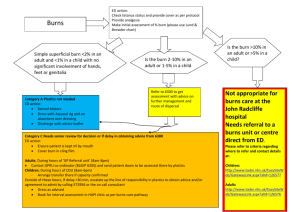
Burns A damage to the skin caused by heat or cold. Types of Burns Chemical Radiation Electrical – there is an entry burn and an exit burn e.g. direct burns, burns within an arc and burns from ignited parts Friction/Abrasion – caused by rough surfaces Thermal – caused by hot liquids and is known as a scald or by touching hot objects as a dry burn Classes of Burns 1st degree burn – only the top layer of the skin is damaged (the epidermis) with swells and is red 2nd degree burn – the epidermis and the dermis are damaged with blisters, red skin and swelling 3rd degree burn – the epidermis, dermis and the rest of the underlying tissue are damaged causing little to no pain because the burn reaches the nerves and the skin charrs Rule of Nines - It is used to estimate a burn’s percentage of your total skin 1. Head – 9% 2. Front – 18% 3. Arms – 18% 4. Back – 18% 5. Legs – 36% 6. Genitalia – 1% Treatment for Burns 1. Cool the affected area with running water for at least 10 minutes. *if running water is unavailable then improvise and use any harmless liquid* 2. Cover the burn with a non-sticky dressing: clingfilm, plastic bag and non-fluffy bandage. 3. Find medical attention and if it is serious call the ambulance. 4. If on fire: Stop, drop, and roll to remove oxygen from fire. Don’ts 1. Do not remove clothes from a burn unless it is a chemical burn. 2. Do not apply oils because it seals in it. 3. Do not pop any blisters because it opens the wound and allows germs to enter. 4. Do not stop cooling before 10 minutes. Infection Control - Keep the wound as clean as possible - Try avoiding contact with blood; use latex gloves or another effective barrier like plastic bags - Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water afterwards - Seek medical advice if concerned