Sierface
Chemistry
Vishal Tiwari
Sikkim
•
occurs only at
Adsoon
Adsorbate
Adsorbent
:
!
:
-
:
accumulation
-
at the bulk
.
not in
of species at surfaces
Édiq )
Substance which accumulates
Material
-
c
-
surface is not
on
which
accumulation
occurs
Removal of adsorbate from adsorbent
.
.
bulk
.
Adsorptioninaetione
Cig
04^12 ,
C' 214th
502
add
_÷÷ii dt÷
charcoal
pyessnr
Pressure is
bcoz
Iii ,
-
É
charcoal
color
Solution
ofdye
C. methylene blue)
adsorption of
gases
add
reduced
on
charcoal
takes place
.
'M
colorless
molecules of
adsorbed
surface
.
due
on
of charcoal
.
.
(
Iii ,
aq
Sol
of
raw
sugar
( color)
#
Air becomes dry
in
%,
colorless
charcoal
presence
of
silica
gel (
.
water molecule )
gets
adsorbed
on
silica gel
.
aHn
.
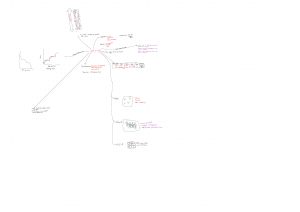
Surface phenomena
Concentration
absorbplion
.
of adsorbate
increases only at surface
and
ex :
-
.
dipped in ink
Suddenly taken out
chalk
S
*
not in bulk
water
vapour
is adsorbed
by silica gel
#
Rate is high in beginning
$ decrease till eqm
.
/
Bulk
/
""
/
water
1
phenomena
.
uniformally distributed
throughout body of material
adsorbate is
.
Chalk
9
dipped
in ink
for long period of time
a
vapour
is absorbed
cacti
by anhydrous
Rate remains constant
throughout the process
.
-
Sorption
:
Adsorption
§
absorption take place
¥É÷÷÷""%%n
tool
0000
188-0708
0000
01000
1¥09
100010
I-iunbalancedresidudfofr-nel.io
.
88%880
I
Bulk particle →
force
is
surface particle
lfnet -107
balanced
To make
fnet.no adsorption
occurs
.
adsorption is
•
•
Due to
an
exothermic
process ( AH
.
=
-
adsorption movement of gas particles
entropy decreases )
Ds=-Ve__
/DG=DH-TAs-|
Ah
Fe
=
=
attraction
reduces
AS -=
.
.
ve
-
-
re
AG-
(TAS)
C- vet
AH 1-
high value
For
)
↳
AH =
-
spontaneous process
ve
•
spontaneous process
AH
should
have
high
-
re
value
.
☐ G= AH
1
f.
-
T
highly
spontaneous
TAI
tire
-
re
{
initially
after
sometime
after
longtime
AH > Toss
rapid
→
adsorption
☐ H=TAS
→
☐ H< TAS
Eqm
:
desorption
physi sorption
Chemisorption
-
(
physical
adsorption)
( chemical adsorption)
Vanderwall force btw
•
•
chemical bond ( ionic/ covalent)
btw adsorbates adsorbent
adsorbates adsorbent
•
St
requires high Energy of
activation ( activated adsorption )
.
•
gt is not
→ a
specific
given surface
any
in nature
does
.
not show
preference for
-
a
gas to
be adsorbent
-
St is
•
•
9T
highly specific in
occurs
only if
chemical bonds
formed
a
are
nature
.
→
Reversible
→ more
adsorption takes
place when
premiere
increased
→
•
since it is
•
is
exothermic
process
.
temp is favorable
at high temp adsorption (physical)
Low
St required
high Energy of
activation
.
a
lrreresibleo
.
decreases
lechatelie-n.ci/o1e
.
.
÷⇐
adfor
lowtempis
favorable
Temp
tliqhtempis
favorable
.
gt
depends
on
nature
of gas
easily liquefiable gas
more adsorbed
9 1- also
.
depend
nature
are
on
of gas
e gains which
.
.
form
bond shows
chemisorption
chemical
or
gases with high critical
is easily adsorbed
temp
.
.
Enthalpy of adsorption
120-40
more
gf is
surface
/
KJ Mot
area more
multilayered
→
.
80-240
ktlmof
)
adsorption
→
→
more
surface
unilayered
.
area more
chemisorb't
Adsorptionisotherm
→
shows
of gas adsorbed
amount
with
pressure /Temp const)
Freudlichisotherm
of
adsorbed
mass
gas
c-
Im
=
P
""
\
(
M"
K
't
adsorbent
pressure
k
,
n
→
depends on
const
( nature of
:
÷"÷
i
249K
adsorbates
adsorbent)
low pressure
moderate
high
i'
pressure
region
n
:
:
-
021,21
-
region
t.p-N-m-kpyr.mn
!
-
nt=0
nm_=kpYn
Im
=
const
.
÷
Take
:
log
§m)
Kp
"n
both sides
c. + M
R
logktn-logphogf .KZ/ickhc=iogxI- - - -i -.#logp
log
=
Adsooptionfromsolwhionphase
%
log
Im
=
K
=
E.
[ og
log
Yn
+
K
""
In log [c)
/
L
"
loge
remain
Promoters
:
unchanged
→
called
do
→
opposite of
$
themselves
catalysis process is
.
substance which enhance
Haber 's Prom
Poison
tioh
the rate
accelerate
Nz 1- 3112
Promoter
-
activity of
¥0s 2MHz
a
called
catalysis
catalyst
.
.
Homogenous Catalyst
Reactant and
:
catalyst both insane
phase
25021-02 (g) " 2503cg )
.
cg)
( ttscooctlz
ce )
(
1214272011
Heterogeneous catalyst
¥
2502¥
02
t
02
MHz
Vegatable
fate ,
,, ,
+
1- Hzocey
( ag ) 1-
H)
1120 ( y)
CH, Coon
Ñ
( c. Hizb
Hz
(9)
1-
can
_É 2503cg ]
É
+413017
NO
1-
Glucose
1420
Nisvegatableghell
CGHIZOG
eaa )
fructose
.
Adsosptiontheoryoftleterogenouscatalyst
① Diffusion of
reactant
to the
②
Adsorption of reactant
③
Reactant molecules combine
on
surface of
catalyst
catalyst
Iz
←
'I
/
.
④ Desorption of Products
⑤ catalyst is again available for farther
occurs
-
,
PM
.
¥
catalystsbowseetivity
city 1- H2O
co + Hz
É
HCO
Carson
crz 03
Enzymecatalyst
Complex nitrogenous organic compound fproteins
Biochemical
catalyst
lnversionofcanesugar
42 Hzz
011µg ,
1-
H2O
É
CGH ,20g 1- CGH, 20g
Glucose
glucose-s.ge?,YffY#zymase-2czHs-on1-
202
fructose
.
starch
I%ialtose
2(CoHio0s)n €1T
starch
Maltose
maltase
421122011
maltose
.
-
glucose
( 12112201
,
.
←
(6171206
=
milk
És
protein
card
ne peptide
protein
-÷÷o
amino acid
.
.
mechanism
steps
E
+
⑨
s
key lock
mechanisms
⑤
→
1991
+
→
EP
→
Et p
.
Haber's
process
Ostwald process
Contact
Decor
Bosch
is
,,
Fe, Cmo )
→
→
→
→
→
"
Pt
V05
Cuclz
fezOztCK03
catalyst
eat
{
u,q--