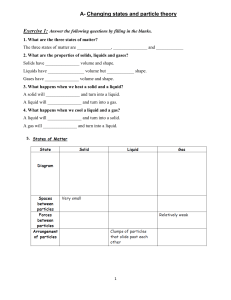
Chapter 1: States of Matter Define matter What is an atom? What is a molecule? What is an ion? Give some properties of solids. Give some properties of liquids. Give some properties of gases. How are solids, liquids and gases different in terms of their arrangement? How are solids, liquids and gases different in terms of their motion? How are solids, liquids and gases different in terms of their proximity (closeness)? How do gases cause pressure? Why does gas pressure increase when the volume of the container is reduced? Why is it dangerous to heat a closed glass jar full of gas? Anything that has a mass and takes up space. Matter can exist in three physical states: solid, liquid and gas. An atom is the smallest particle that cannot be broken down by chemical means. A molecule is a particle of two or more atoms joined together. An ion is formed when an atom or a group of atoms loses or gains electrons. A solid has a definite shape and volume, but cannot flow. A liquid has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container. It can flow. A gas has no definite volume. It can spread everywhere throughout its container. Solids – have fixed pattern Liquids – no fixed pattern Gases – random arrangement Solids – vibrate in fixed position Liquids – can slide past each other Gases – move everywhere rapidly Solids – close together Liquids – close together but not as close as solids Gases – far apart Gas particles collide with each other and with the walls of their container. They exert force on the walls when they collide, this causes pressure. The particles get closer together and hit the wall of the container more often. If we heat a gas in a closed container, as the temperature increases, the gas particles move faster and hit the walls of the container with increased force, thus creating higher pressure and this might lead to breakage of the glass jar. What is the name of the process where a solid turns directly into gas, or vice versa? What is the difference between evaporation and boiling? A change of state from solid to liquid is _______ A change of state from liquid to solid is _______ When a gas is cooled, it ___________ What is a volatile liquid? Sublimation. Evaporation takes place throughout the process of heating the liquid, while boiling happens only at a specific temperature. Melting. Freezing. Condenses. This is a liquid which evaporates easily and has a relatively low boiling point, e.g. ethanol, water. While a substance is melting, or a It stays the same until it has completely liquid is boiling, what happens to melted/boiled the temperature? Explain in terms of kinetic particle Increasing heat energy increases the theory, how a solid changes to a vibrations of the particles in the solid. So the liquid. temperature of the solid increases. The forces of attraction between the particles are weakened enough so that the particles begin to slide over each other. The substance melts. During the process of melting, The energy supplied is going to break the the temperature of a substance bonds (forces of attraction) between the remains constant despite particles instead of raising the temperature. application of heat. Why? Explain in terms of kinetic particle When gas particles encounter cooler theory, how a gas condenses. surfaces, they lose energy and can’t move as rapidly. They come close together and weak bonds are formed between the particles. The substance becomes a liquid. What does the presence of Lowers melting point, and raises the boiling impurities do to the melting point point of a substance and boiling point? What is Brownian motion? The irregular movement of tiny particles suspended in a liquid or gas. This was discovered by Robert Brown. How does Brownian motion provide evidence for kinetic particle theory? Brownian motion is caused by the random, regular bombardment (hitting) of visible particles, by even smaller particles of the liquid or gases they are suspended in, which cannot be seen. What is diffusion? The random movement of particles from region of high concentration to low concentration. Why does diffusion occur in gases Molecules in gases and liquids are constantly and liquids? moving, colliding with each other and changing directions. What factors affect the rate of The mass of the particles: the heavier the diffusion? particles, the slower they diffuse. The temperature: the higher the temperature, the faster the diffusion. What is a pure substance? When a substance is made of only one thing. In what areas is purity very important? How do you know if a substance is pure? How do melting point and boiling point change with impurities? What is the difference between the solute and the solvent? What happens to the solubility of a solid as the temperature is increased? Making medicinal drugs Making baby food Certain industrial processes Most pure substances have distinct melting and boiling points. The boiling point of water is 100°C. The boiling point is increased by impurities. The melting point is decreased by impurities. The solute is the solid that dissolves, and the solvent is the liquid in which it dissolves to form a solution It generally increases.