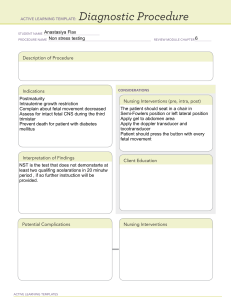
NCM 209 Care of Mother, Child, and Population Group at Risk or with Problems • ampulla (fallopian tube) – egg and sperm fertilize • ovulation – 14 days after mestruation PRENATAL CARE – prevent occurrence of complication - THE PURPOSE OF PRENATAL CARE IS TO ENSURE AN UNCOMPLICATED PREGNANCY AND THE DELIVERY OF A LIVE AND HEALTHY INFANT. BALANCE OF FORCES IN PREGNANCY • FETAL SURVIVAL • MATERNAL SURVIVAL 5 Branches of Maternal Health • Nutrition – fat and protein demand (2nd half) • Prenatal Care – DOH standard prenatal care (2004) • Safe Delivery • Breastfeeding • Family Planning Prenatal Care • Regular prenatal care increases the chances of a healthy mother and child after birth. • Early detection of congenital & birth defects • Prenatal immunizations can prevent mother-tochild-transmission and infection. (dec. the risk of infections and diseases) DOH STANDARDS OF PRENATAL CARE 1. WEIGHT – pattern of weight is more important than the amount of weight gained 2. HEIGHT BMI: <18.5 = underweight (intrauterine growth retardation) 18.5-24.9 (18.5-20.8) = normal 25-29.9 (29) = overweight (preeclampsia; edema) 30-34.9 = obesity I 35-39 = obesity II 40 above = extreme obesity 2nd to 3rd trimester - inc. 340 (330) kcal - inc. Vit. C = help dec. risk of premature rupture of membrane (PROM) = help inc. cervical collagen helps ripen and promotes effacement and dilatation of cervix during delivery - folic acid (doubled) = reduce risk of neural tube defects 3. BLOOD PRESSURE - 10 mmHg systolic and 15 mmHg diastolic (normal) - diastolic = 100 BP on close watch (borderline) – BP might continue to rise 4. FHT - 120-160 bpm; regular and strong (normal) - inc. or dec. = gasping for oxygen 5. FUNDIC HEIGHT - measurement of symphysis pubis - uterine size correlates with the fetal growth • 5th month = 20 cm (umbilicus) • 6th month = 21-24 cm • 7th month = 25-28 cm • 8th month = 29-30 cm • 9th month = 30-34 cm 6. LEOPOLD’S MANEUVER – fetal presentation, position, lie, attitude * let patient void to prevent discomfort fir A. Fundal Grip – presenting part; presentation, position (right hand = push, left hand = palpate) B. Umbilical Grip – extremeties, fetal back, and FHT (usually in the LLQ); position C. Pawlick’s Grip – engagement D. Pelvic Grip – attitude; degree of flexion (head) 7. TT IMMUNIZATION TETANUS TOXOID WHEN TO GIVE TT 1 ANYTIME DURING PREGNANCY TT 2 4 WEEKS AFTER TT 1 TT 3 6 MONTHS AFTER TT 2 TT 4 1 YEAR AFTER TT 3 TT 5 – booster dose 1 YEAR AFTER TT 4 8. DIET • Calories • Proteins – tissue growth and repair; growth of maternal tissues • Water – all body tissues • Calcium – bone and tooth miniralization and calcification (mother and fetus) • Vitamin D – for calcium to be absorbed by the body • Iron – blood loss 9. DANGER SIGNS OF PREGNANCY a. vaginal bleeding (no matter how small – seek medical attention) b. inc. temp which cannot be relieved by antipyretics c. difficulty in urinating = edema, headaches, inc. BP d. swelling of breasts e. blurring of vision f. tingling sound of ears – pregnancy induced hypertension g. postpartum blues postpartum depression 10. BREASTFEEDING • RA 7600 – Rooming In and Breastfeeding Act of 1992 • EO 51 of 1986 – Milk Code (signed by former pres. Noynoy Aquino) • RA 10028 – Expanded Breastfeeding Promotion Act of 2009 amendinf RA 7600 11. FAMILY PLANNING Methods: • Natural o Abstinence o Fertility Awareness Method (FAM) – like calendar method o Lactation Amenorrhea Method (LAM) o Basal Body Temperature (BBT) – check temp every morning; fertile = inc. temp o Billings’ Method – base on vaginal mucosa; secretions o Symptothermal Method – combination of BBT and Billings’ • Artificially o Intrauterine Device (IUD) o Oral Contraceptive Pills (PO) o Depo Provera Injectables – white and cloudy (IM) o Implant – suppress ovulation (lasts for 3 years) o Condom o Cervical Cap – to close the cervix o Spermicidal Gel – gel that kills sperm • Surgical Contraceptive o Tubal Ligation o Vasectomy 12. POSTPARTUM CARE - includes breastfeeding, diet, hygiene, meds, getting ready to go home health teachings - plain water for breast washing before feeding - perineum is susceptible to infection, bruises, lacerations - lochia can be a cause of infection - perineal care: front to back - elimination process: empty bladder every 4-6 hrs after delivery - decrease in aldosterone = decrease in sodium retention • Intake and Output: monitored due to risk for urinary infection urinary stasis catheterization • constipation is common due to slow peristalsis • prevention of back strain • infant needs o sleep 16-20 hrs/day o eat 2- 4 hrs o wake when sleeping to eat • When am I going to feed by baby when awake? o infant signals : hand raising and opening, when baby turn to you when you rub his/her cheek with your finger/cloth o bathe baby 6 hrs after delivery o breastmilk has different colors depending on mother’s intake o breastmilk in fridge: ▪ single door: 2 weeks ▪ double door chiller freezer: 3 months - 6 months ▪ deep freezer: 1 year *if milk bottle has been opened and consumed but has left overs, never return in the bottle and in the fridge *if mother complains of sore nipples, assess, encourage use of pump, DO NOT stop breastfeeding and DO NOT use formula milk High Risk Mom According to DOH: - 1st pregnancy = hospital delivery to prevent maternal death - lying ins do not accept pregnant mothers for delivery without prenatal care to prevent maternal death What is High Risk Pregnancy? poor maternal or fetal outcome due to : medical – no prenatal checkups reproductive – having early or late pregnancy (highly recommended age: 25 years old) Psychosocial Obstetrical – delay on decision to look for a place to deliver baby SCREENING Diagnostic and Laboratory Examinations Screening – identifies patients who are at risk Diagnostic Test - confirmation of a particular disease COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT ➢ Hemoglobin ▪ helps determine if pt. has anemia, polycytemia (abnormally high erythrocytes count; high risk for jaundice – liver damage), assess pt. to treatment (see if there are imrovements) ▪ anemia = less oxygenation, dec. RBC content (due to dec. hemoglobin and erythrocytes = fatigue, fainting) o physiologic anemia – alleiviated by repositioning; nursing interventions o pathologic anemia – bone marrow supression ▪ inc. hemoglobin = dehydration o 14-18 g/dL – males o 12-16 g/dL – females (lesser than males because of menstruation) ➢ Hematocrit ▪ amount of space/volume of RBC takeup in the bood ▪ dec. hematocrit = anemia, hemodilation ▪ inc. hematocrit = hemoconcentration, polycytemia caused by blood loss ➢ Leukocyte (WBC) ▪ inc. leukocytes = indicates infection ➢ Thrombocytes (platelet) ▪ smallest type of blood cells ▪ for blood clotting ▪ inc. thrombocyte = blood clot forming in the blood vessels o alteration to oxygenation of the brain = stroke o hardening of blood vessels (part. arteries) = atherosclerosis ➢ Blood Typing ▪ may be part of NCP or NI pt. with CBC related complications ➢ Rhesus Factor ▪ isoimmunization (+/-) or sensitization URINALYSIS - determine if pt. is drinking enough water (6-8 glasses a day) - signify nephrological order - blood content (yellow almost red) ➢ Pus cells – identify if mother is having UTI (predispose fetus to intrauterine growth retardation, nephronia; mother to nephrolithiasis, hypertension) ➢ Bacteria – “ ➢ Protein/albumin – (+) = pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH) ➢ Sugar – GDM/ history of DM ➢ Squamous epithelial cells – inflammation to urinary tract system PAP SMEAR (Papanicolaou Smear) - Procedure to check cervical anomalies ULTRASONOGRAPHY ➢ Transabdominal – noninvasive, painless; *allow pt. to empty bladder ➢ TRANSVAGINAL ULTRASOUND – inserted in vagina; to clearly show where cells are forming *full bladder/partially full or empty bladder - to justify AOG of patient - observation of FHT at 11 weeks - measurement of biparietal - determine birth weight (macrosomia) - location of placenta - identify placental grading (detect fetal death) – FDIU (remote areas) BLOOD GLUCOSE TEST - detect sugar level in body ➢ FBS (Fasting Blood Sugar) ▪ no intake/ NPO for 8 hours ▪ test for iron deficiency (fasting 12 hours) ▪ N: 100 mg/dL ▪ DM: 125 mg/dL ▪ Borderline: bet. 100 and 125 mg/dL ➢ HGT (Hemo Glucose Test)/CBG (Capillary Blood Glucose) ▪ consentration of blood glucose in the blood ▪ N: 72-99 ▪ HGT = ward ▪ 5 hours before meal ▪ 2 hour before procedure ➢ OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test) ▪ tested on blood samples ▪ normal diet for 3 days and no diuretics before test ▪ 10 hours fasting ▪ patient should be at rest ▪ done early in the morning ➢ OGCT (Oral Glucose Challenge Test) ▪ tested on urine and blood samples ▪ checks how body takes glucose ▪ test for GDM ▪ prior to test, 50 g intake of sugar; after 1 hr, take blood and urine samples ➢ 2 HRS. POST PRANDIAL ▪ Test blood glucose ▪ Done after meal ▪ 75 g of sugar/carbohydrates AMNIOCENTESIS - examination to take amniotic fluid (invasive) - guided by ultrasound - detect genetic abnormalities and fetal lung maturity - risk: fetal infection, rupture of membrane, preterm labor, fetal injury ▪ Chorionic Villi Sampling o to determine fetal karyotype o performed 10 to 12 weeks AOG o uses bigger syringe (50 cc syringe) o 1 out of 200 are at risk o complications: fetal loss, RBOW, possible fetal limb reduction Maternal Alpha-Feto Protein - to detect neural tube defects Fetal neural tube defect: ➢ anencephaly – birth defect, baby is born without parts of brain and skull ➢ gastroschisis defect in abdominal wall; baby’s intestines are found outside baby’s wall ➢ spina bifida – failure of closure of caudal end; can’t walk most of the time (undergo PT) ➢ 2 major serum proteins (synthesized predominantly on the liver and yolk sac) ▪ Albumin ▪ Alpha-Feto protein DOPPLER VELOCIMETRY - waves that measure the velocity of RBC movement (non-invasive) - decreased = associated with poor neonatal outcome; deformities PERCUTANEOUS UMBILICAL BLOOD SAMPLING - complications: cord lacerations, preterm labor, premature rupture of membrane, thromboembolism BIOPHYSICAL SCORING 30 minutes observation by USD 5 markers: ➢ non stress test - hypoxemia (low level of oxygen in the blood) - hypoxia (inadequate oxygen delivery to body tissues) - FHR reacts with movement hypoxia leads to acidosis - 32 to - 120-160 (at rest) - Ex. 162 (moving) ➢ fetal breathing - inc. 2 within 1 episode - 30 sec. (per episode) - more than 30 (abnormal) ➢ amniotic fluid - 20 cm (hydramnios) - 5 cm below (oligohydramnios) - more than 30 (polyhydramnios) - N: 50-20; start to decrease at 39 weeks ➢ fetal body movement - done after 27 weeks AOG - expect for 3 or more movements of body and limbs ➢ fetal tone - N: 120-160 - Flexion seen in biophysical scoring in ultrasound BPS RESULT INTERPRETATION 8 – 10 - Normal fetus 6 - chronic asphyxia - repeat the procedure after 24 hours 4 - abnormal result 2 - ill fetus, terminate pregnancy NON STRESS TEST (NST) 2 - 2 or more FHT acceleration per movement 1 - <2 accelerations per movement 0 - no acceleration FETAL BREATHING 2 - 1 episode/30 minutes lasting 30 seconds 0 - no episode - more than 30 minutes - not lasting 30 seconds AMNIOTIC FLUID INDEX 2 - fluid filled pocket of 1 cm or more 0 - no amniotic fluid or less than 1 cm in every pocket FETAL BODY MOVEMENT 2 - 3 or more discrete movement of limbs and body in 30 minutes 1 - less than 3 movements 0 - no movements FETAL TONE 2 - 1 or more episodes of active extension with return to flexion of limbs and trunk 1 - slow extension with return to flexion 0 - no movements HEPATITIS B DETERMINATION - Quantitative = serum titer check; degree of immaturity to disease or virus - Qualitative 1 Hepatitis B Antigen (HBSAg) 2 reactive - positive 3 non-reactive – negative 4 Hepatitis B Antibiodies (HBSAb) ➢ qualitative ➢ quantitative CONTRACTION STRESS TEST (CST) ➢ done after 32 weeks AOG ➢ EFM – record response of FHR to stress induced by uterine contraction; *check FHR after contraction (fetal distress) ➢ Negative - normal; no fetal heart deceleration ➢ Positive - abnormal; with deceleration] ➢ stimulate nipple = help contraction (monitor) ➢ IV (oxytocin) = continuously monitor FETOSCOPY - Direct visualization of the fetus through a scope - Obtain sample tissues or blood - May perform intrauterine fetal surgery FETAL MOVEMENT COUNTING - Done after 27 weeks AOG - Twice daily for 20-30 minutes - Normal – 5-6movements in 20-30 minutes - Abnormal – less done 3 movements in 1 hour MEDICAL COMPLICATIONS DURING PREGNANCY • CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS (most common) PREGNANCY ➢ Increase blood volume 40 – 50% - double record due to growing fetus ➢ Increase cardiac output ➢ Decrease B during first trimester ➢ Increase size of ventricular chamber ❖ LEFT TO RIGHT SHUNTING - septum completely absent; foramen ovale... ❖ ATRIAL – SEPTAL DEFECT ➢ asymptomatic ➢ increase pulmonary blood flow ➢ pulmonary hypertension ❖ VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT ➢ left ventricular hypertrophy ➢ pulmonary hypertension ➢ biventricular hypertrophy ➢ no separation; septum not closed, inc. blood flow = pulmonary hypertension ❖ PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSUS ➢ rare ➢ early surgical repair ➢ similar with VSD ➢ no valve ➢ instead of aorta, goes to pulmonary artery ➢ hole bet. aorta anf pulmonary artery ❖ RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE ➢ Group A Beta Hemolytic Streptococcus ➢ Inflammatory process ➢ Autoimmune disease ➢ Scarring of the valves – stenosis of the valve ➢ Common in tonsilitis ➢ inc. blood volume = inc. cardiac output ✓ SIGNS AND SYMTOMS OF CARDIAC DISEASES • Shortness of breath – exertions • Palpitations • Orthopnea - breathlessness • Expectoration of blood – vomit blood • Cyanosis – bluish discoloration • Murmur – extra heart sounds • Heart enlargement – inflammation o ✓ FUNCTIONAL CLASSIFICATIONS OF CARDIAC DISEASES • CLASS 1 - asymptomatic = no limitations • CLASS II - symptomatic but with normal activities • CLASS III - symptomatic and with less than normal activities enlargement of jugular vein – right sided • CLASS IV - symptomatic and at rest - inability to carry any physical activity - contraindicated to have any physical activity JUDGMENT OF SAFETY OF PREGNANCY Conception should be prevented if: 1. Severe heart disease 2. Functional classification: class III-IV 3. History of heart failure 4. Pulmonary hypertension 5. Right to left shunting 6. Severe arrhythmia 7. rheumatic fever 8. Combined valve disease 9. Acute myocarditis MANAGEMENT OF CARDIAC DISEASES o termination of pregnancy by CS • Weight reduction • Rest • prevent infection • Digoxin – calcium channel blocker (help with contraction of heart) • Diuretics – water pills that help get rid of sodium and water Two types: ▪ Potassium-sparing diuretics - needed for heart contraction = inc. urine output, sparing potassium ▪ Plain diuretics NURSING CARE OF CARDIAC DISEASES ➢ Vital signs ➢ Provide rest ➢ Emotional support ➢ I & O monitoring ➢ Proper nutrition – dec. sodium intake, avoid fats/oily foods ➢ Carry out medical orders • GESTATIONALDIABETES MELLITUS - will only occur during pregnancy - metabolic diorder = characterized by hyperglycemia - result to insulin depletion - impaired of carbohydrate metabolism Two classifications: ▪ TYPE I (diagnosed at an early age) o formerly called “insulin dependent” o common to younger individuals acute: polyuria, polydipsia, weight loss ▪ TYPE II (diagnosed to older patient; current obesity) o most common o insulin resistance – inadequate insulin production o free from symptoms o may lead to ketoacidosis RISK FACTORS CAUSING GDM ➢ Obesity ➢ Family history ➢ Personal history ➢ Sedentary lifestyle ➢ Improper diet PATHOPHYSIOLOGY GDM = chronic disorder - Body requires energy Human Placental Lactogen + diabetogenics (cortisol, glucagon, adrenaline, growth hormone) Decrease Insulin sensitivity Hyperglycemia Estrogen & Progesterone crosses placenta Hyperinsulinemia (fetus large in size) Fetal Hyperglycemia Build up of fat (macrosomia) Increased insulin Fetal Hyperinsulinemia Growth hormone Increase ATP in cells MACROSOMIA 1. anabolic phase 2. catabolic phase (usually happens on 2nd phase or second half) Respiratory Distress Syndrome FETAL/NEONATAL COMPLICATIONS OF GDM ➢ Fetal hyperglycemia – high blood glucose ➢ Fetal Hyperinsulinemia – high insulin production ➢ Macrosomia – result of high maternal level of blood glucose from fetus derives glucose ➢ Prematurity – born before 37 weeks of gestation ➢ Respiratory Distress – result of high levels of insulin, fetal enzymes needed for surfactant in lungs (by fetus), dec. production of lung surfactant ➢ Neonatal Hypoglycemia – low blood glucose MATERNAL COMPLICATIONS OF GDM ➢ Preeclampsia ➢ Polyhydramnios – high amniotic fluid index; result in fetal urination = fetal hyperglycemia ➢ Infection - glaucoma ➢ Dystocia – inappropriate pubic bone : shoulder ➢ Postpartum Bleeding – laceration, incision, episiorrhaphy, ectopic pregnancy, hemorrhage, uterine atony ➢ Birth canal trauma – large baby, not proportionate pelvic inlet ➢ Caesarean delivery – CPD, fetal distress, macrosomic baby Fasting & 2 hours postprandial venous plasma sugar during pregnancy. FASTING RESULT <100 mg/dl 2HRS POST PRANDIAL < 145mg/ dl. >125 mg/ dl >200 mg/ dl. Diabetic Not diabetic ORAL GLUCOSE CHALLENGE TEST ➢ fasting post-midnight ➢ blood and urine specimen are obtained ➢ 50 grams glucose intake ➢ after 1 hour, blood and urine specimen is obtained ➢ A value above 130 – 140 gms/l one hour after is used as threshold for performing a 3-hour OGTT. Prerequisites of OGTT: ➢ Normal diet for 3 days before the test. ➢ No diuretics 10 days before. ➢ At least 10 hours fast. ➢ Test is done in the morning at rest. CRITERIA FOR OGTT The maximum blood glucose values during pregnancy: • fasting 90 mg/dl • one hour 165 mg/dl • 2 hours 145 mg/dl • 3 hours 125 mg/dl MANAGEMENT OF GDM ➢ Insulin – normalize glucose level ➢ Diet – 3 meals, 3 snacks ➢ Exercise Substance Abuse During Pregnancy TERATOGEN ✓ Any agents that interferes with normal embryonic development ALCOHOL – patent teratogen (ethyl alcohol) ✓ CNS Depressant ✓ Reduce Anxiety ✓ Sedation ✓ Respiratory Depressant ALCOHOL EFFECTS ON FETUS ➢ Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) ➢ Intrauterine Growth Restriction ➢ Preterm Delivery ➢ Missing limbs Opioids (party drugs) – permanent damage to fetus Maternal Effects: ▪ Spontaneous abortion ▪ Hepatitis Neonatal Effects: ▪ Neonatal Withdrawal Syndrome – hyperirritability (characteristic) ▪ Respiratoty Distress ▪ Autonomic Disturbances ▪ Gastrointestinal dysfunction CNS Depressants: ➢ Morphine ➢ Heroin ➢ Methadone ➢ Analgesics STIMULANTS – present in soda and coffee ➢ Cocaine ➢ Amphetamine ➢ Ecstasy ➢ Caffeine EFFECTS OF STIMULANTS ➢ Increase Concentration ➢ Alertness ➢ Paranoia ➢ Hypertension ➢ Psychosis STIMULANTS’ EFFECTS ON FETUS ➢ Preterm labor ➢ Spontaneous abortion ➢ Placental abruption ➢ Fetal hypertension PREGNANCY SMOKING Nicotine - Overall reduction of fetal growth - Vasoconstriction = dec. blood flow and supply of nutrients - Double risk of growth retardation ➢ Higher rates of spontaneous abortion, placenta previa, ➢ Preterm labor ➢ Low birth weight infant ➢ Fetal hypertension MARIJUANA ➢ Relaxant ➢ Hallucination ➢ Short term Memory loss ➢ Low birth weight Infant Tetrahydroconnabinol - active component of marijuana that crosses placenta - upto 30 days Lifetime Effects of Substance Abuse ➢ Physical deformities ➢ Mental Retardation ➢ Developmental Problem (END OF FIRST PRESENTATION)