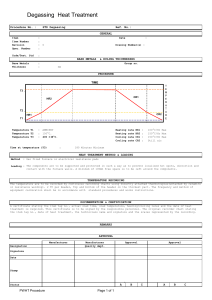
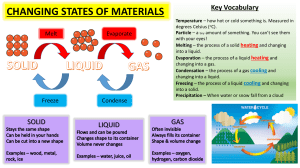
The Importance Of PWHT on Structural Steels. Structural steels play a vital role in numerous industries, including construction, infrastructure development, and manufacturing. Ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of steel components is of paramount importance. One crucial technique used to enhance the properties of welded structural steels is Post Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT). PWHT involves subjecting welded structures to controlled heating and cooling processes, which significantly impact the microstructure and mechanical properties of the steel. This essay aims to explore the importance of PWHT on structural steels by examining its effects on reducing residual stresses, improving toughness and ductility, minimizing distortion, and enhancing corrosion resistance. Welding introduces high localized temperatures and rapid cooling rates, leading to the formation of residual stresses in structural steels. These stresses can compromise the structural integrity of welded components, making them susceptible to cracking, distortion, and premature failure. PWHT offers a practical solution by effectively reducing residual stresses. The heat treatment process allows for the redistribution of stresses through controlled heating and slow cooling, resulting in a more uniform stress distribution. This stress relief minimizes the likelihood of cracking and distortion, thus enhancing the weldment's overall performance. Welding can introduce undesirable changes in the microstructure of steel, such as the formation of brittle phases, heat-affected zone (HAZ) softening, and grain coarsening. These alterations can significantly affect the toughness and ductility of the welded joint. PWHT serves as a critical step in mitigating these issues. By subjecting the welded structure to elevated temperatures, PWHT promotes the transformation of brittle microstructures into tougher ones, such as tempered martensite or bainite. Moreover, the controlled heating and slow cooling rates during PWHT allow for uniform grain refinement, which further improves toughness and ductility. Consequently, the risk of brittle fracture is reduced, enhancing the structural integrity and safety of welded components. Welding-induced thermal cycles often result in dimensional distortions in welded structures. Distortions can be problematic, especially in applications where precision and fit-up are crucial, such as in large-scale construction projects or fabrication of pressure vessels. PWHT plays a pivotal role in distortion control. By exposing the welded assembly to carefully controlled heating and cooling, PWHT allows for the relaxation of residual stresses that contribute to distortion. This process minimizes the overall distortion and helps maintain the desired shape and dimensional accuracy of the welded structure. Consequently, PWHT contributes to the efficient assembly of complex structures, reducing the need for costly rework and ensuring compliance with design specifications. Structural steels are often exposed to harsh environmental conditions, including moisture, chemicals, and corrosive agents. Welding can exacerbate corrosion susceptibility due to the formation of regions with altered microstructures and a higher concentration of residual stresses. PWHT aids in enhancing the corrosion resistance of welded structures. Through controlled heating and slow cooling, PWHT promotes the formation of a more stable and corrosion-resistant microstructure. Additionally, PWHT relieves residual stresses, minimizing the occurrence of stress corrosion cracking. The improved corrosion resistance provided by PWHT ensures the longevity and reliability of structural steel components, particularly in applications exposed to corrosive environments. Post Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT) is an essential process for ensuring the integrity, longevity, and performance of welded structural steels. By addressing the challenges posed by residual stresses, PWHT plays a critical role in reducing the risk of cracking, distortion, and premature failure. The controlled heating and cooling rates during PWHT promote