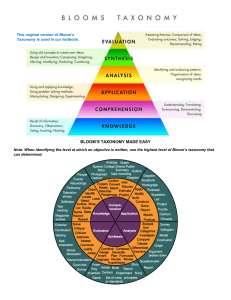
Thesis Statement: Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, a highly useful framework, is a valuable tool for understanding educational material. This analysis will contain the origin and purpose of Bloom's Taxonomy, its practical applications, any significant opposition that the framework has faced, and its effectiveness when used with education standards. Introduction: Importance of critical thinking for college students Definition and characteristics of critical thinking Application of Bloom’s Taxonomy (Three domains of learning objectives) Developing Critical Thinking Skills: Definition and cognitive process of critical thinking Utilizing logic to evaluate and construct arguments A critical mindset vs an uncritical one Introduction to Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: Overview of Bloom's Taxonomy Development and purpose of Bloom's Taxonomy Focus on the cognitive domain Research on Bloom's Taxonomy: Research on Bloom's Taxonomy Analysis of what Bloom's Taxonomy is History of its development, purpose, and practical applications Addressing criticisms and evaluating effectiveness Conclusion: Significance of critical thinking Importance and value of Bloom's Taxonomy for understanding educational material Sources: Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., & Bloom, B. S. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives. New York, NY: Longman. Forehand, M. (2018). Bloom's taxonomy. Salem Press Encyclopedia of Education (4th ed.), 1-3. Retrieved from Research Starters database. Critical But Helpful Thinking; Bloom’s Taxonomy Critical thinking is an essential skill for not only college students but any student of any grade or learning style. It grants them the ability to navigate the complex and harsh ideologies that challenge their own. While an uncritical mind accepts information at face value, a critical mind goes through the steps of; examining anything put in front of them, analyzing it for faults or how it affects them , and evaluating how useful it is. Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives is a valuable tool for developing critical thinking skills. Not only did the history of Bloom’s Taxonomy greatly affect its purpose, the practical application will also change due to this. Facing criticisms and challenges, it has grown just as much as students have, and its effectiveness with education standards has not suffered because of this. Being able to take this mindset and apply it to one’s life, while accepting the criticisms just as Bloom’s Taxonomy has, will help push one’s career further. Delving into Bloom's Taxonomy, it is important to understand the definition and process of critical thinking. Critical thinking involves examining, inquiring, analyzing, interpreting, evaluating, considering, resolving, and refining. It is not one but all of those and can not function without being able to follow that process. This requires utilizing logic to evaluate and construct arguments. It is just as important as thinking about what you say, before you say it. The world has infinite things to look at and just as many thoughts can be drawn about them.. Critical thinking is not just examining oneself, but looking at and analyzing everything around them too. It emphasizes evaluating the important, noticeable aspects around them. To help educators better organize their educational objectives across three domains (cognitive-affective-psychomotor) Bloom's Taxonomy can provide them with an efficient framework They have broken down cognitive levels into stages versus continuous degrees while creating memory recall development methods like remembering-understanding-applying-analyzing-evaluating etcetera no matter its unique contributions to curriculum design, it is. It is also essential not to overlook the contributions of taxonomies for the other domains while emphasizing the cognitive domain. To understand and use Bloom's Taxonomy, you must grasp its components and purpose, as Bloom and colleagues did when they first created it. They sought to improve instructional design by categorizing educational objectives through their taxonomy. The framework gives teachers a methodical way to develop effective learning experiences with cognitive levels at different stages. Beyond considering theoretical frameworks like these for how they organize objectives, it is important in exploring their pragmatic applications too that will leapfrog any practical steps in making progress in our understanding of such approaches like Bloom's Taxonomy Educators have been able to define the curriculum using this framework creating learning outcomes and assessing students' progress through sharing clarity around shared vocabulary But even with mainstream acceptance one cannot ignore the criticisms or limitations imposed on how educators rely solely on it. Some claim that Bloom's Taxonomy oversimplifies complex processes, lacks creativity or reduces emphasis on critical analysis; scholars are scrutinizing such claims always. Criticism aside, this approach still has its strengths since it offers a useful structure for educators designing meaningful learning experiences while evaluating student development regularly throughout In conclusion, teachers must acknowledge both limitations as well as benefits of using Bloom's Taxonomy and continue exploring complementary frameworks that align with their curricula. Critical thinking is a vital skill for college students, and Bloom's Taxonomy serves as a valuable tool for cultivating this skill. By understanding it, educators can leverage Bloom's Taxonomy to enhance instructional design and promote more efficient ways of thinking. While it is important to recognize the limitations, its advantages in education heavily increases its value. As students embrace critical thinking through the lens of Bloom's Taxonomy, it will enable them to thrive in a world that doesn’t wait for them. Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., & Bloom, B. S. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives. New York, NY: Longman. Forehand, M. (2018). Bloom's taxonomy. Salem Press Encyclopedia of Education (4th ed.), 1-3. Retrieved from Research Starters database. Critical But Helpful Thinking; Bloom’s Taxonomy Critical thinking is an essential skill not only for college students but for students of any grade or learning style. It gives people the power to navigate any challenging ideas that might surprise them. While an uncritical mind accepts information at face value, a critical mind engages in a systematic process of examining, analyzing, and evaluating information. Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational Objectives serves as a valuable tool for developing critical thinking skills. Its historical significance has greatly influenced its purpose, and its practical application continues to evolve in response to the criticisms and challenges that are constantly thrown at it. By adopting the mindset of Bloom's Taxonomy and embracing criticism, individuals can propel their careers and personal growth to new levels that were not previously obtainable. To delve into Bloom's Taxonomy, it is important to understand the definition and process of critical thinking. Critical thinking involves a range of cognitive processes, including examining, inquiring, analyzing, interpreting, evaluating, considering, resolving, and refining. It is not merely one of these processes, but a combination of them, and it cannot function without following this systematic approach. The ability to do one of them is useful, but being able to properly combine them and utilize it to its full potential is what makes critical thinking so useful. Critical thinking requires the use of logic to evaluate and construct arguments. It is as important as thinking before speaking, as it enables people to make sense of a large amount of information that might plague them. Critical thinking is not limited to self-examination but also involves examining and analyzing everything that surrounds them, emphasizing the evaluation of anything significant. Bloom's Taxonomy offers educators an efficient framework for organizing educational objectives that spans across three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. While the cognitive domain is the most emphasized, it is important to acknowledge the contributions of taxonomies from the other domains. Bloom's Taxonomy breaks down cognitive levels into stages, facilitating the development of memory recall strategies. Its unique contributions to the future of a course cannot be overlooked, as it provides teachers with a systematic way to develop effective learning experiences. These learning experiences influence students and creates a helpful cycle of learning that can be carried on after school and into later parts of life. However, when exploring the practical application of Bloom's Taxonomy, it is important to consider both its framework and how easy it is to use. Teachers and mentors alike have been able to redefine their course using this framework, creating clear learning objectives and assessments that are catered toward the students area of education. By using Bloom's Taxonomy, teachers can provide students with meaningful learning experiences that teach critical thinking skills. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations imposed on relying solely on Bloom's Taxonomy. Some argue that it oversimplifies complex processes, lacks creativity, or reduces the emphasis on critical analysis. Despite the criticisms, Bloom's Taxonomy remains a valuable approach to education. It offers teachers a structured framework that can easily be branched off of if the need arises. Designing meaningful learning experiences is made much easier and the ability to regularly assess student development is equally as helpful. The taxonomy promotes communication and collaboration between educators. It encourages them to continuously improve their teaching practices by incorporating feedback and integrating the advice. In conclusion, educators must recognize both the limitations and benefits of using Bloom's Taxonomy while exploring ways to branch off of the existing framework. Their goal is to align it with what they are trying to teach and to build more from it. By embracing critical thinking through the lens of Bloom's Taxonomy, students can thrive in a world that demands their analytical skills and adaptability. It provides a foundation for developing critical thinking skills and fosters an environment where students can freely question and learn without unnecessary negativity. This integration of critical thinking and acceptance of criticism is similar to the evolution of Bloom's Taxonomy. Individuals should learn from it and push their careers and personal growth to new heights. Anderson, L. W., Krathwohl, D. R., & Bloom, B. S. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives. New York, NY: Longman. Forehand, M. (2018). Bloom's taxonomy. Salem Press Encyclopedia of Education (4th ed.), 1-3. Retrieved from Research Starters database.