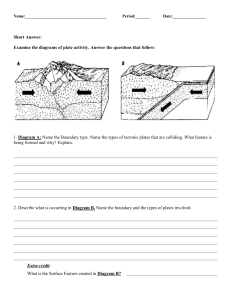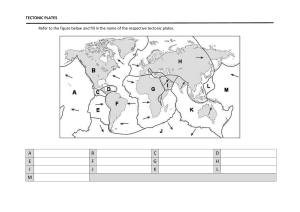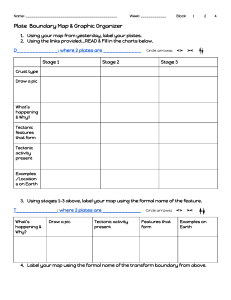
Plate Tectonics What is the lithosphere? a The crust b The upper mantle c The lower mantle d A and B e All of the above Fill in the blanks using the word options: mantle, crust, tectonic, lithosphere ______ plates are a block of _______ that consists of the _______and the rigid, outermost part of the ______. lithosphere mantle crust Matching Terms Match the following terms and definitions by dragging a line between them. Continental Drift boundary between two tectonic plates that are tectonic plates that are moving away from each other when two tectonic plates collide, and one plate moves under the other and sinks into the mantle Pangea Sea-floor spreading boundary formed by the collision of two plates Mid-ocean ridge where tectonic plates meet Subduction A place where sea-floor spreading has occured Subduction zones theory of plate tectonics regions where subduction occurs explains how large pieces of Earth’s outermost layer, called tectonic plates, move and change shape boundaries tb the boundary between two tectonic plates that are scraping past each other horizontally d a ring of volcanoes g around the Pacific Plate convergent boundary The process of new oceanic crust forming as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies divergent boundary The theory that all continents were once one land mass that separated and drifted apart over time. transform boundary the landmass that existed when all continents were joined ring of fire Sort the tectonic plate movement by its effect: Does it destroy crust, or does it create new crust? mid-oceanic ridge Sea-floor spreading convergent boundary mountain ranges divergent boundary subduction Destroys Crust Creates Crust Land formations Match which land formation is caused by which kind of tectonic plate movement. continental-continental convergent fault lines continental-oceanic convergent islands oceanic-oceanic convergent valleys oceanic-oceanic divergent mountain ranges continental-continental divergent mid-ocean ridges transform volcanoes Fill in the blanks about transform boundaries and earthquakes. Plates separated by a fault do not glide past each other. in the rocks causes the plates to lock. The friction, or , builds until they SNAP! The sudden release of is what we feel during an .