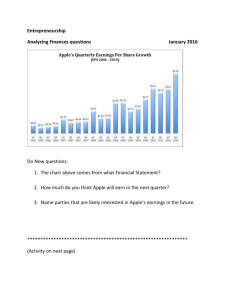
1 The Value Chain and Customer Value Creation Student Name Institutional Affiliation Course Name Instructor Name Insert Date 2 The Value Chain and Customer Value Creation The business management concept of the value chain was introduced and described by Michael Porter. The concept of value chain involves all aspects of a business’s operational activities and can be studied in combination with the supply chain (1). While the supply chain focuses on the procurement process of goods and services from suppliers, a value chain studies the value added at various intervals through a series of activities or processes that aim to create profitable value for a product offering. In general, value-chain business activities are usually divided into primary activities and secondary activities. The primary activities are directly related to the creation of a good or service. The support activities are those that help in enhancing the efficiency and work of an offering to obtain a stronger competitive advantage among peers. An analysis of Starbucks (SBUX) can help to further illustrate and understand the value chain concept. The Starbucks journey began with a single store in Seattle in the year 1971. From there it grew to become one of the most recognized brands in the world. Starbucks’ mission is, per its website, “to inspire and nurture the human spirit-one person, one cup, and one neighborhood at a time.” (2). 3 Primary Activities (i) Describe the decision-making process for a market-oriented firm regarding its value chain. How does it determine which value-adding activities it should perform? Give examples to illustrate. (ii) Consider Porter’s “generic strategies”. How do different generic strategies result in different decisions regarding value chain activities? What are the implications for the ability of the firm to succeed in creating sustainable competitive advantages? (ii) What does this imply for the firm’s resources, their competences and capabilities? Since firms do not have perfect knowledge of their customers, what types of competences and capabilities are necessary for superior firm performance? 4 References