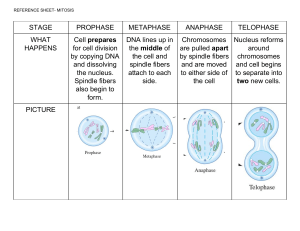
Biology Chromosomes Structure DNA Transcriptions and Translation - The Triplet Code o Gene: A sequence of nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule that codes for the production of a specific sequence of amino acids, that in turn make up a specific polypeptide (protein) o Codons: Three triplets of bases that codes for a specific amino acid Some of the triplet codes are start and stop signals: ensures the DNA is read correctly; tell the cell when to start or stop (met-AUG start) Degenerate: 61 different triplets (minus 3 for stop signals) to minimize the impacts of mutations Universal: every organism uses the same code for the same amino acid Non-overlapping o Anti-codon: tRNA molecules that has a triplet of unpaired bases at one end - Transcription o Location: in the nucleus o Process: DNA is unwound and the hydrogen bonds broke mRNA produces a complimentary copy of the DNA RNA polymerase bonded RNA nucleotides together to form the sugarphosphate backbone of the molecule After being transcribed, the double-strand reforms The mRNA leaves the nucleus through a pore in the nuclear envelope - Translation: o Location: in the cytoplasm o Process: mRNA attaches to the ribosome tRNA carry complementary anticodon to the codon of the mRNA The ribosomes move along the mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction The amino acid chain is then formed Meiosis and Mitosis - Meiosis o Produces 4 daughter cells that are genetically different from each other and from the parent cell o Sources of genetic diversity: Independent Assortment: The alleles of two or more different genes get sorted into the gametes independently Homologous line up in random orientations in metaphase Crossing over The process where chromatid breaks down in mitosis and rejoins to the chromatid o Process: Prophase I: DNA condenses and become visible as chromosomes DNA is being replicated and each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids The homologous pair become close to each other for crossing over between non-sister chromatids The centrioles migrate to the opposite pores and spindle is formed Nuclear envelop breaks down and the nucleolus disintegrates Metaphase I: The bivalents line up along the metaphase plate, and the spindle fibers are attached to the centromeres Anaphase I: Chromosomes are being pulled to the opposite of the spindles The chromosomes are divided in half Telophase I: Chromosomes arrive at different poles Spindle fibers start to break down Nuclear envelop form around the two groups of chromosomes Cytokinesis: Cell surface membrane pinch inward to create a cleavage furrow The end product in two haploid cells Prophase II: