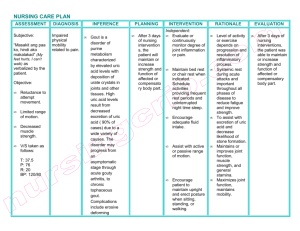
Gout: Expert Gout Nursing Assignment Assistance to Enhance Clinical Skills What is Gout? Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that usually affects the joints, most commonly the big toe. It is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, which leads to intense pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in the affected area. Gout typically occurs when the body produces excessive amounts of uric acid or fails to eliminate it efficiently. Uric acid is a natural waste product formed when the body breaks down purines, which are found in certain foods and beverages. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and is excreted through the kidneys. However, if there is an overproduction of uric acid or the kidneys are unable to remove it effectively, it can accumulate and form needle-like crystals in the joints. Gout attacks often come on suddenly and are characterized by severe pain and inflammation in the affected joint. The affected area may become hot, swollen, and extremely sensitive to touch. Gout attacks can last for a few days to several weeks and may recur periodically if left untreated. Certain Risk Factors Can Increase The Likelihood Of Developing Gout, Including: 1. Diet: Consuming foods rich in purines, such as organ meats, seafood, red meat, and sugary beverages, can raise uric acid levels. 2. Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to higher uric acid production and reduced elimination. 3. Genetics: Gout can run in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. 4. Age and gender: Men are more prone to gout, particularly after the age of 30, while women's risk increases after menopause. 5. Certain medical conditions: Conditions like kidney disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome can increase the risk. Treatment for gout aims to manage pain, reduce inflammation, and lower uric acid levels to prevent future attacks. This may involve medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, or corticosteroids. Lifestyle modifications like dietary changes, weight loss, increased fluid intake, and avoiding alcohol and sugary drinks can also help manage gout. If you suspect you have gout or experience symptoms of a gout attack, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Certainly! Here's Some More Information About Gout: If left untreated or poorly managed, gout can lead to complications over time. These can include the formation of tophi, which are lumps of uric acid crystals that can develop in the joints, cartilage, or soft tissues. Tophi can be visible under the skin and cause joint deformities. They may also lead to chronic inflammation and damage to the affected joints, impairing their normal function. Chronic gout, also known as gouty arthritis, can cause persistent pain and joint stiffness. It may affect multiple joints simultaneously, such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers. In some cases, gout can even affect the kidneys, leading to the formation of uric acid crystals in the kidneys and potentially causing kidney stones or more serious conditions like kidney damage or kidney stones. To prevent gout attacks and manage the condition effectively, healthcare providers often recommend a combination of medication and lifestyle modifications. Medications commonly used for long-term gout management include urate-lowering therapy (ULT), such as allopurinol or febuxostat, which helps reduce uric acid levels in the blood. ULT is often prescribed to individuals who have recurrent gout attacks, tophi, or associated complications. In terms of lifestyle changes, adopting a gout-friendly diet can be beneficial. This involves avoiding or limiting foods high in purines, such as organ meats, shellfish, red meat, and certain types of fish like sardines and anchovies. Additionally, reducing alcohol consumption, especially beer, and maintaining a healthy weight can help lower the risk of gout attacks. Increasing fluid intake, particularly water can help promote the excretion of uric acid from the body. Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and can also contribute to better management of gout. Regular exercise is generally recommended, but it's important to choose activities that are gentle on the joints, as high-impact exercises may trigger gout attacks. Low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are often well-tolerated and can help maintain joint flexibility and overall fitness. It's worth noting that gout management is a long-term commitment, and it's important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan. They can monitor your condition, adjust medications if necessary, and provide guidance on lifestyle modifications to help you effectively manage gout and reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. Remember, this information is not a substitute for medical advice, so it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized recommendations. What Are The 4 Stages Of Gout? A gout is a form of arthritis that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to intense pain, swelling, and inflammation. Gout typically progresses through four stages, each characterized by distinct symptoms and levels of severity. In this article, we will explore these stages in detail, providing a comprehensive understanding of the progression of gout. 1. Introduction Gout is a complex condition that develops over time. Understanding the different stages of gout is crucial for effective diagnosis, management, and treatment. Let's delve into each stage and explore their characteristics. 2. Stage 1: Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia In the initial stage of gout, known as asymptomatic hyperuricemia, individuals have elevated levels of uric acid in their blood, but they do not experience any symptoms. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, substances found in certain foods and produced naturally by the body. While asymptomatic, it is important to monitor uric acid levels and adopt a healthy lifestyle to prevent the progression of gout. 3. Stage 2: Acute Gouty Arthritis Stage 2, acute gouty arthritis, is characterized by sudden and severe attacks of joint pain and inflammation. These attacks often occur at night and can be triggered by factors such as alcohol consumption, high-purine foods, stress, or certain medications. The affected joint, most commonly the big toe, becomes red, swollen, and extremely tender. The pain is often described as excruciating and can last for several days or weeks if left untreated. 4. Stage 3: Intercritical Gout After the initial acute attack subsides, gout enters stage 3, known as intercritical gout. During this stage, the symptoms disappear, and the affected individual returns to a relatively normal state. However, it is essential to note that intercritical gout is not a symptom-free period but rather a gap between acute attacks. Without proper management, further attacks are likely to occur. 5. Stage 4: Chronic Tophaceous Gout If left untreated or inadequately managed, gout can progress to its final stage, chronic tophaceous gout. This stage is characterized by the formation of tophi, which are lumps or nodules that develop under the skin. Tophi are caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, cartilage, bones, and soft tissues. These deposits can cause joint deformities, chronic pain, and reduced mobility. 6. Conclusion Understanding the four stages of gout is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals. Early detection and appropriate management can help prevent the progression of gout and minimize its impact on daily life. If you suspect you may have gout or are experiencing symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. In conclusion, gout progresses through four distinct stages: asymptomatic hyperuricemia, acute gouty arthritis, intercritical gout, and chronic tophaceous gout. Each stage presents its own set of symptoms and challenges. Early diagnosis, proper management, and lifestyle modifications are essential in preventing the progression of gout and reducing its impact on daily life. If you suspect you may have gout or experience any symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Gout Nursing Assignment Help Sure, I can help you with your gout nursing assignment help. A gout is a form of arthritis that occurs when there is a buildup of uric acid in the body, leading to the formation of urate crystals in the joints. It commonly affects the big toe but can also occur in other joints such as the ankles, knees, wrists, and fingers. Here Are Some Key Points To Consider For Your Gout Nursing Assignment: 1. Assessment: As a nurse, your initial assessment should focus on gathering information about the patient's symptoms, medical history, and any factors that may contribute to gout development such as obesity, hypertension, or a high-purine diet. Pay attention to the affected joints, their appearance, and any signs of inflammation or tophi (deposits of urate crystals). 2. Pain management: Gout is characterized by severe pain during acute attacks. You can help manage the patient's pain by administering prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or colchicine as directed. Educate the patient about the importance of adhering to the medication regimen and monitoring for any adverse effects. 3. Lifestyle modifications: Gout is often associated with dietary and lifestyle factors. Advise the patient to limit alcohol consumption, particularly beer, as it can increase uric acid levels. Encourage the patient to maintain a healthy weight, engage in regular physical activity, and consume a low-purine diet. Provide resources and education on dietary modifications, such as avoiding foods rich in purines (e.g., organ meats, shellfish) and promoting hydration. 4. Education on medications: Educate the patient about the purpose, dosage, and potential side effects of prescribed medications, such as NSAIDs, colchicine, and urate-lowering drugs (e.g., allopurinol, febuxostat). Emphasize the importance of adherence to medication therapy to prevent future gout attacks. 5. Fluid intake: Encourage the patient to maintain an adequate fluid intake to promote urine output and help flush out uric acid from the body. Aim for at least 2-3 liters of fluid intake per day unless contraindicated due to underlying health conditions. 6. Follow-up and monitoring: Schedule follow-up appointments with the patient to assess their response to treatment, monitor serum uric acid levels, and evaluate the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications. Collaborate with the healthcare team to adjust medication dosages as needed. 7. Comorbidity management: Gout is often associated with other comorbid conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease. Coordinate with other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive management of the patient's overall health. Remember to support your nursing interventions and recommendations with evidence-based practice guidelines and references. If you have any specific questions or need further assistance, feel free to ask. Nursing Assignment Help is a service that offers assistance and support to nursing students with their academic assignments. Whether it's a research paper, case study, essay, or any other nursing-related task, this service aims to provide expert guidance and resources to help students excel in their studies. The professionals providing nursing assignment help are typically experienced in the field of nursing and possess a strong background in healthcare. They understand the specific requirements and expectations of nursing assignments, and they can offer valuable insights, research assistance, and advice to students. Students may seek nursing assignment help for various reasons. It could be due to a lack of time to complete assignments, difficulty understanding the subject matter, or the need for additional support in organizing and presenting information effectively. The service aims to alleviate these challenges and enable students to submit well-written and thoroughly researched assignments. By availing of nursing assignment expert, students can benefit from personalized assistance tailored to their specific needs. This may include topic selection, literature review, data analysis, proofreading, and editing. The objective is to enhance students' understanding of nursing concepts, improve their academic performance, and develop their critical thinking and writing skills. It is important to note that nursing assignment help is intended to supplement students' learning and should be used responsibly. Students should actively engage with the provided materials and seek clarification when needed to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. Overall, "Nursing Assignment Help" aims to support nursing students in achieving their academic goals and gaining a deeper understanding of nursing concepts through professional guidance, resources, and personalized assistance. Thank You…..