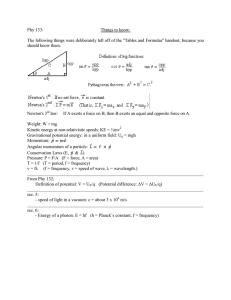
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ID: A Physics 1. Work is done when a. the displacement is not zero. b. the displacement is zero. c. the force is zero. d. the force and displacement are perpendicular. 4. 2. The length of a force vector represents the a. cause of the force. b. direction of the force. c. magnitude of the force. d. type of force. 3. 5. Which of the following forces arises from direct physical contact between two objects? a. gravitational force b. fundamental force c. contact force d. field force 6. Which of the following equations expresses the work-kinetic energy theorem? a. ME i ME f b. c. d. W net PE W KE W net KE 7. Friction converts kinetic energy to a. mechanical energy. b. potential energy. c. nonmechanical energy. d. total energy. 1 Name: ________________________ ID: A 8. Which of the following statements does not describe force? a. Force causes objects at rest to remain stationary. b. Force causes objects to start moving. c. Force causes objects to stop moving. d. Force causes objects to change direction. 10. How much power is required to lift a 2.0 kg mass at a speed of 2.0 m/s? a. 2.0 J b. 4.0 J c. 9.8 J d. 39 J 11. What is the common formula for work? Assume that W is the work, F is a constant force, v is the change in velocity, and d is the displacement. a. W = Fv b. W = Fd 9. In which of the following scenarios is no net work done? a. A car accelerates down a hill. b. A car travels at constant speed on a flat road. c. A car decelerates on a flat road. d. A car decelerates as it travels up a hill. 12. Question : 12-13 2 c. W = Fd 2 d. W = F2 d Name: ________________________ ID: A 13. 14. What is the average power supplied by a 60.0 kg person running up a flight of stairs a vertical distance of 4.0 m in 4.2 s? a. 57 W b. 240 W c. 560 W d. 670 W 18. What is the kinetic energy of a 0.135 kg baseball thrown at 40.0 m/s? a. 54.0 J b. 87.0 J c. 108 J d. 216 J 19. If a nonzero net force is acting on an object, then the object is definitely a. at rest. b. moving with a constant velocity. c. being accelerated. d. losing mass. 15. As a basketball player starts to jump for a rebound, the player begins to move upward faster and faster until his shoes leave the floor. At the moment the player begins to jump, the force of the floor on the shoes is a. greater than the player’s weight. b. equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the player’s weight. c. less than the player’s weight. d. zero. 20. Which of the following energy forms is associated with an object in motion? a. potential energy b. elastic potential energy c. nonmechanical energy d. kinetic energy 16. A horizontal force of 200 N is applied to move a 55 kg television set across a 10 m level surface. What is the work done by the 200 N force on the television set? a. 550 J b. 2000 J c. 6000 J d. 11000 J 21. 17. A more powerful motor can do a. more work in a longer time interval. b. the same work in a shorter time interval. c. less work in a longer time interval. d. the same work in a longer time interval. 3 Name: ________________________ ID: A 22. In which of the following scenarios is work done? a. A weightlifter holds a barbell overhead for 2.5 s. b. A construction worker carries a heavy beam while walking at constant speed along a flat surface. c. A car decelerates while traveling on a flat stretch of road. d. A student holds a spring in a compressed position. 28. What are the units of the coefficient of friction? a. N b. 1/N c. N 2 d. The coefficient of friction has no units. 29. A force does work on an object if a component of the force a. is perpendicular to the displacement of the object. b. is parallel to the displacement of the object. c. perpendicular to the displacement of the object moves the object along a path that returns the object to its starting position. d. parallel to the displacement of the object moves the object along a path that returns the object to its starting position. 23. What is the potential energy of a 1.0 kg mass 1.0 m above the ground? a. 1.0 J b. 9.8 J c. 10 J d. 96 J 24. Which form of energy is involved in weighing fruit on a spring scale? a. kinetic energy b. nonmechanical energy c. gravitational potential energy d. elastic potential energy 30. If the mass in a horizontal mass-spring system was doubled, the elastic potential energy in the system would change by a factor of a. 0 (no change). b. 1/2. c. 2. d. 4. 25. If the sign of work is negative, a. the displacement is perpendicular to the force. b. the displacement is in the direction opposite the force. c. the displacement is in the same direction as the force. d. no work is done. 31. Two perpendicular forces, one of 45.0 N directed upward and the other of 60.0 N directed to the right, act simultaneously on an object with a mass of 35.0 kg. What is the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 2.14 m/s 2 b. 3.00 m/s 2 c. 5.25 m/s 2 d. 1.41 m/s 2 26. Which are simultaneous equal but opposite forces resulting from the interaction of two objects? a. net external forces b. field forces c. gravitational forces d. action-reaction pairs 32. A worker does 25 J of work lifting a bucket, then sets the bucket back down in the same place. What is the total net work done on the bucket? a. –25 J b. 0 J c. 25 J d. 50 J 27. In which of the following sentences is work used in the everyday sense of the word? a. Lifting a heavy bucket involves doing work on the bucket. b. The force of friction usually does negative work. c. Sam and Rachel worked hard pushing the car. d. Work is a physical quantity. 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A 33. 36. A hockey stick hits a puck on the ice. Identify an action-reaction pair in this situation. a. The stick exerts a force on the puck; the puck exerts a force on the stick. b. The stick exerts a force on the puck; the puck exerts a force on the ice. c. The puck exerts a force on the stick; the stick exerts a force on the ice. d. The stick exerts a force on the ice; the ice exerts a force on the puck. 34. Which of the following is the tendency of an object to maintain its state of motion? a. acceleration b. inertia c. force d. velocity 37. A waitperson carrying a tray with a platter on it tips the tray at an angle of 12 below the horizontal. If the gravitational force on the platter is 5.0 N, what is the magnitude of the force parallel to the tray that tends to cause the platter to slide down the tray? (Disregard friction.) a. 0.42 N b. 1.0 N c. 4.9 N d. 5.0 N 35. Which of the following is a true statement about the conservation of energy? a. Potential energy is always conserved. b. Kinetic energy is always conserved. c. Mechanical energy is always conserved. d. Total energy is always conserved. 38. The magnitude of the gravitational force acting on an object is a. frictional force. b. weight. c. inertia. d. mass. 5 Name: ________________________ ID: A 39. QUESTION 43,44,45 40. 41. 6 Name: ________________________ ID: A 42. A book with a mass of 2.0 kg is held in equilibrium on a board with a slope of 60.0 by a horizontal force. What is the normal force exerted on the book? a. 39 N b. 61 N c. 15 N d. 34 N 47. A child pulls a balloon for 12 m with a force of 1.0 N at an angle 60 below horizontal. How much work does the child do on the balloon? a. –10 J b. –6.0 J c. 6.0 J d. 12 J 48. A sled weighing 1.0 10 2 N is held in place on a frictionless 20.0 slope by a rope attached to a stake at the top. The rope is parallel to the slope. What is the normal force of the slope acting on the sled? a. 94 N b. 47 N c. 37 N d. 34 N 43. A hammer drives a nail into a piece of wood. Identify an action-reaction pair in this situation. a. The nail exerts a force on the hammer; the hammer exerts a force on the wood. b. The hammer exerts a force on the nail; the wood exerts a force on the nail. c. The hammer exerts a force on the nail; the nail exerts a force on the hammer. d. The hammer exerts a force on the nail; the hammer exerts a force on the wood. 49. There are six books in a stack, and each book weighs 5 N. The coefficient of static friction between the books is 0.2. With what horizontal force must one push to start sliding the top five books off the bottom one? a. 1 N b. 5 N c. 3 N d. 7 N 44. A leaf falls from a tree and lands on the sidewalk. Identify an action-reaction pair in this situation. a. The tree exerts a force on the leaf; the sidewalk exerts a force on the leaf. b. The leaf exerts a force on the sidewalk; the sidewalk exerts a force on the leaf. c. The leaf exerts a force on the tree; the sidewalk exerts a force on the leaf. d. The leaf exerts a force on the sidewalk; the tree exerts a force on the leaf. 50. Which of the following is a form of mechanical energy? a. internal energy b. chemical potential energy c. gravitational potential energy d. electrical energy 45. The equation for determining gravitational potential energy is PE g = mgh. Which factor(s) in this equation is (are) not intrinsic to an object? a. m b. g c. h d. both g and h 51. Why doesn’t the principle of mechanical energy conservation hold in situations when frictional forces are present? a. Kinetic energy is not completely converted to a form of potential energy. b. Potential energy is completely converted to a form of gravitational energy. c. Chemical energy is not completely converted to electrical energy. d. Kinetic energy is completely converted to a form of gravitational energy. 46. A late traveler rushes to catch a plane, pulling a suitcase with a force directed 30.0 above the horizontal. If the horizontal component of the force on the suitcase is 60.6 N, what is the force exerted on the handle? a. 53.0 N b. 70.0 N c. 65.2 N d. 95.6 N 7 Name: ________________________ ID: A 52. 53. A net force of 6.8 N accelerates a 31 kg scooter across a level parking lot. What is the magnitude of the scooter’s acceleration? a. 0.22 m/s 2 c. 3.2 m/s 2 b. 0.69 m/s 2 d. 4.6 m/s 2 8 Name: ________________________ ID: A 54. The free-body diagram shown above represents a car being pulled by a towing cable. In the diagram, the 5800 N force is a. the gravitational force acting on the car. b. the backward force the road exerts on the car. c. the upward force the road exerts on the car. d. the force exerted by the towing cable on the car. 58. 55. The free-body diagram shown above represents a car being pulled by a towing cable. In the diagram, which of the following is the gravitational force acting on the car? a. 5800 N b. 775 N c. 14 700 N d. 13 690 N 56. A single force acts on an object. The components of this force act along the +x-axis and the –y-axis. The single force that will bring the object into equilibrium has components that act along the a. +x-axis and +y-axis. b. +x-axis and y-axis. c. x-axis and +y-axis. d. x-axis and y-axis. 59. The statement by Newton that for every action there is an equal but opposite reaction is which of his laws of motion? a. first b. second c. third d. fourth 57. Which of the following is the rate at which work is done? a. potential energy b. kinetic energy c. mechanical energy d. power 60. A newton is equivalent to which of the following quantities? a. kg b. kgm/s c. kgm/s 2 d. kg(m/s) 2 9 Name: ________________________ ID: A 61. A car goes forward along a level road at constant velocity. The additional force needed to bring the car into equilibrium is a. greater than the normal force times the coefficient of static friction. b. equal to the normal force times the coefficient of static friction. c. the normal force times the coefficient of kinetic friction. d. zero. 64. Which of the following has the greatest power output? a. a weightlifter who lifts a 250 N weight 2.1 m in 3.0 s 62. A crate is carried in a pickup truck traveling horizontally at 15.0 m/s. The truck applies the brakes for a distance of 28.7 m while stopping with uniform acceleration. What is the coefficient of static friction between the crate and the truck bed if the crate does not slide? a. 0.400 b. 0.365 c. 0.892 d. 0.656 b. a mechanic’s lift that raises a 1.2 10 4 N car 2.1 m in 12 s c. a car engine that does 1.2 10 3 J of work in 5.0 s d. a crane that lifts a 2.5 10 4 N beam at a speed of 1.2 m/s 65. A free-body diagram represents all of the following except a. the object. b. forces as vectors. c. forces exerted by the object. d. forces exerted on the object. 66. Which of the following energy forms is associated with an object due to its position? a. potential energy b. positional energy c. total energy d. kinetic energy 63. A construction worker pushes a wheelbarrow 5.0 m with a horizontal force of 50.0 N. How much work is done by the worker on the wheelbarrow? a. 10 J b. 55 J c. 250 J d. 1250 J 67. 68. What causes a moving object to change direction? a. acceleration b. velocity c. inertia d. force 10 Name: ________________________ ID: A 69. Which statement about the acceleration of an object is correct? a. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net external force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. b. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net external force acting on the object and directly proportional to the mass of the object. c. The acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to the net external force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. d. The acceleration of an object is inversely proportional to the net external force acting on the object and directly proportional to the mass of the object. 72. If the displacement of a horizontal mass-spring system was doubled, the elastic potential energy in the system would change by a factor of a. 1/4. b. 1/2. c. 2. d. 4. 73. A crate is released on a frictionless plank inclined at angle with respect to the horizontal. Which of the following relationships is true? (Assume that the x-axis is parallel to the surface of the incline.) a. F y = F g b. c. Fx = 0 F y = Fx d. none of the above 74. In general, Fnet equals a. Ff. b. Fg. c. Fn. d. F. 70. A child moving at constant velocity carries a 2 N ice-cream cone 1 m across a level surface. What is the net work done on the ice-cream cone? a. 0 J b. 0.5 J c. 2 J d. 20 J 75. How much elastic potential energy is stored in a bungee cord with a spring constant of 10.0 N/m when the cord is stretched 2.00 m? a. 10.0 J b. 20.0 J c. 40.0 J d. 200 J 71. 11 Name: ________________________ ID: A 76. 77. Gravitational potential energy is always measured in relation to a. kinetic energy. b. mechanical energy. c. total potential energy. d. a zero level. A variable force acts on a body and causes the body to accelerate in the direction of the force. The force is plotted as a function of the distance 78. What are the units for a spring constant? a. N b. m c. Nm d. N/m moved. On the graph obtained, the work done by the force is represented by the (A) slope of the curve (B) area under the curve (C) point at which the curve intersects the distance axis (D) point at which the curve intersects the force axis (E) difference between the initial and final point- of the curve 12 Name: ________________________ ID: A 79. 80. As an object falls toward Earth, a. the object does not exert a force on Earth. b. the object exerts a downward force on Earth. c. Newton’s third law does not apply. d. the upward acceleration of Earth is negligible because of its large mass. 13 Name: ________________________ ID: A 81. If friction is the only force acting on an object during a given physical process, which of the following assumptions can be made in regard to the object’s kinetic energy? a. The kinetic energy decreases. b. The kinetic energy increases. c. The kinetic energy remains constant. d. The kinetic energy decreases and then increases. 82. 83. A measure of the quantity of matter is a. density. b. weight. c. force. d. mass. 85. A free-body diagram of a ball falling in the presence of air resistance would show a. only a downward arrow to represent the force of air resistance. b. only a downward arrow to represent the force due to gravity. c. a downward arrow to represent the force due to gravity and an upward arrow to represent the force of air resistance. d. an upward arrow to represent the force due to gravity and a downward arrow to represent the force of air resistance. 84. 86. Ball A has triple the mass and speed of ball B. What is the ratio of the kinetic energy of ball A to ball B. a. 3 b. 6 c. 9 d. 27 14 Name: ________________________ ID: A 87. According to Newton’s second law, when the same force is applied to two objects of different masses, a. the object with greater mass will experience a great acceleration, and the object with less mass will experience an even greater acceleration. b. the object with greater mass will experience a smaller acceleration, and the object with less mass will experience a greater acceleration. c. the object with greater mass will experience a greater acceleration, and the object with less mass will experience a smaller acceleration. d. the object with greater mass will experience a small acceleration, and the object with less mass will experience an even smaller acceleration. 89. Which of the following are examples of conservable quantities? a. potential energy and length b. mechanical energy and length c. mechanical energy and mass d. kinetic energy and mass 90. 88. 15 Name: ________________________ ID: A 91. 92. Which of the following is the cause of an acceleration? a. speed b. inertia c. force d. velocity 16 Name: ________________________ ID: A 93. 94. A sled traveling at a speed of 3.0 m/s slows to a stop 4.0 m from the point where its passenger rolled off. What is the magnitude of the horizontal net force that slows the 110 N sled? (Assume ag = 9.81 m/s 2 .) a. 130 N b. 34 N c. 37 N d. 13 N 95. Which of the following formulas would be used to directly calculate the kinetic energy of an object with mass m bouncing up and down on a spring with spring constant k? 1 a. KE 2 kx 2 1 b. KE 2 kx 2 c. KE 2 mv 2 d. KE 2 mv 2 1 1 96. Which of the following equations is not an equation for power, P, in terms of work, W, displacement, d, time interval, t, force, F, and/or velocity, v? d a. P F t W b. P t c. P Fv Fv d. P t 17 Name: ________________________ ID: A 97. In the free-body diagram shown above, which of the following is the gravitational force acting on the balloon? a. 1520 N b. 950 N c. 4050 N d. 5120 N 101. Question : 105-106 98. Which of the following refers to the sum of kinetic energy and all forms of potential energy? a. total energy b. energy c. nonmechanical energy d. mechanical energy 99. A ball is dropped from a person’s hand and falls to Earth. Identify an action-reaction pair in this situation. a. The hand exerts a force on the ball; Earth exerts a force on the hand. b. Earth exerts a force on the ball; the hand exerts a force on Earth. c. Earth exerts a force on the hand; the hand exerts a force on the ball. d. Earth exerts a force on the ball; the ball exerts a force on Earth. 100. Which of the following energy forms is not involved in hitting a tennis ball? a. kinetic energy b. chemical potential energy c. gravitational potential energy d. elastic potential energy 18 Name: ________________________ ID: A 102. 103. Which of the following is the rate at which energy is transferred? a. potential energy b. kinetic energy c. mechanical energy d. power 104. A 3.00 kg toy falls from a height of 1.00 m. What will the kinetic energy of the toy be just before the toy hits the ground? (Assume no air resistance and that g = 9.81 m/s 2 .) a. 0.98 J b. 9.8 J c. 29.4 J d. 294 J 105. 106. Which of the following parameters does not depend on how resistant a spring is to being compressed or stretched? a. compression distance b. relaxed length c. spring constant d. stretching distance 107. The main difference between kinetic energy and potential energy is that a. kinetic energy involves position, and potential energy involves motion. b. kinetic energy involves motion, and potential energy involves position. c. although both energies involve motion, only kinetic energy involves position. d. although both energies involve position, only potential energy involves motion. 19 Name: ________________________ ID: A 108. 109. In which of the following sentences is work used in the scientific sense of the word? a. Holding a heavy box requires a lot of work. b. A scientist works on an experiment in the laboratory. c. Sam and Rachel pushed hard, but they could do no work on the car. d. John learned that shoveling snow is hard work. 110. Which of the following are not units of power? a. hp b. J c. W d. Js 111. Newton’s third law of motion involves the interactions of a. one object and one force. b. one object and two forces. c. two object and one force. d. two objects and two forces. 20 Name: ________________________ ID: A 112. 21