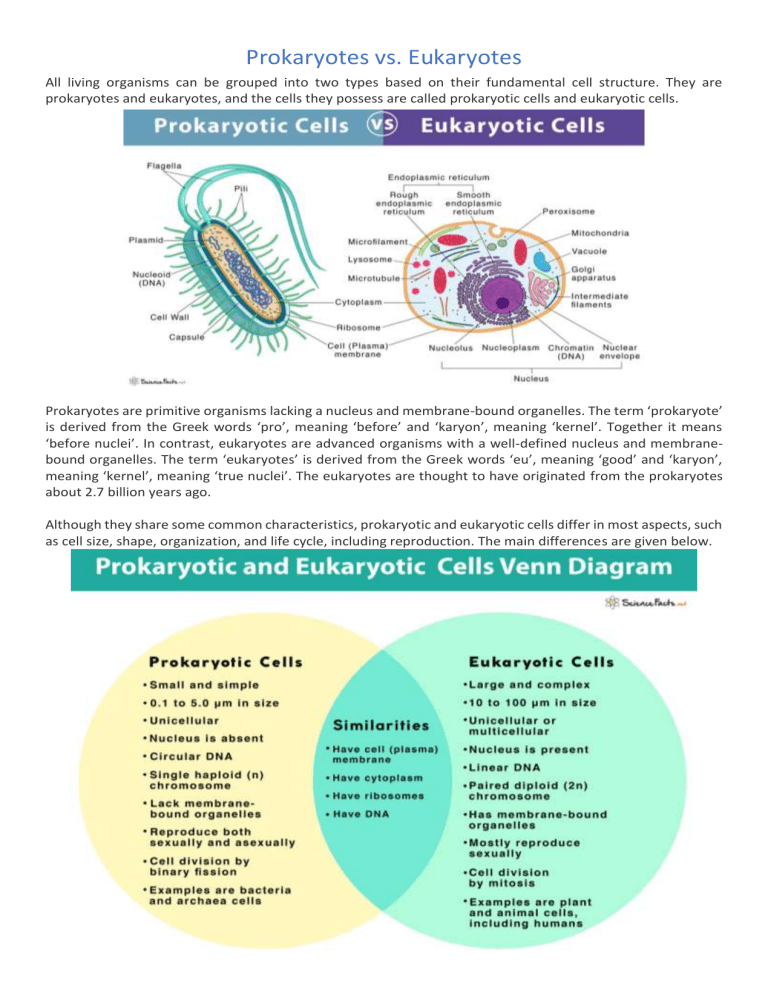
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes All living organisms can be grouped into two types based on their fundamental cell structure. They are prokaryotes and eukaryotes, and the cells they possess are called prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes are primitive organisms lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The term ‘prokaryote’ is derived from the Greek words ‘pro’, meaning ‘before’ and ‘karyon’, meaning ‘kernel’. Together it means ‘before nuclei’. In contrast, eukaryotes are advanced organisms with a well-defined nucleus and membranebound organelles. The term ‘eukaryotes’ is derived from the Greek words ‘eu’, meaning ‘good’ and ‘karyon’, meaning ‘kernel’, meaning ‘true nuclei’. The eukaryotes are thought to have originated from the prokaryotes about 2.7 billion years ago. Although they share some common characteristics, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in most aspects, such as cell size, shape, organization, and life cycle, including reproduction. The main differences are given below. What is the Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Basis Prokaryotic Cell 1. Examples Cells of bacteria, archaea or Cells of plants, animals, fungi, algae, archaebacteria, and cyanobacteria or and protozoa (protists) blue-green algae 2. Type Unicellular 3. Size diameter) 4. Type Organization (in 0.1 to 5.0 μm of Simple Eukaryotic Cell Unicellular or multicellular 10 to 100 µm Complex 5. Cell Wall Usually presentMade of peptidoglycan or mucopeptide Usually absentIf present (in plants and fungi) made of cellulose 6. Nucleus Absent. Instead, have a nucleoid that is devoid of the membrane Present and membrane-bound 7. DNA Circular, double-strandedFound freely in the cytoplasmNaked (not bound to proteins)Little repetitive DNA and no introns Linear, double-strandedFound within the nucleusBound to histone proteinsA large amount of repetitive DNA and introns 8. Chromosome Single haploid (n) chromosome Number Paired diploid (2n) chromosome 9. Plasmid Present. Absent. 10. type type, with 50S and 30S subunitsSmaller in size compared to the eukaryotic cell 80S type, with 60S and 40S subunitsLarger in size compared to the prokaryotic cell Absent Present Ribosome 70S 11. Mitochondria