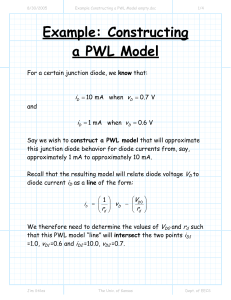
04b. AIV - Simplified QA Sunday, April 9, 2023 10:40 AM AIV: Q1: How to find lines subject to AIV? 1. Follow the T1- QUALITATIVE ASSESSMENT (below snap) for preliminary screening. 2. Follow the below steps to calculate PWL as per T2.7 HIGH FREQUENCY ACOUSTIC excitation (EI Guidelines) STEP 2 a. Applicable for Gas Service / Mixed Service with Gas Flow > 50% b. Calculate MACHNO & PWLi using following process parameters: i. P1, P2 (Upstream & Downstream Pressure) ii. Te (Upstream Temp) iii. W (Mass flow rate) iv. Mw (Molecular Weight) c. If Mach No >1 (Sonic Flow) then PWL = PWLi + SFF(6) SFF - Sonic Flow Correction factor Else PWL = PWLi d. If PWL > 155DB, then AIV RISK is HIGH. e. PWL supplied by valve manufactures shall not be used for assessment method in EI guidelines. Q2: What are the lines generally subject to AIV? 1. PSV Downstream & Flare Headers 2. Restriction Orifice (RO) 3. Control Valves / Blow down Valves Q3: How do you calculate LOF for branch? 1. Calculate N (Number of cycles to failure) based on following: a. Header Pipe Dia & Thk (D,T) b. Branch Pipe Dia & Thk (d, t) c. PWL at location of interest 2. Calculate FLM (Fatigue Life Modifiers) a. FLM1 (to account for D/d) b. FLM2 (to account for weldolet) c. FLM3 (to account for duplex material) 3. N = N * FLM1 * FLM2 * FLM3 4. Calculate of Lf using N (Lf shall be 0 to 1) 5. LOF = Lf (if Lf >= 0.5) else LOF = 0.29 Q4: How do you calculate LOF for support locations? 1. In general, LOF not calculated at support locations. Instead clamp type and full encirclement pad is used. 2. In P79, LOF calculate at support locations suing branch pipe dia & thk same as header pipe dia & thk. Q5: How to calculate PWL considering attenuation and additional sources? Learning Page 1 Source: GN-44-005 (Guidance Note:Assessment of Acoustically Induced Vibration) Q6: What are the mitigations / recommendation for AIV lines? 1. For RO, use multistage restriction orifice. Calculate pressure drop at each stage and PWL can be calculated based on last stage delta P. 2. For CV/BDV, use low noise trim valves. Generally vendor provides low noise trim based on vendor calculated PWL. The PWL reduction due to low noise trim shall be obtained from vendor and reduced from calculated PWL in STEP2. 3. Use of contoured fittings (Sweepolet / Welding Tee) can reduce LOF. 4. Increase the Header Pipe Thickness. 5. Increase branch diameter. 6. Change routing: Increase the length form source to branch 7. Change routing: Modify the tapping location prior to high PWL source tapping on header. 8. Avoid welded supports, use clamp type support / welded with full encirclement pad. Q7: LOF and mitigations for AIV? LOF >= 1: further detail study using FEA is required. 1.0 > LOF >= O.5: Mitigations in Q7 should be taken. 0.5 > LOF >= 0.3: No action for AIV (as high frequency acoustic affects only main pipe, not SBC. Refer Note-2) 0.3 > LOF: Only Visual inspection. Q8: Does SBC assessment required for AIV? SBC assessment not required for AIV except other excitation mechanism affect the line. Hence no recommendation of SBC bracing given for AIV line. Learning Page 2