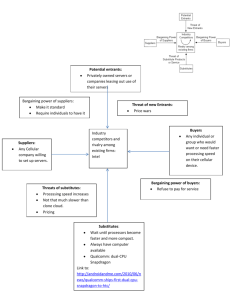
Porter's Five Forces Model Presented by Group 8 Background Porter's five forces analysis is a framework that attempts to analyze the level of the competition within an industry and business strategy development. The principal innovator of this analysis is Michael E. Porter of Harvard University. Components of Porter's Five Forces Model Bargaining power of buyers Threat of new entrants Bargaining power of suppliers Threat of substitutes Rivalry inside the industry Threat of new entrants The threat of new entrants is high when it is relatively easy for new competitors to enter the industry and gain a foothold, which can increase competition, drive down prices, and reduce profit margins for existing firms. On the other hand, the threat of new entrants is low when there are significant barriers to entry that make it difficult for new competitors to enter the market and compete with existing firms. Examples of barriers to entry that can reduce the threat of new entrants include economies of scale, proprietary technology, brand recognition, high capital requirements, regulatory barriers, and access to distribution channels. These barriers can make it difficult for new firms to establish themselves in the market and compete with established players. Threat of substitutes The substitutes can be defined as the products of other industries that have ability to satisfy similar needs. Example: Coffee can be a substitute for tea, as it can be also used as a caffeine drink in the morning. When the number of substitute product changes, the demand of a related product also gets affected. When the number of substitute product increases, the competition also increases as the customers have more alternatives to select from. This forces the companies to raise or lower down the prices. Hence, it can be concluded that the competition created by the substitute firms is "price competition". Bargaining power of buyers The bargaining power of buyers is high when buyers have significant leverage in the market and can influence the price, quality, and terms of sale for products or services. On the other hand, the bargaining power of buyers is low when buyers have limited leverage and must accept the terms set by the firms in the industry. Factors that can affect the bargaining power of buyers include the number of buyers in the market, the size and concentration of buyers, the availability of substitute products or services, the level of product differentiation, and the importance of the product or service to the buyer. For example, if there are only a few large buyers in the market, they may have more bargaining power because they represent a significant portion of the market demand. Additionally, if there are many substitutes available for a product or service, buyers may have more bargaining power because they can easily switch to another supplier if they are unhappy with the terms offered by their current supplier. Bargaining power of Suppliers The bargaining power of suppliers is high when suppliers have significant leverage in the market and can influence the price, quality, and availability of inputs or resources required by firms in an industry. On the other hand, the bargaining power of suppliers is low when suppliers have limited leverage and must accept the terms set by the firms in the industry. Factors that can affect the bargaining power of suppliers include the number of suppliers in the market, the size and concentration of suppliers, the uniqueness of the inputs or resources supplied, the availability of substitute inputs or resources, and the importance of the input or resource to the firm. For example, if there are only a few large suppliers in the market, they may have more bargaining power because they represent a significant portion of the market supply. Additionally, if the input or resource supplied is unique and not easily substituted, the supplier may have more bargaining power because the firm is more dependent on them. Rivalry inside the industry For most industries the intensity of competitive rivalry is the major determinant of the competitiveness of the industry. Potential factors: Sustainable competitive advantage through innovation Competition between online and offline companies Level of advertising expense Powerful competitive strategy Firm concentration ratio Degree of transparency Question Time Group 8 Anna Beatrice Mangalindan Diana Rose Ann Mancilla Andirine Quiambao