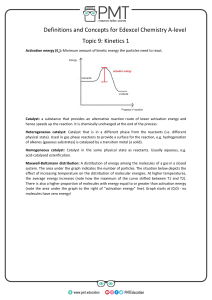
OBJECTIVES describe the concept of catalyst present catalyst as an effective means of affecting the reaction rate realize the importance of catalyst and how it affects your life. CATALYST WHAT IS A CATALYST? the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering its activation energy due to the participation of a substance called CATALYST. When this catalyst added to reaction it increase the rate of reaction by providing an alternate reaction pathway with a lower energy (Ea). In Biochemistry they are called ENZYMES. 2 TYPES OF CATALYSTS 1.ORGANIC-known as enzymes and their role is to catalyze and regulate specific reactions in living organisms. 2.INORGANIC-are often metallic compounds with a high surface energy. This high surface energy assists in the breaking of chemical bonds present in the reactant molecules. THE EFFECT OF A CATALYST ON RATE OF REACTION explains how adding a catalyst affects the rate of reaction. It assumes familiarity with basic concepts in the collision theory of reaction rates, and with the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution. MAXWELL-BOLTZMANN DISTRIBUTION describes the distribution of speeds among the particles in a sample of gas at a given temperature. The distribution is often represented graphically, with particle speed on the x-axis and relative number of particles on the y-axis. ACTIVATION ENERGY Is the minimum amount of energy that is required to activate atoms or molecules to a condition in which they can undergo chemical transformation or physical transport. ACTIVATION ENERGY Is the minimum amount of energy that is required to activate atoms or molecules to a condition in which they can undergo chemical transformation or physical transport. Guide questions Based on the diagram given, how does the energy of the reactants compare with the energy of the products? If the energy of the reactant is greater than the energy of the product, will energy be released or absorbed by the reaction? Why do you think so? If the condition were reversed (to that of no 2) what do you think will happen and why? The net amount of energy in the breaking and forming of bonds determines if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic.