correction of error affecting prior year’s earnings Downloaded by Shaena Mae (maeshaenaclumidao@gmail.com)