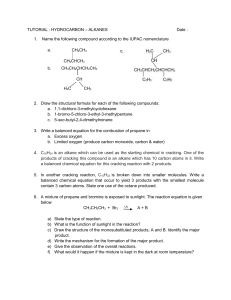
www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Topic 5 – Fossil Fuels Formation of fossil fuels Coal: Millions of years ago, plants on the earth surface died and covered by sand and mud. In time, heat, pressure and bacterial reaction gradually change the dead plant into coal. Petroleum and natural gas: Millions of years ago, marine plants and animals died and covered by sand and mud. In time, heat pressure and bacterial reaction gradually change the dead bodies into petroleum and natural gas. Fractional distillation of petroleum Petroleum is a mixture of many different kinds of hydrocarbons. Fractional distillation is to separate them for different purposes. Petroleum is first heated to about 400oC in a furnace. Compounds with low boiling point will vapourize, while others remain liquid. This mixture is then pumped into a fractionating tower. Different compounds will be collected at different levels. Fraction Boiling point Number of carbons in Uses each molecule Refinery gases <40 1-4 Making Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) Petrol 5-10 Fuel for cars 40-170 Naphtha Kerosene Gas oil Manufacturing town gas 170-250 250-350 10-14 14-25 Fuel for aircraft Diesel fuel Fuel oil Fuel for ship Lubricating oil and waxes Bitumen Lubricating oil for machines; making candles Surfacing roads and roofs www.chemistryhk.com >350 Above 25 Page 1 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Different air pollutants Pollutants Source Effect Remedies NOx Direct combination of N2 and O2 at high temp in car engine / in lightning. Acid rain, irritant to respiratory system, forms smog Install catalytic converter SO2 Combustion of S containing fuel Acid rain, irritant to respiratory system Use fuel with lower S content use of scrubber CO Incomplete combustion of fossil fuel Toxic, lowers the oxygen carrying capability of blood by forming stable carboxyhaemoglobin with haemoglobin, causes dizziness or even dealth Install catalytic converter, increase the amount of O2 in the combustion process Particulates Incomplete combustion of fossil fuel Irritant to respiratory system Install electrostatic precipitator in chimney, Install filtering system, Fine tune the engine regularly. Unburnt hydrocarbon Incomplete combustion of petroleum products Carcinogenic, toxic forms smog Install catalytic converter www.chemistryhk.com Page 2 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Homologous series Members in the same homologous series have: 1. Same functional group 2. Differs from next by a CH2 unit 3. Have Gradual change in physical properties. 4. Have similar chemical properties. Name of homologous series Functional group Example Alkane (CnH2n+2) ----- CH3CH2CH3 Alkene (CnH2n) Alkyne (CnHn-2) > C=C < —C≡C— CH2=CH2 H—C≡C—H Alkanol —O—H CH3CH2OH —NH2 CH3CH2NH2 Alkanal Alkanone Alkanoic acid Amide Anime www.chemistryhk.com Page 3 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Properties of alkanes Physical properties: The melting point and boiling point rise as the number of carbon atoms in the alkanes increase. Chemical properties: Combustion: alkanes burn completely with sufficient oxygen supply. alkane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water e.g. CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O Substitution reaction: hydrogen atoms can be replaced by chlorine or bromine. Replacement of chlorine is faster. A substitution reaction is a reaction in which an atom (or a group of atoms) of a molecule is replaced by another atom (or a group of atoms). CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl CH3Cl + Cl2 → CH2Cl + HCl CH2Cl + Cl2 → CHCl3 + HCl CHCl3 + Cl2 → CCl4 + HCl (chloromethane) (dichloromethane) (trichloromethane) (tetrachloromethane, carcinogenic) Condition: Heat or ultraviolet light In general, substitution reactions of alkanes consist of three steps 1. initiation (how the reaction gets started) 2. propagation (how the reaction proceeds) 3. termination (how the reaction stops) Free radicals, a very reactive species, are involved in the reaction process. www.chemistryhk.com Page 4 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk What is cracking? Cracking is breaking of large molecules into smaller molecules. In a cracking process, a very long alkane is broken down into a long alkane and a small alkene. Methods of cracking Heat is required in cracking process, so the process is also called thermal cracking. However, cracking is usually carried out at a lower temperature and pressure with catalyst of Al2O3 + SiO2 and the process is called catalytic cracking. Thermal cracking: 700oC + 30 atm Catalytic cracking 500oC + 1 atm + catalyst Importance of cracking cracking breaks a long alkane into a shorter alkane and a small alkene. This converts the less demanded heavy oil to petrol to meet the demand. The unsaturated alkene is more reactive than alkane. It is used as the raw material of production of a lot of chemicals (e.g. plastic). Making of town gas Town gas is made from catalytic cracking of naphtha. Liquid naphtha is heated into vapour. It is then mixed with steam and pass through a hot nickel catalyst at 700oC. An odourant is also add to make town gas leakage can be detected easily. C5H12 + 5H2O → 5CO + 11H2 C5H12 + 10H2O → 5CO2 + 16H2 2CO + H2 → CO2 + CH4 CO + H2O → CO2 + H2 Heat change in reaction We can find the heat change by this formula: ΔH = Hp – Hr. (ΔH = heat change, Hp = heat content of the product, Hr = heat content of reactant) Exothermic reaction is a reaction that gives out heat energy (ΔH is negative). Endothermic reaction is a reaction that takes in heat energy (ΔH is positive). Burning of petrol Complete combustion: 2C8H18 + 25O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O Incomplete combustion (insufficient oxygen): 2C8H18 + 17O2 → 16CO + 18H2O www.chemistryhk.com Page 5 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Addition reaction of alkenes Addition reaction is a reaction in which two or more compound react to give a single product. React with bromine: When an alkene is shaken with bromine in 1,1,1-trichloroethane, its orange colour will disappear. React with acidify potassium permanganate solution When an alkene is shaken with acidify potassium permanganate solution, its purple colourless will disappear. Thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic Hardness Thermoplastic Soft Thermosetting plastic Hard Flexibility Flexible Non-flexible Ease to melt Melt upon heating Do not melt upon heating Structure Separated polymer chains. Polymer chains with crosslinks forming 3-dimension network of bond. Examples Polythene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, perspex, nylon Urea-methanal www.chemistryhk.com Page 6 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Polymerization Addition polymerization is a process of repeatly joining together many monomers to form polymers. No elimination smell molecule occurs. Be careful with the term ‘addition polymerization’, NOT ‘additional polymerization’. Polythene Low density polythene (LDPE): Light, flexible, low melting point. High density polythene (HDPE): Tougher, higher melting point, transparent Polystyrene Polystyrene: Transparent, brittle, hard Expended polystyrene: White, extremely light. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) PVC: Stiff, brittle PVC with plasticizer: Flexible. Perspex Perspex: Strong, rigid, highly transparent. www.chemistryhk.com Page 7 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Condensation polymerisation Condensation polymerisation is a process which repeatly joining together monomers to form polymers. Small molecules (e.g. H2O, HCl, NH3) are always eliminated. Nylon Nylons are polyamides which contain the amide linkage. Nylons are formed by condensation polymerisation. We make nylon-6-6 in laboratory by adding aqueous solution of hexane-1,6-diamine in 1M sodium hydroxide solution to a solution of hexanedioyl dichloride in 1,1,1-trichloroethane. They are immiscible, A layer of nylon will form at the surface between them. Nylon has high melting point (200oC) and tensile strength. www.chemistryhk.com Page 8 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Polyester Polyesters contain the ester linkage. Polyesters are formed by condensation polymerization. Similar to formation of ester, A dioic acid and a diol condenses together with elimination of water molecule to form an ester molecule. Since each monomer has two function groups, it is capable to condense repeatedly to form a very long chain polymer. Pollution problems associated with disposal of plastic waste Pollution problems: 1. Most plastic are non-biodegradable. 2. Burning of plastic give off poisonous gases such as hydrogen chloride and chlorine. (Can use scrubbers to remove) 3. Plastic waste in sea poses directly danger the marine lives. (a) Small fishes die when their digestive tracts are clogged by fragments of plastic bags. (b) Sea animals suffocated to death by plastic bags. www.chemistryhk.com Page 9 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Alkanols Alkanols can be represented by: R—O—H (R is alkyl group, O—H is hydroxyl group) Preparation of ethanol In laboratory: we preparation ethanol by fermentation in laboratory. 1. Add a spoonful of ‘living’ yeast to a dilute solution of glucose in a conical flask. 2. Leave it for a few days. The maximum concentration of ethanol by fermentation is 18%, because the yeast dies at this concentration. 3. To increase the concentration, we can use fraction distillation. In industry: we pass the ethene with steam over a catalyst of phosphoric acid at 300oC and 65 atm. CH2=CH2 + H2O → CH3CH2OH Uses of alkanols 1. Alkanols as fuels e.g. CH3CH2OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O 2. Alkanols as solvents (it dissolve oil and it is miscible with water) 3. 4. 5. Alkanols in alcoholic drinks (all alcoholic drinks contain alkanols) Production of vinegar (vinegar is a dilute solution of ethanoic acid) Production of ester Properties of alkanols Physical properties: Boiling point: boiling point increase as the number of carbon in the molecule increase. Solubility: the solubility decreases as the length of the alkyl group increase. It is because the hydroxyl group tends to mix with water. When the length alkyl group increases, the influence of hydroxyl will decrease. www.chemistryhk.com Page 10 www.chemistryhk.com Instagram: garychemistryhk Chemical properties: 1. Reaction with Concentrated hydrochloric acid HCl + CH3CH2OH →CH3CH2Cl + H2O 2. Oxidation reactions When using acidify potassium dichromate as oxidizing agent: When using acidify potassium permanganate as oxidizing agent: When we heat alkanols with oxidizing agent in a reflux condenser, ethanoic acid will form. We can separate it from the mixture by distillation. 3. Esterification (condensation reaction) 1. 2. 3. 4. Add 2 cm3 ethanol, 1 cm3 ethanoic acid and 3 drop of conc. sulphuric acid (catalyst) into a test tube. Warm the test tube in warm water bath for 5 minutes. Pour the mixture into cold water. An insoluble layer of ester forms on the water, ethanoic acid and ethanol dissolve in the water. Naming of ester: name R1 first e.g. methyl ethanoate for e.g. ethyl ethanoate for www.chemistryhk.com Page 11