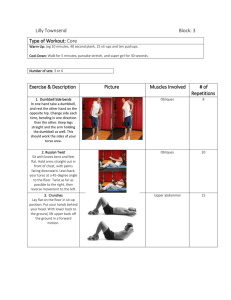
7 Day training program by Ilan Eibenschutz Day 1: Full-Body Strength 1. Squats: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, lower your body by bending your knees and pushing your hips back, keeping your chest upright. Return to the starting position by extending your knees and hips. 2. Push-ups: Start in a plank position with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Lower your body until your chest nearly touches the floor, then push back up to the starting position. 3. Bent-over rows: Hold a dumbbell in each hand, hinge forward from the hips while keeping your back flat, and let the weights hang straight down. Pull the weights up toward your torso by bending your elbows, squeezing your shoulder blades together. Lower the weights back down. 4. Lunges: Stand with your feet hip-width apart. Step forward with one leg and lower your body until both knees are bent at a 90-degree angle. Push back up to the starting position and repeat on the other leg. 5. Overhead press: Hold a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder height with your palms facing forward. Press the weights overhead by extending your arms until they are fully extended. Lower the weights back down to shoulder height. 6. Plank: Start in a push-up position with your elbows resting on the floor, forearms parallel to your body. Engage your core and hold your body in a straight line from head to toe, avoiding sagging or arching. 7. Russian twists: Sit on the floor with your knees bent, heels on the ground, and lean back slightly. Hold a medicine ball or weight with both hands in front of your chest. Twist your torso to one side, then twist to the other side, touching the ball to the floor on each side. Day 2: Cardiovascular Endurance 1. Jumping jacks: Stand with your feet together and arms by your sides. Jump up, spreading your feet wide and raising your arms overhead. Jump again, returning to the starting position. 2. High knees: Stand tall and rapidly drive your knees upward, trying to bring them as close to your chest as possible, while jogging in place. 3. Mountain climbers: Start in a push-up position. Alternate driving your knees towards your chest, as if you are climbing a mountain, while keeping your upper body stable. 4. Burpees: Begin in a standing position, then lower into a squat position with your hands on the ground. Kick your feet back into a push-up position, perform a push-up, then quickly bring your feet back to the squat position. Jump up explosively, reaching your arms overhead. 5. Cycling or running: Either hop on a stationary bike and pedal at a moderate intensity for 20 minutes or go for a 20-minute run at a moderate pace. 6. Jump rope: Hold the handles of a jump rope in each hand and swing the rope over your head. Jump over the rope as it passes under your feet, repeating for the desired duration. 7. Stair climbing: Find a set of stairs and climb them, one step at a time, focusing on maintaining a steady pace. Repeat for 10 flights of stairs. Day 3: Core Focus 1. Bicycle crunches: Lie on your back with your knees bent and hands behind your head. Bring one knee towards your chest while simultaneously twisting your upper body to bring the opposite elbow towards the knee. Repeat on the other side. 2. Plank with hip dips: Begin in a forearm plank position. Lower your hips to one side, keeping your core engaged, then return to the center and lower your hips to the other side. 3. Russian twists with medicine ball: Sit on the floor with your knees bent and feet lifted off the ground. Hold a medicine ball or weight with both hands in front of your chest. Twist your torso to one side, then twist to the other side while balancing on your glutes. 4. Leg raises: Lie on your back with your legs extended. Lift both legs off the ground while keeping them straight, then lower them back down without touching the floor. 5. Side plank: Lie on your side with your elbow directly beneath your shoulder and your legs stacked on top of each other. Lift your hips off the ground, forming a straight line from your head to your feet. Hold the position, then switch to the other side. 6. Reverse crunches: Lie on your back with your legs bent and knees pulled towards your chest. Lift your hips off the ground by curling your pelvis towards your chest, then lower them back down. 7. Dead bug exercise: Lie on your back with your arms extended towards the ceiling and your knees bent at a 90-degree angle. Extend one leg straight out while simultaneously lowering the opposite arm towards the floor. Return to the starting position and repeat on the other side. Day 4: Upper Body Strength 1. Dumbbell bench press: Lie on a bench with a dumbbell in each hand at chest level. Push the dumbbells upward until your arms are fully extended, then lower them back down to chest level. 2. Lat pulldowns: Sit at a lat pulldown machine with your knees secured under the pads. Grasp the bar with a wide grip and pull it down towards your chest, squeezing your shoulder blades together. Slowly return to the starting position. 3. Dumbbell shoulder press: Hold a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder height with your palms facing forward. Press the weights overhead by extending your arms until they are fully extended. Lower the weights back down to shoulder height. 4. Tricep dips: Position your hands on a stable surface (e.g., a bench or parallel bars) behind you with your fingers facing forward. Lower your body by bending your elbows until your upper arms are parallel to the ground, then push back up to the starting position. 5. Bicep curls: Hold a dumbbell in each hand with your palms facing forward. Curl the weights upward by bending your elbows, squeezing your biceps at the top of the movement. Lower the weights back down to the starting position. 6. Push-ups with hand placement variation: Perform push-ups with different hand positions, such as wide push-ups, narrow push-ups, and diamond push-ups. Each variation targets different muscles in the chest, shoulders, and triceps. 7. Superman pose: Lie face down on the floor with your arms extended in front of you and your legs straight. Simultaneously lift your arms, chest, and legs off the ground, engaging your lower back muscles. Hold the position for a few seconds, then lower back down. Day 5: HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) 1. Perform each exercise for 30 seconds, with 10 seconds of rest in between. Complete three rounds. 2. Burpees: Perform a squat thrust, then immediately jump explosively into the air, reaching your arms overhead. 3. Mountain climbers: Start in a push-up position. Alternate driving your knees towards your chest, as if you are climbing a mountain, while keeping your upper body stable. 4. Jump squats: Begin in a squat position, then explosively jump up into the air, extending your body fully. Land softly back into the squat position and repeat. 5. Plank jacks: Start in a forearm plank position. Jump both feet out wide, then quickly jump them back together, maintaining a strong core. 6. High knees: Stand tall and rapidly drive your knees upward, trying to bring them as close to your chest as possible, while jogging in place. 7. Skaters: Start by standing on one foot and leap sideways to the other side, landing on the opposite foot. Swing your arms to help generate momentum and maintain balance. 8. Russian twists: Sit on the floor with your knees bent, heels on the ground, and lean back slightly. Hold a medicine ball or weight with both hands in front of your chest. Twist your torso to one side, then twist to the other side, touching the ball to the floor on each side. Day 6: Lower Body Strength 1. Barbell squats: Stand with a barbell resting across your upper back and shoulders. Lower your body into a squat position by bending your knees and hips, keeping your chest upright. Return to the starting position by extending your knees and hips. 2. Romanian deadlifts: Hold a barbell or dumbbells in front of your thighs with a shoulder-width grip. Hinge forward from your hips while keeping your back flat, allowing the weights to lower towards your feet. Push your hips forward to return to the starting position. 3. Walking lunges with dumbbells: Hold a dumbbell in each hand, step forward with one leg, and lower your body until both knees are bent at a 90-degree angle. Push back up and bring your back leg forward into the next lunge. Repeat on the other leg. 4. Glute bridges: Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground. Push through your heels to lift your hips off the ground until your body forms a straight line from your knees to your shoulders. Lower your hips back down and repeat. 5. Calf raises: Stand with the balls of your feet on an elevated surface (e.g., step or weight plate) and your heels hanging off the edge. Raise your heels as high as possible by pushing up with your toes, then lower them back down. 6. Step-ups: Stand facing a sturdy step or bench. Step onto the step with one foot, pushing through your heel to lift your body up onto the step. Step back down and repeat on the other leg. 7. Leg press: Sit in a leg press machine with your feet placed shoulder-width apart on the footplate. Push the footplate away from your body by extending your knees and hips, then slowly lower it back down. Day 7: Active Recovery and Flexibility 1. Light jogging or brisk walk: Go for a 20-minute light jog or brisk walk to get your body moving and increase blood flow. 2. Foam rolling or self-massage: Use a foam roller or massage ball to target tight muscles and release tension. Spend at least 10 minutes rolling over various muscle groups. 3. Dynamic stretching routine: Perform a series of dynamic stretches to improve mobility and warm up your muscles. Examples include leg swings, arm circles, and torso rotations. 4. Yoga or Pilates session: Engage in a 30-minute yoga or Pilates session to improve flexibility, balance, and core strength. Choose poses or exercises that focus on stretching and relaxation. 5. Deep breathing exercises: Practice deep breathing exercises to promote relaxation and reduce stress. Breathe in deeply through your nose, expanding your belly, and exhale slowly through your mouth. 6. Light resistance band exercises for upper and lower body: Use a resistance band to perform gentle exercises targeting your upper and lower body muscles. Examples include bicep curls, shoulder presses, and glute bridges. 7. Meditation or relaxation practice: Set aside 10 minutes for meditation or relaxation exercises. Find a quiet space, close your eyes, and focus on your breath or engage in guided meditation to calm your mind and promote overall well-being. Remember to adjust the weights and repetitions based on your fitness level and gradually increase the intensity as you progress. Stay hydrated, take rest days as needed, and always prioritize proper form and technique to prevent injury. Enjoy your workout program! Understanding the Benefits of Exercise: Regular exercise offers numerous benefits for both physical and mental well-being. By engaging in a diverse range of workouts, you can experience the following advantages: Improved strength and endurance: Strength training exercises, such as squats, push-ups, and dumbbell exercises, help build muscle strength and endurance. This enables you to perform daily activities with greater ease and reduces the risk of injury. Enhanced cardiovascular fitness: Cardiovascular exercises like jumping jacks, high knees, and cycling improve heart health, increase lung capacity, and boost overall endurance. They also help burn calories, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Core stability and balance: Core-focused exercises, including planks, Russian twists, and leg raises, target the muscles in your abdomen, lower back, and pelvis. A strong core improves stability, balance, and posture, reducing the risk of back pain and enhancing athletic performance. Increased flexibility and mobility: Incorporating stretching exercises, yoga, and Pilates sessions into your routine can improve flexibility, joint range of motion, and overall mobility. This leads to better movement efficiency, reduces muscle imbalances, and decreases the likelihood of injuries. Weight management and body composition: A well-rounded exercise program, combined with a balanced diet, can help with weight management and body composition goals. Strength training promotes muscle growth, which can increase your metabolic rate and assist in burning calories even at rest. Stress reduction and mental well-being: Exercise stimulates the release of endorphins, also known as "feel-good" hormones, which help reduce stress, alleviate anxiety, and boost mood. Regular physical activity has been linked to improved mental health, better sleep quality, and increased self-confidence. Cognitive function and brain health: Research suggests that exercise positively impacts cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health. Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, promotes the growth of new neurons, and enhances cognitive abilities, such as attention and concentration. Tips for Success: Gradually progress: Start with weights and intensity levels that challenge you without compromising form or risking injury. Gradually increase the weights, repetitions, or duration as your fitness improves. Listen to your body: Pay attention to how your body feels during and after workouts. If you experience pain or discomfort, modify the exercise or consult with a healthcare professional. Warm-up and cool-down: Prioritize a warm-up before each workout, which can include light cardio and dynamic stretching, to prepare your muscles for activity. Likewise, cool down with static stretches and deep breathing exercises to help your body recover. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to maintain proper hydration levels. Dehydration can negatively impact performance and overall well-being. Rest and recovery: Allow your body sufficient time to rest and recover between workouts. This helps prevent overuse injuries and ensures optimal performance during subsequent sessions. Consistency is key: Strive for consistency in your exercise routine. Aim to perform the workouts as scheduled, but also listen to your body's needs. It's better to have a modified workout or rest day than to push yourself when fatigued or injured. Seek professional guidance: If you're new to exercise or have specific health concerns, consider consulting with a qualified fitness professional or healthcare provider. They can help tailor the program to your individual needs and ensure proper form and technique. Remember, exercise should be enjoyable and sustainable. Find activities you genuinely enjoy to maintain motivation and make fitness a lifelong pursuit. Embrace the educational aspect of this program to understand the benefits of each workout and how they contribute to your overall health and well-being.