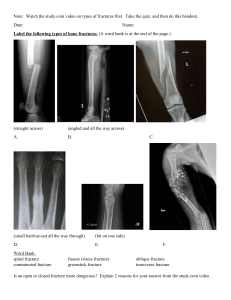
! A F?=GHI !"#$%$"& B :BCDE > C Updated: 6/13/2021 > Tibial Tubercle Fracture #" " #" #" #" # 8 $ 4.4 of 63 Ratings Matthew J. Steffes MD % Expert Comments Topic Podcast Eric Shirley MD TOPIC FLASHCARDS QUESTIONS EVIDENCE VIDEOS / PODS CASES Review Topic 2 13 17 1 3 & TOPIC ' Images ' Summary ' Tibial Tubercle Fractures are common fractures that occur in adolescent boys near the end of skeletal growth during athletic activity. ( Diagnosis can be confirmed with plain radiographs of the knee. ( Treatment may be nonoperative or operative depending on location of the fracture, degree of displacement, and any associated injuries. ( Epidemiology ' Incidence less than 1% of pediatric fractures ( ) Demographics males >> females ages 12 - 15 (approaching skeletal maturity) ( ) ) Risk factors most common in basketball, football, sprinting and high jump ( ) Pathophysiology ' Mechanisms of injury a concentric contraction of the quadriceps during jumping an eccentric contraction of the quadriceps during forced knee flexion ( ) ) Associated conditions compartment syndrome (4%) meniscal tears with Type III injuries ( ) ) Anatomy ' Osteology proximal tibia has two ossification centers * primary ossification center (proximal tibial physis) secondary ossification center (tibial tubercle physis or apophysis) insertion of patellar tendon physeal closure occurs from posterior to anterior and proximal to distal, with the tibial tubercle the last to fuse places distal secondary center at greater risk of injury in older children ( ) + + + + + Muscles extensor mechanism exerts great force at secondary ossification center ( ) Blood Supply recurrent anterior tibial artery can be lacerated ( ) Classification ' Based on level of fracture and presence of fragment displacement Type III most common ( ) Ogden Classification (modification of Watson-Jones) Type I Fracture of the secondary ossification center near the insertion of the patellar tendon * Type II Fracture propagates proximal between primary and secondary ossification centers * Type III Coronal fracture extending posteriorly to cross the primary ossification center * , Type IV Fracture through the entire proximal tibial physis * , Type V Periosteal sleeve avulsion of the extensor mechanism from the secondary ossification center * Modifier: A (nondisplaced), B (displaced) Presentation ' Symptoms sudden onset of pain generally occurs during the initiation of jumping or sprinting inability to immediately ambulate knee swelling/hemarthrosis with Type III injuries ( ) + ) ) Physical exam inspection & palpation knee effusion tenderness at the tibial tubercle evaluate for anterior compartment firmness ROM & instability extensor lag or extensor deficiency in Type II or III injuries ( ) + + + ) + - - . retinacular fibers may allow for active extension neurovascular exam monitor for increasing pain suggestive of compartment syndrome - - . + ) + Imaging ' Radiographs recommended views AP lateral optional views internal rotation view will bring the tibial tubercle into profile * comparison views of contralateral knee in younger pediatric patients findings widening or hinging open of the apophysis fracture line may be seen extending proximally and variable distance posteriorly anterior swelling may be the only sign in the setting of a periosteal sleeve avulsion (type V injury) patella alta ( ) + + ) + + ) + + + + CT ( ) ) can be useful to evaluate for intra-articular or posterior extension arteriogram if concern for popliteal arterty injury should not delay intervention in setting of compartment syndrome + MRI * generally not indicated useful for determining fracture extension in a nondisplaced Type II injury or type V injury ( ) ) Treatment ' Nonoperative long leg cast in extension for 6 weeks indications Type I injuries or those with minimal displacement (< 2 mm) acceptable displacement after closed reduction/cast application ( ) + + + Operative open reduction internal fixation with arthrotomy +/- arthroscopy, +/- soft tissue repair - - - . . indications Type II-IV fractures - need to visualize joint surface for perfect reduction and evaluate for intra-articular pathology soft tissue repair for Type V (periosteal sleeve) fracture ( ) + + + Techniques ' Open reduction and internal fixation approach midline incision to the fracture site technique evaluate and clean fracture site remove any soft tissue (periosteum) interposition anatomic reduction of fracture fragments internal fixation with 4.0 cancellous, partially threaded screws ( ) + ) + + + + * larger screws can be used but may cause soft tissue irritation in the long-term smooth K wires for younger child (>3y from skeletal maturity) postoperative care immobilization non-weightbearing in long leg cast or brace for 4-6 weeks rehabilitation progressive extensor mechanism strengthening return to sports no sooner than 3 months pros & cons pros anatomic reduction and stable fixation excellent healing potential may allow for earlier range of motion cons incision and associated complications hardware irritation can necessitate implant removal + + ) + + ) + + ) + + + + + + + Open reduction and internal fixation with arthrotomy or arthroscopy approach midline approach and parapatellar arthrotomy joint surface must be visualized to assure anatomic reduction alternatively, arthroscopy can be used to directly assess the articular reduction technique same as above evacuate intra-articular hematoma visualize joint surface to achieve anatomic reduction evaluate for meniscal tears and repair or debride as appropriate if soft tissue repair indicated postoperative care immobilization long leg cast for 4-6 weeks non-weight bearing rehabilitation progressive extensor mechanism strengthening return to sports at 3 months pros & cons pros addresses intraarticular extension and soft tissue injuries cons arthrotomy may require longer immobilization and/or rehabilitation ( ) + + + ) + + + + ) + + + + + + + + + + + Soft tissue repair similar to above approach midline incison to fracture site technique evaluate soft tissue injury remove any soft tissue interposition (periosteum) heavy suture repair of periosteum back to the secondary ossification center postoperative care immobilization long leg cast for 8-10 weeks prolonged immobilization needed due to soft tissue (rather than bone) healing rehabilitation progressive extensor mechanism strengthening return to sports no sooner than 3 months pros & cons prolonged healing time given to soft tissue healing ( ) ) + ) + + + ) + + + ) + + ) + Complications ' Recurvatum deformity more common than leg length discrepancy growth arrest anteriorly and posterior growth continues leading to decrease in tibial slope ( ) ) Compartment syndrome * related to injury of anterior tibial recurrent artery - - ( ) . . . . . Stiffness ( Bursitis most common complication following surgical repair due to prominence of screws and hardware about the knee, resolved upon hardware removal ( ) ) Vascular Injury to popliteal artery as it passes posteriorly over distal metaphyseal fragment ( ) Prognosis ' High rate of fracture union and return to sports with approriate treatment ( Low incidence of leg length discrepancy given age at which this injury occurs ( / FLASHCARDS (2) Tibial Tubercle Fracture ' OBC Complications What specific arterial injury is associated with compartment syndrome? ; by Ben Sharareh CARDS > Previous !$(@$; 0 Show Bullets Next ? 1 QUESTIONS (13) ' QUESTIONS > ! (@$<A 1 = < (OBQ18.73) Which of the following is the likely mechanism of injury shown in Figure A? QID: 212969 A, FIGURES: 1 !"##$%#&'("$)'*+$,-./0'1#23$1("*0.1*'(" 2 !"##$#&*#"3'("$)'*+$+.43*0'"5$1("*0.1*'(" 3 6'0#1*$78()$*($*+#$."*#0'(0$9"## 4 !"##$#&*#"3'("$)'*+$5.3*0(1"#4'-3$1("*0.1*'(" 5 !"##$%#&'("$)'*+$+.43*0'"5$1("*0.1*'(" Select Answer to see Preferred Response - EVIDENCE (17) ' evidenceFootprint 2 HIDE EVIDENCE Sort by EF L1\L2 Evidence Date PMID: 23147615 J Pediatr Orthop. 2012 De… - Tibial tubercle fractures: complications, classification, and the need for intra-articular assessment. Pandya NK Edmonds EW Roocroft JH Mubarak SJ & Pediatrics - Tibial Tubercle Fracture C - CORE :$; Pandya NK, JPO 2012 3 FREE PDF ... 336 views 12/1/2012 336 responses 2.7 " #" #" #" #" # PMID: 19308478 J Child Orthop. 2009 Jun;3… - Classification of proximal tibial fractures in children. Mubarak SJ Kim JR Edmonds EW Pring ME Bastrom TP. & Pediatrics - Tibial Tubercle Fracture C - CORE Mubarak SJ, JCO 2009 :$< 40 views 3 FREE PDF 6/1/2009 40 responses 2.7 " #" #" #" #" # PMID: 8403649 Clin Orthop Relat Res. 199… - Compartment syndrome complicating tibial tubercle avulsion. Pape JM Goulet JA Hensinger RN. & Pediatrics - Tibial Tubercle Fracture D - TESTED Pape JM, CORR 1993 :$< ... 92 views 3 FREE PDF 10/1/1993 92 responses 2.7 " #" #" #" #" # See More 4 VIDEOS & PODCASTS (2) All 5 4 Videos (1) ' Podcasts (1) Login to View Community Videos 5/15/2016 Tibial Tubercle Avulsions Indications and Techniques - Drs Jazrawi & Pediatrics - Tibial Tubercle Fracture = 1525 views 4.8 " #" #" #" #" # (8) Pediatrics | Tibial Tubercle Fracture 6 10/18/2019 & Pediatrics - Tibial Tubercle Fracture 6 Listen Now 19:15 min 500 plays 5.0 " #" #" #" #" # (4) 7 CASES (3) ' 8/5/2020 : Pediatric Tibial Tubercle Fracture (C101553) Jacob Triplet & Pediatrics - Tibial Tubercle Fracture > 598 8 7 2 1 9 3/3/2020 : Bilateral Tibial Tubercle Fractures in 12F (C101392) Panagiotis Poulios & Pediatrics - Tibial Tubercle Fracture ? 128 8 12 2 0 9 10/27/2015 : Tibial Tubercle Fracture in 11M (C2414) Alceu Fornari Chueire & Pediatrics - Tibial Tubercle Fracture > 9474 8 5 2 17 9 9 EXPERT COMMENTS (0) ' Please login to add comment. NO COMMENTS ! TOPICS TECHNIQUES QBANK PRODUCTS TRAUMA TRAUMA CASES PEAK & STUDY PLANS SPINE SPINE VIDEOS PASS SHOULDER & ELBOW SHOULDER & ELBOW KNEE & SPORTS KNEE & SPORTS PEDIATRICS PEDIATRICS RECON RECON HAND HAND FOOT & ANKLE FOOT & ANKLE PATHOLOGY PATHOLOGY BASIC SCIENCE APPROACHES POSTS EVIDENCE SELF-ASSESSMENT EXAM POCL FREE CME TESTIMONIALS Feedback ANATOMY ABOUT HELP OUR TEAM FAQ COMPANY PLATFORM TUTORIAL VIDEOS PRIVACY POLICY PASS TUTORIAL VIDEOS CONTACT US IPHONE APP ANDROID APP PRIVACY POLICY TERMS OF USE Copyright © 2022 Lineage Medical, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 @