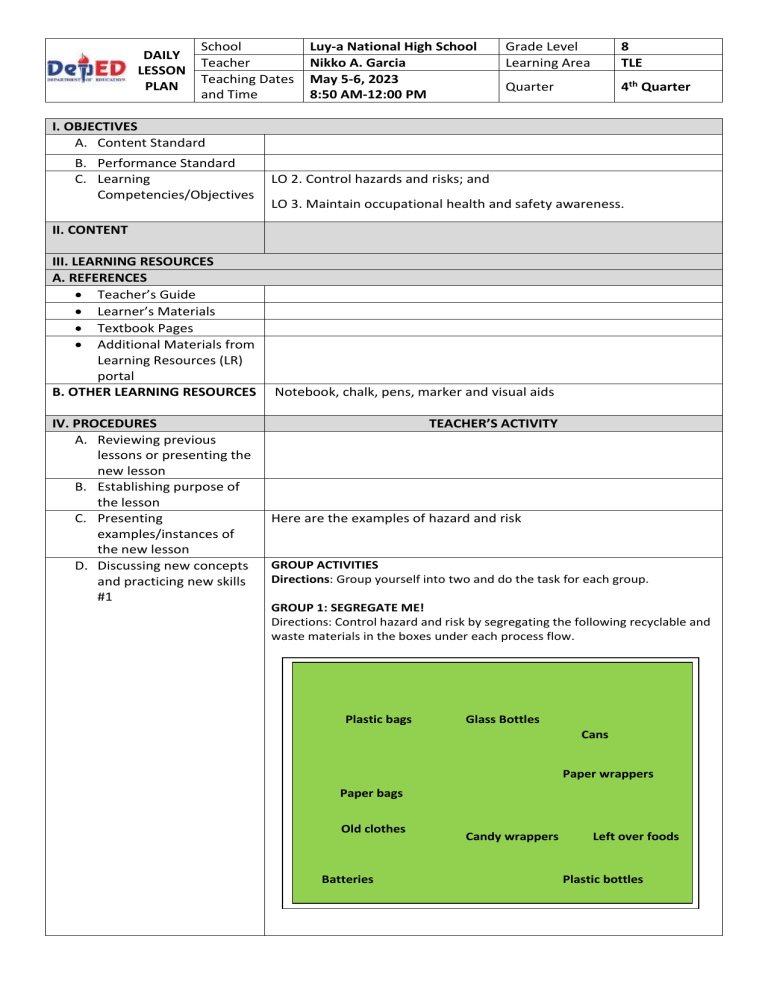
DAILY LESSON PLAN School Teacher Teaching Dates and Time Luy-a National High School Nikko A. Garcia May 5-6, 2023 8:50 AM-12:00 PM Grade Level Learning Area 8 TLE Quarter 4th Quarter I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standard B. Performance Standard C. Learning Competencies/Objectives LO 2. Control hazards and risks; and LO 3. Maintain occupational health and safety awareness. II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. REFERENCES Teacher’s Guide Learner’s Materials Textbook Pages Additional Materials from Learning Resources (LR) portal B. OTHER LEARNING RESOURCES IV. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lessons or presenting the new lesson B. Establishing purpose of the lesson C. Presenting examples/instances of the new lesson D. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #1 Notebook, chalk, pens, marker and visual aids TEACHER’S ACTIVITY Here are the examples of hazard and risk GROUP ACTIVITIES Directions: Group yourself into two and do the task for each group. GROUP 1: SEGREGATE ME! Directions: Control hazard and risk by segregating the following recyclable and waste materials in the boxes under each process flow. Plastic bags Glass Bottles Cans Paper wrappers Paper bags Old clothes Batteries Candy wrappers Left over foods Plastic bottles GROUP 2: BEWARE! Directions: Maintain occupational health and safety awareness by identifying the following wastes. Put a check (√) mark according to the types, properties and effects to human health and environment. Types Properties Effects to Human Health and Environment Biodegrad Nonbiodegrad able able Hazardou Nons Hazardous Wastes Solid 1. styro cup 2. candy wrapper 3. syringe 4. paint 5. left over foods 6. Glass bottles 7. pesticide 8. cooking oil 9. paper wrapper 10. old clothes Liquid RUBRICS RUBRICS FOR THE ACTIVITIES Description 10 8 Was able to Clarity and undertand Understanding the task clearly. Presentation Speed and Time E. Discussing new concepts and practicing new skills #2 Was able to understand the task but not clearly by giving 2-3 wrong answers Presentation Presentation is orderly is orderly and effective 5 Score 3 Was not able to Was not understand the able to task by giving 4-5 understand incorrect the task at answers all Presentation is not orderly Finished the Finished the Finished the task before task on time task 3 minutes the given late after the time given time Little or No attempt at all to explain Finished the task 5 minutes or more after the given time Total Score SAFETY REGULATIONS 1. The Philippines Clean Air Act of 1999 The Clean Air Act is the constitutional law designed to make sure that all Filipinos have air that is safe to breathe. Public health protection is the primary goal, though the law also seeks to protect our environment from damage caused by air pollution. In 1999, Congress enacted Republic Act No. 8749, otherwise known as the Philippine Clean Air Act, a landmark legislation setting a comprehensive air quality management policy and program which aims to achieve and maintain healthy air for all the people in the Philippines. The Clean Air Act is guided by the following principles: a. Protect and advance the right of the people to a balanced and healthful ecology in accord with the rhythm and harmony of nature; b. Promote and protect the global environment while organizing the primary responsibility of local government units to deal with environmental problems; c. Recognize that the responsibility of cleaning the habitat and environment is primarily area-based; and d. Recognize that a clean and healthy environment is for the good of all and should therefore be the concern of all. 2. Waste management is the collection, transport, processing, recycling or disposal of waste materials. Waste Management program helps manage hazardous chemical, radioactive, medical and other wastes safely and legally. Types of Waste Waste includes all items that people no longer have any use for, which they either intend to get rid of or have already discarded. Many items can be considered as waste like household rubbish, sewage sludge, wastes from manufacturing activities, packaging items, discarded cars, old televisions, garden waste, old paint containers and others. Thus all our daily activities can give rise to a large variety of different wastes arising from different sources. A. Solid wastes Solid waste is defined as any waste that is dry in form and is discarded as unwanted. It can describe the solid waste from general housekeeping as residential waste, refuse, household waste or domestic waste. Examples are plastics, styrofoam containers, bottles, cans, papers, scrap iron, and other trashes. B. Liquid Wastes Liquid waste includes human waste, runoff (storm water or flood water), sullage, industrial wastewater and other forms of wastewater from different sources. Examples are chemicals, oils, waste water from ponds. Classification of waste according to their properties A. Bio-degradable Biodegradable wastes are those that can be broken down (decomposed) into their constituent elements by bacteria and other microorganisms. The term can be applied to both liquid and solid waste. Examples are Human and animal wastes, food waste, paper, and agricultural wastes. B. Non-biodegradable Non-biodegradable trash is any discarded item that cannot be broken down by living organisms. Non-biodegradable trash accumulates in the environment because it cannot return to its origins. Examples are plastics, bottles, old machines, containers and others. Classification of Wastes According to their Effects on Human Health and the Environment A. Hazardous wastes – are unsafe substances used commercially, industrially, agriculturally, or economically. Examples are paint, motor oil, pesticide, drain opener, prescription drugs, air fresheners, batteries. B. Non-hazardous – are safe substances used commercially, industrially, agriculturally, or economically. Examples are papers, cardboard, linings, wrappings, paper packaging materials or absorbents. Process Flow of Waste Management The process flow refers to the 3 (or 4) Rs of reduce, reuse, recycle, and recover which classify waste management strategies according to their desirability. The Rs are meant to be a hierarchy, in order of importance. However, the waste hierarchy has 5 steps: reduce, reuse, recycle, recovery, and disposal. Reduce - to buy less and use less. Reuse - elements of the discarded item are used again. Recycle - discards are separated into materials that may be incorporated into new products. Recover - capturing useful material for waste to energy programs. 3. Disaster Preparedness and Management aims to reduce, or avoid the potential losses from hazards, assure prompt and appropriate assistance to victims of disaster, and achieve rapid and effective recovery. Disaster Management Cycle • Mitigation - Minimizing the effects of disaster. Examples: building codes and zoning; vulnerability analyses; public education. • Preparedness - Planning how to respond. Examples: preparedness plans; emergency exercises/training; warning systems. • Response - Efforts to minimize the hazards created by a disaster. Examples: search and rescue; emergency relief. • Recovery - Returning the community to normal. Examples: temporary housing; grants; medical care. F. Developing Mastery (Leads to formative assessment) G. Finding practical application of concepts and skills in daily living H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson How can you relate our lesson today in your daily life as a student or household caretaker? Think of a scenario or situation/s. EXIT CARD Directions: On a sheet of paper and complete the following prompts: The most important thing I learned about Personal Protective Equipment is _____________________________________________. The two (2) things I still want to know more about Personal Protective Equipment are (1) (2) __________________________________ __________________________________ The question/s I still have in mind is/are: _______________________________________________ ___________________________________________ I. Evaluating learning J. Additional activities for application or remediation SLOGAN Directions: Make a Slogan out of the following topics: • • • • Clean Air Act Electrical and Fire Safety Code Waste Management Disaster Preparedness and Management Workmanship Content (details of the output and appropriateness) Compliance to standards Totality (appearance, physical impact) Neatness V. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of students who require additional activities for remediation C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work?” F. Which difficulty did I encounter that my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? Prepared by: NIKKO A. GARCIA - 30% - 30% 20% 10% 10% Practice Teacher Noted by: FLORAPE BARACHINA Cooperating teacher