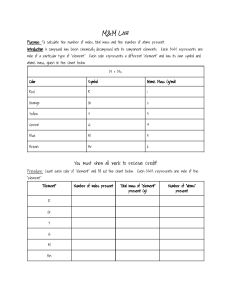
Chemistry: 2nd Semester Exam Select the correct oxidation numbers for the following elements. 1. Oxygen in O2 a. -2 b. +2 c. -1 d. +1 e. 0 2. Sodium in NaCl a. -2 b. +2 c. -1 d. +1 e. 0 3. Phosphorus in H3PO4 a. -5 b. -3 c. 0 d. +3 e. +5 4. H in H2O a. -2 b. +2 c. -1 d. +1 e. 0 5. O in H2O a. -2 b. +2 c. -1 d. +1 e. 0 6. In which substance does bromine have an oxidation number of +1? a. Br2 b. HBr c. HBrO d. HBrO2 7. Which species is the oxidizing agent in the following reaction? Cl 2(aq) + 2I- (aq) I2(aq) + 2Cl- (aq) a. Cl2 b. 2Ic. I2 d. 2Cl8. Consider the following: 2MnO4- + 5H2SO3 2Mn2+ + 3H2O + 5SO42- + 4H+ Which of the following elements does not experience a change in oxidation number? a. S in H2SO3 b. O in MnO4c. Mn in MnO49. In which of the following unbalanced equations does chromium undergo oxidation? a. Cr3+ Cr b. Cr3+ Cr2+ c. Cr3+ Cr2O72d. CrO42- Cr2O7210. In a redox reaction, the species which loses electrons is ___ . a. reduced b. oxidized c. neutralized 11. Consider the following: Cl2 ClO3The balanced half reaction is: a. Cl2 + 3H2O ClO3- + 6H+ + 5eb. Cl2 + 3H2O 2ClO3- + 6H+ + 4ec. Cl2 + 6H2O + 2e- 2ClO3- + 6H2 d. Cl2 + 6H2O 2ClO3- + 12H+ + 10e- Label the Acid, Base, Conjugate Acid, and Conjugate Base HC 2 H 3 O 2 + H 2 O H 3 O + + C 2 H 3 O 2 12. HC2H3O2 serves as the a. Acid b. Base 13. H2O serves as the a. Acid b. Base 14. H3O+ serves as the a. Acid b. Base 15. C2H3O2 serves as the a. Acid b. Base c. Conjugate Acid d. Conjugate Base c. Conjugate Acid d. Conjugate Base c. Conjugate Acid d. Conjugate Base c. Conjugate Acid d. Conjugate Base 16. A pH of _____ indicates that the solution is neutral. a. Less than 7 b. 7 17. A pH of _____ indicates that the solution is acidic. a. Less than 7 b. 7 18. A pH of _____ indicates that the solution is basic. a. Less than 7 b. 7 -5 19. What is the pH of a 2.0 x 10 M solution of HCl? a. 5.0 b. 4.7 20. What is the pH of a 3.2 x 10-2 M solution of LiOH? a. 1.5 b. 3.2 21. What is the pOH of a solution with a pH of 9.0? a. 5.0 b. 4.7 22. What is the pOH of a 3.2 x 10-2 M solution of NaOH? a. 1.5 b. 3.2 23. If [H3O+] = 1.0 x 10-5 M, then pOH = a. 5 b. 9 24. What is the chemical formula of sulfuric acid? a. H2S b. HS c. HSO3 25. What is the chemical formula of nitrous acid? a. H2N b. HN c. HNO3 26. What is the chemical formula of hydrochloric acid? a. H2Cl b. HCl c. HClO3 27. Which of the following acids is considered a strong acid? a. HC2H3O2 b. HI c. HCN c. Greater than 7 d. 14+ c. Greater than 7 d. 14+ c. Greater than 7 d. 14+ c. 9.3 d. 14 c. 10.3 d. 13 c. 9.3 d. 14 c. 10.3 d. 13 c. 11 d. 14 d. H2SO4 e. HSO4 d. HNO2 e. HNO4 d. HClO2 e. HClO4 d. H2S e. HF 28. Write the equilibrium constant: Pb3(PO4)2(s) ⇌ 3Pb2+(aq) + 2PO43-(aq) a. b. c. d. [3𝑃𝑏 2+] [2𝑃𝑂4 3−] [Pb3 (PO4 )2 ] [𝑃𝑏 2+]3 [𝑃𝑂4 3−]2 [Pb3 (PO4 )2 ] [Pb3 (PO4 )2 ] [𝑃𝑏 2+]3 [𝑃𝑂4 3−]2 [𝑃𝑏 2+ ]3 [𝑃𝑂4 3− ]2 Consider the following reaction for # 2-7 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) 29. What would happen if the O2(g) was removed? a. Reactants favored b. Products favored 30. What would happen if the pressure was increased? a. Reactants favored b. Products favored 31. What would happen if the amount of SO3(g) is increased? a. Reactants favored b. Products favored 32. What would happen if a catalyst were added? a. Reactants favored b. Products favored 33. What would happen if the temperature was increased (ΔH = -) a. Reactants favored b. Products favored 34. What would happen if SO2(g) was added? a. Reactants favored b. Products favored c. No change c. No change c. No change c. No change c. No change c. No change 35. The mechanism has been proposed for the formation of ethylbenzene: 1. CH3CH2Br + AlBr3 AlBr4- + CH3CH2+ (fast) 2. CH3CH2+ + C6H6 C6H6CH2CH3+ (slow) 3. C6H6CH2CH3+ + AlBr4- AlBr3 + HBr + C6H5CH2CH (fast) What is the catalyst? a. CH3CH2Br b. AlBr3 c. CH3CH2+ d. HBr 36. Which step is the rate determining step (see the mechanism above)? a. Step 1 b. Step 2 c. Step 3 37. For a reaction 2A + B 2C, with the rate equation: Rate = k[A]2[B] a. The order with respect to A is 1 and the order overall is 1. b. The order with respect to A is 2 and the order overall is 2. c. The order with respect to A is 2 and the order overall is 3. d. The order with respect to B is 2 and the order overall is 2. e. The order with respect to B is 2 and the order overall is 3. 38. Given the following data for this reaction: NH4+(aq) + NO2-(aq) N2(g) + 2H2O(l) EXPT [NH4+] [NO2-] RATE 1 0.010 M 0.020 M 0.020 M/s 2 0.015 M 0.020 M 0.030 M/s 3 0.010 M 0.010 M 0.005 M/s The rate law for the reaction is: a. Rate = k[NH4+][NO2-] b. Rate = k[NH4+]2[NO2-]2 c. Rate = k[NH4+]2[NO2-] d. Rate = k[NH4+][NO2-]2 39. When one mole of LiBr is dissolved in one kilogram of water, the concentration is (reported in units of mol/kg) a. 0.5 Molarity b. 0.5 molality c. 1.0 Molarity d. 1.0 molality 40. Water is a good solvent because of its ionic bonds a. True b. False 41. Water in sea water is a solute a. True b. False 42. When temperature rises, the solubility of a solid in a liquid is a. Not affected b. Increased c. Eliminated d. Decreased 43. Vinegar can dissolve in water so it is a. Immiscible b. Miscible c. Insoluble d. Dehydrated 44. How many liters of 2 M solution can be made using 320 g of CuF2? a. 2.1 L b. 3.8 L c. 0.78 L d. 1.6 L 45. What is the molality of a solution containing 125.0 g of water and 0.356 g of sodium hydroxide? a. 0.071 m b. 0.082 m c. 0.009 m d. 0.35 m 46. An aqueous solution of an unknown compound has a freezing point of -1.74 ° C, what is the molality of the solution (Kf = -1.86 ° CK/mole)? a. 0.132 m b. 3.22 m c. 0.935 m d. 2.13 m What is the strongest intermolecular attraction that affects the following compounds? 47. CH4 a. London Dispersion b. Dipole-Dipole c. H-bonds 48. HF a. London Dispersion b. Dipole-Dipole c. H-bonds 49. H2O a. London Dispersion b. Dipole-Dipole c. H-bonds 50. BrCl a. London Dispersion b. Dipole-Dipole c. H-bonds 51. The most abundant substance in a solution is the solvent a. True b. False 52. If a molecule is polar, it must have hydrogen bonding as an intermolecular force. a. True b. False 53. Hydrogen bonds are very strong bonds a. True b. False 54. Dipole-Diploe interactions are the weakest kinds of interactions a. True b. False 55. Hydrogen bonds occur when hydrogen is bonded to fluorine, nitrogen, or oxygen a. True b. False 56. ΔH fusion occurs when a substance is going from a liquid to a gas a. True b. False 57. If 1200. J of thermal energy is added to 52.0 g of water at an initial temperature of 30.8° C, what will its final temperature be (Remember: T = final temperature – initial temperature)? a. 40.2 ° C b. 31.2 ° C c. 36.3 ° C d. 39.1 ° C 58. Calculate the enthalpy of combustion (H) of ethylene, C2H4. C2H4(g) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. a. -1411 kJ b. -1254 kJ c. -732 kJ d. -627 kJ An energy diagram that is higher on the left side (start of the reaction) than the right side (end of the reaction) a. Has a –ΔH and is exothermic b. Has a +ΔH and is exothermic c. Has a –ΔH and is endothermic d. Has a +ΔH and is exothermic A negative ΔG indicates that a reaction a. Is spontaneous b. Is not spontaneous c. May be spontaneous Which of these symbols represent the measure of randomness in a system? a. E b. äE c. S d. äS What symbol is used to represent specific heat? a. sh b. csp c. Q d. H For this reaction at 25°C, ΔH° = -1854 kJ and ΔS° = -236 J/K. CH3COCH3(g) + 4O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) What is the value of ΔG° for this reaction? a. -1784 kJ b. -1848 kJ c. -1924 kJ d. 68500 kJ 64. A gas has an initial pressure of 2.4 atm and an initial volume of 150 mL. What is the final pressure if the final volume is 435 mL? a. 1.2 atm b. 0.83 atm c. 0.74 atm d. 2.3 atm 65. A sample of air has a volume of 550.0 mL at 106° C. At what temperature will its volume be 700.0 mL at constant pressure? a. 480 K b. 260 K c. 130 K d. 650 K 66. A sample of air at 104° C and 0.870 atm occupies a volume of 3.0 L. What volume would this gas occupy at 60. ° C and 1.7 atm? a. 0.14 L b. 2.5 L c. 4.1 L d. 1.4 L 67. What is the volume of 2.0 mol of F2 at 100 K and 150 atm? (R=0.0821 L atm/K mol) a. 0.067 L b. 0.014 L c. 0.11 L d. 0.29 L 68. A typical silicon chip, such as those in electronic calculators, has a mass of 2.3 x 10 -4 g. Assuming the chip is pure silicon, how many silicon atoms are in such a chip? a. 4.9 x 1018 b. 1.4 x 1020 c. 3.9 x 1021 d. 2.6 x 1027 69. The combustion reaction of C3H8O with O2 is represented by this balanced chemical equation: 2 C3H8O + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 8 H2O When 3.00g C3H8O and 7.38 g O2 are combined, how many moles of which reagent remain? a. 0.006 moles O2 b. 0.022 moles C3H8O c. 0.22 moles O2 d. 0.18 moles C3H8O 70. What is the molar mass of CH? a. 1.008 g/mole b. 12.01 g/mole c. 13.02 g/mole d. 18.00 g/mole 71. 200 grams of CaCO3 contains how many moles? a. 1 mole b. 2 moles c. 20000 moles d. 1.2 x 1027 moles 72. Using the following balanced equation, how many moles of H2 are produced when using 1 mole of Al? 2Al + 6HCl 2 AlCl3+ 3H2 a. b. c. d. 1 mole 1.5 moles 2 moles 3 moles Answer key available at: https://www.yourclassroomhelper.com/home/exams (Free Download)