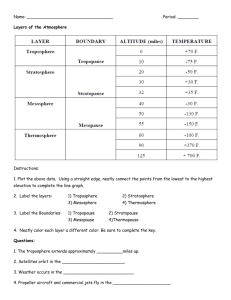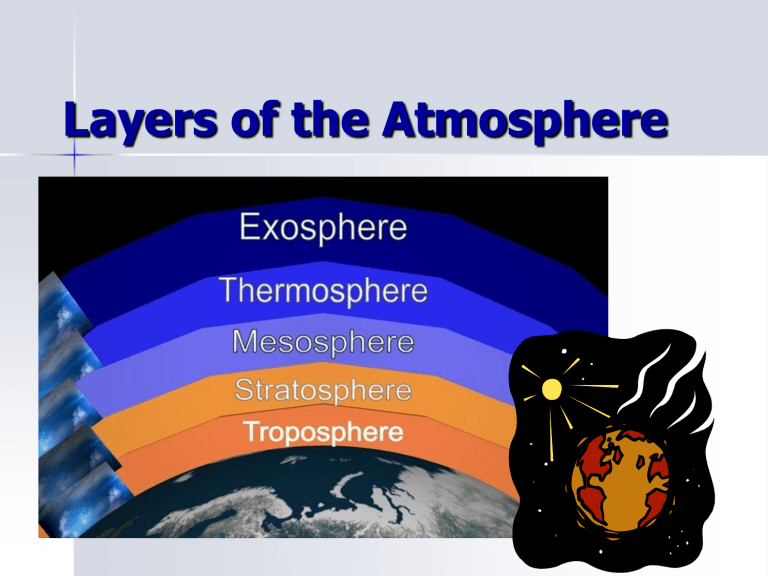
Layers of the Atmosphere Basis for Layers Layers are based on TEMPERATURE CHANGE within the layer. As you move up through the troposphere, temperature decreases. As you move up through stratosphere, temperature increases. As you move up through the mesosphere, temperature decreases As you move up through the thermosphere, temperature increases. As you move up through the exosphere, temperature increases. These are the layers in order from the Earth upwards Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere The Troposphere Lowest and thinnest layer. 7.5 miles/12.5km above earth’s surface. 90% of the atmosphere’s mass Densest layer. “Tropo” means turning or changing conditions. Weather occurs here and therefore clouds. The Troposphere We live in it. Temperature is warmer at the surface and decreases with altitude. the air temperature begins to decrease up to -52°C Temperature of the Troposphere temperature at surface is warmed by the earth absorbing energy from the sun. Convection currents carry the heat upward, so the air cools as it rises. Heat moves throughout (within) our atmosphere in CONVECTION CURRENTS The Stratosphere “Strato” means layer or spreading out. -52°C to -3°C 30mi above earth’s suface. Contains the ozone layer which absorbs energy and causes the temperature to rise. The ozone layer protects the surface from dangerous UV rays (ultraviolet radiation from the Sun). Temperature and the Stratosphere Ozone, made of oxygen, absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun, causing the temperature to increase. The Mesosphere “Meso” means middle 31 - 50mi above earth’s suface. Coldest layer down to 1480 F (-1000C) Not enough oxygen to breathe Most meteors burn up here Temperature and the Mesosphere This layer does not absorb energy from the sun, so it starts to cool again. The Thermosphere “Thermo” means heat Very hot (over 1000°C), but since air is so thin (not very dense) it would not feel warm at all. So even though it is very hot (over 1000°C), it would feel cold because there are so few particles to transfer heat to you. least dense absorbs solar radiation The space shuttle orbits here. reflects radio waves It takes special instruments to measure the temperature. Temperature and the Thermosphere Solar radiation first hits this layer, so the few particles that are here can gain lots of energy. They move rapidly, so they have a very high temperature. But the air is so thin here that it takes special instruments to measure the temperature accurately. The Exosphere “Exo” means outer Extends for 1000’s of miles the interface between Earth and space No definite edge Molecules gradually escape out into space Air is extremely thin. Satellites travel here because there is very little friction with air. Altitude and Density As the air pressure decreases, the density of the air decreases. The air particles are not squashed together as tightly the higher one goes. This is caused by gravity! The air at sea level and at 6km has the same 21% oxygen, but at 6km there are fewer molecules, so you take in less oxygen with each breath.