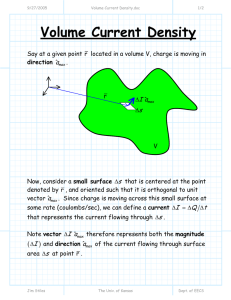
Example: Constructing a PWL Model

1/4
Example: Constructing a PWL Model
For a certain junction diode, we know that: i
D
= 10 mA when v
D
= and i
D
= 1 mA when v
D
=
Say we wish to construct a PWL model that will approximate this junction diode behavior for diode currents from, say, approximately 1 mA to approximately 10 mA.
Recall that the resulting model will relate diode voltage V
D to diode current i
D as a line of the form: i
D
=
⎛ 1 ⎞
⎝ r d
⎠ v
D
−
⎛
⎝
V r
D d
0
⎞
⎠
We therefore need to determine the values of V
D0
and that this PWL model “line” will intersect the two points
=1.0, v
D1
=0.6 and i
D2
=10.0, v
D2
=0.7. r i d such
D1
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
The slope of this line must therefore be: m = v i
D
D
2
2
−
− i v
D
D
1
1
=
Thus our PWL model resistor value r d r d
=
1 m
=
must be:
Or in other words, r d
= .
Ω .
Q: Wow! That’s a
very small
resistance value. Are you
sure
we calculated r d correctly?
A: Typically, we find that the resistor value in the
PWL model is small. In fact, it is frequently less than 1 Ω when we attempt to match the junction diode curve in a “high” current region (e.g., from i
D
=50 mA to i
D
=500 mA).
Now that we have determined r d
, we can insert either point into the model line equation and solve for the equations:
V
D0
.
For example, i
D 1
=
⎛ 1 ⎞
⎝ r d
⎠ v
D 1
−
⎛
⎝
V r
D d
0
⎞
⎠
or i
D 2
=
⎛ 1 ⎞
⎝ r d
⎠ v
D 2
−
⎛
⎝
V r
D d
0
⎞
⎠
2/4
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
3/4 become either:
V
D 0
=
= v
D 1
− i r d
= or
V
D 0
=
= v
D 2
− i r d
=
In other words, we can use either point to determine V
D0
.
Our PWL model is therefore:
+ i
D i
D
= ⎨
⎪
⎧
⎪⎪
⎪⎩
0 v
D −
0.589
0.0111 0.0111
for mA for v
D v
D
<
>
0.589 V
0.589 V v
−
D
+
0.589V
−
11.1 Ω
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS
4/4
Now, compare this PWL model to the CVD model:
+ i
D + i
D v
−
D
PWL
+
0.589V
−
11.1 Ω v
−
D
CVD
+
0.70V
−
Note that the CVD model can be viewed as a PWL model with
V
( V
D0
= 0.7 V and r d
= 0.0. Compare those values with our model
D0
= 0.589 V and r d
= 11.1
Ω )— not much difference!
Thus, the PWL model is not a radical departure from the CVD model (typically V
DO is close to 0.7 V and r d
is very small).
Instead, the PWL can be view as slight improvement of the
CVD model.
Jim Stiles The Univ. of Kansas Dept. of EECS