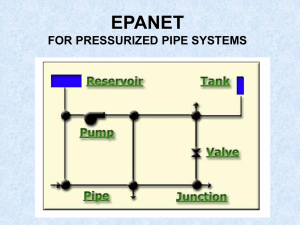
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 119 No. 17 2018, 2849-2853 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ Special Issue http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ An Overview of water distribution network design Manoj Nallanathel [ 1 ], B. Ramesh [ 2 ], A P Santhosh [ 3 ] Assistant Professor [ 1 ], Professor [ 2 ], Bachelor of Engineering [ 3 ] Department of Civil Engineering, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Chennai - 602105 jonamcivil@gmail.com [ 1 ], ramesh.bhaskar@gmail.com [ 2 ], sandy.926464@gmail.com [ 3 ] Abstract: Water distribution network(WDN) is combination of hydraulic components which transports the water from water resources to the consumers in time. Resources such as ground water, lake, river, etc. Mode of transportation are open channel, closed conduit, water stored in lorry tanks are used based on the conditions. Then the transported water should be stored, storages can be concrete tank, over tank in the domestic water supply. Good WDN should supply the water at enough pressure to the consumer’s tap which should be good in quality and should be easy to operate and maintain. When we prefer overhead tank the WDN system will be mostly gravity system only. Because due to elevation of tank, the pressure at node is quite reasonable which satisfies the consumers need. This total WDN can be designed and run the hydraulic analysis in the EPANET software. This paper gives a brief explanation of EPANET software which is useful to design water distribution network (WDN). Keywords: Water distribution network (WDN), pressure, Overhead tank, discharge, loop ends. EPANET allows to modify tank filling and emptying timings 1.INDRODUCTION EPANET is software which is used to design the water distribution piping systems. EPANET performs to reduce the age of water. It tracks the amount of flow of water from a given node to all other nodes in the WDN. extended period simulation of the water movement and quality behavior within pressurized pipe networks. Pipe networks which consist of pipes, nodes, pumps, valves, and storage tanks or reservoirs. EPANET allows the user to check the flow of water in each pipe, the pressure at each node, the height of the water in each tank in the entire network. EPANET's Windows user interface provides a visual network editor that simplifies the process of building piping network models and editing their properties and data. EPANET allows the user to check the quality of the water throughout the network. EPANET can give an idea to the engineer after designing such as idea about diameter of pipe, soil exploration, which type of pipe material should be used, how much discharge should be maintained and so on. Courtesy : Google image while designing the network the junctions are interlinked with pipes. The pressure at the junctions majorly depends upon elevation, base demand and demand pattern. Demand pattern is a multiplier of the base demand at particular junction at certain hour of a day. Demand pattern represents the peak and 2849 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Special Issue non peak hour of the day. Here some of advantages of EPANET are mentioned below: All calculations are done by itself and so quick while calculating. Changes can be done easily. Software itself warns about any error while simulation. Output and results can be summarized in tables with graphics. 2. fig no: 2. Water network of kimilili region LITERATURE REVIEW [1] R Sathyanathan, 2016 done a project based on WDN throughout the SRM university using EPANET software. In the project they explain about the pressure at junctions in peak and non-peak hours and gives the clarity about the loop ends in the campus. The diameter of pipe throughout the network is 250 mm. The source of water is lake which is located inside the campus, by using pumps the water is extracted and distributed in the campus. After analyzing the results came to know the pressure is enough to serve the [4] Shivalingaswami.S. Halagalimath, 2016 designs a WDN for the Bagalkot city, Karnataka. The Water distribution network consists of one tank, 120 junctions, 186 pipes and only one tank which has to be serve water for 13104 people in the study region. After networking and editing the properties of pipe, nodes parameters such as length, diameter, elevation and basic demand and run the analysis, checked the results. The study includes determination of quantity of water used, head losses in various pipelines and the pressure head at the nodes. In the consumers in the campus. [2] Mohammed N. Almasri PhD, 2008 done a journal paper on EPANET software, which gives detailed explanation of the software, and also did a small WDN for the simulation. The author also explains about the branched networks, loop ends, EPANET elements like pipes, valves, junctions, reservoirs, pumps, tanks etc., results, it was found that the resulting pressure and velocity satisfies enough to provide the water to the consumers in the study region. [5] Kakadiya Shital, 2016 done a case study on Punagam area of Surat city which has the area of 600.83 Ha and population of 2,22,252. In the project the authors done an [3] Christopher Bwire, 2015 investigates the activities of Kimilili Water Supply network in Bungoma County in the terms of demands, variation in pressure from the treatment plant to consumers using EPANET. Later getting the results from the simulation, 80% of nodes receives the pressure of more 16m which is sufficient to fill the tanks. The minimum pressure maintained is 10m. Pressure reducing valves also provided in the network to avoid water hammer in the taps. 2850 experiment on the existing water network and design the same existing water network in the EPANET software and check the results obtained from software and compare it to the manual calculations. The network completely divided into two zones which is totally consists of 109 junctions, 144 pipes. At the end of analysis the pressure and velocity at the junctions is quite enough to provide the water to the customers. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics [6] Arunkumar M., 2011 The study examined the water demand analysis of Public Water Supply in Municipalities using EPANET 2.0 software with the aim of providing effective planning, development and operation of water supply and distribution networks which is one of the most essential components of urban infrastructure. The network is used as intermittent water supply network to the people in Avadi, Chennai. Where the water is supplied in a particular number of hours such as 4 or pressure or not. But CPHEEO states that the minimum pressure is 12m, which is sufficient to serve the end users also in this region. Special Issue consumers. After collecting data of distribution networks of Limbayat zone pressure, they compute the flow velocity in each and every pipe using EPANET and After obtaining the results, they compared actual and computed results. [8]. Rasooli Ahmadullah 2016, examined the Kabul city water distribution network and also explained about the loop end problems in WDN. To get the map of WDN they used ArcGIS and imported the map to EPANET in the form of. inp form and starts designing and simulating the network and solves the problem due to the loop ends. In this project the author picks the Hardy cross method to [7] Darshan Mehta, studied about the water scarcity problem in the Limbayat zone, which is located in Surat city. The main reason of the scarcity is pressure fluctuation and may be some leakages in the network. So by using hydraulic simulation software he studied the Limbayat zone water supply system in order to improve the analysis the network. Hardy cross method gives more precision that the any other method for solving. This method can be done for the loop Water distribution networks also. The advantage of this method is simple math and self correction. He also recommended the engineers to use Hardy cross method who works in the water networking field. performance and quality of water which is supplied to the 3. CONCLUSION From the above papers we came to know about the the software and simulation will be successful and errors can basic knowledge of how to use EPANET software and how be avoided as much as possible. Loop ends also want to kept it works. Almost all the authors who worked on this software in mind while designing the network. According to the gives the output as comparison between already existing location of loop ends only the network should be WDN and virtual WDN. If we are careful at giving the input manipulated. Here I conclude some of the authors and their data i.e. diameter, length, elevation, demand to the WDN in respective works in this field are mentioned below table. TABLE NO: 1 CONCLUSION AND REMARKS Sl no Author and year of Description Remarks Worked on the WDN in SRM university Analyzed the WDN in the SRM campus and Chennai concluded that resulted pressure and velocity is publication 1 R. Sathyanathan (2016) enough to serve the consumers. 2 Christopher Bwire (2015) Investigated the kimilili water water supply Concluded that the minimum pressure head is 10m system in Bungoma. which is enough pressure to serve the customers. 2851 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics 3 4 Special Issue Rasooli Ahmadullah Studied already existing water network in Explained mainly about loop ends and also Hardy (2016) Kabul city cross method, which is useful to analyze the WDN. Arun kumar M (2011) Examined the municipal water supply in Analyzed the intermittent water supply and also Avadi, Chennai design period of the network. The minimum pressure is 12m which satisfies the dead end users also. Kakadiya Shital (2016) 5 Checked the activity of WDN of Punagam Analyzed the WDN and it was founded that area of Surat city. velocity and pressure at all the nodes is adequate enough to provide water to customers. 4. REFERENCES 1. R. Sathyanathan, Mozammil Hasan, V.T. Deeptha, “Water by using EPANET: A Case Study of Surat City” Global Distribution Network Design for SRM University using Research and Development Journal for Engineering, Recent EPANET”Asian Journal of Applied Sciences (ISSN: 2321 – Advances in Civil Engineering for Global Sustainability, 089) Volume 04 – Issue 03, June 2016. March 2016. 2. Mohammad N. Almasri PhD, “Simulation of Water 6. Arunkumar M, NethajiMariappan V.E., “WATER Distribution Networks the Use of EPANET” An-Najah DEMAND National University. SUPPLY USING EPANET SOFTWARE” International ANALYSIS OF MUNICIPAL WATER Journal on Applied Bioengineering, Vol. 5, No.1, Jaunary 3. Christopher Bwire, Richard Onchiri, NjengaMburu, 2011. “Simulation of Pressure variations within Kimilili water supply system using EPANET” International Journal of Civil 7. Darshan Mehta, Krunal Lakhani, Divy Patel, Govind Patel Engineering and Technology (IJCIET), ISSN 0976 – 6308 “STUDY OF WATER DISTRIBUTION NETWORK (Print), ISSN 0976 – 6316(Online), Volume 6, Issue 4, April USING EPANET” International journal of advanced (2015). research in Engineering, Science and Management. Vijaykumar.H, 8. RASOOLI Ahmadullah, KANG Dongshik, “Designing of Nagaraj.S.Patil, “Hydraulic modeling of water supply network Hydraulically Balanced Water Distribution Network Based using of on GIS and EPANET” (IJACSA) International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), Volume: 03 Issue: 03, Advanced Computer Science and Applications,Vol. 7, No. 2, Mar-2016. 2016. 5. KakadiyaShital, MavaniKrunali, Darshan Mehta, Vipin 9. Yadav, “Simulation of Existing Water Distribution Network https://www.epa.gov/water-research/epanet 2008. 4. Shivalingaswami.S. EPANET” Halagalimath, International Research Journal 2852 EPANET, Water research, US EPA 2853 2854