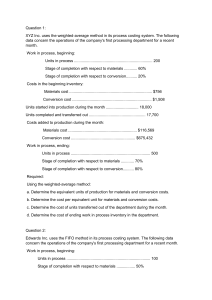
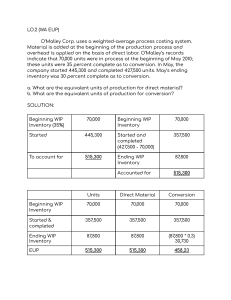
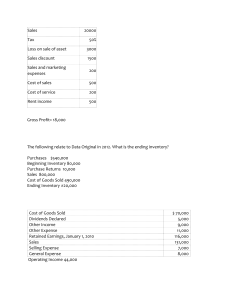
Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions CHAPTER 7 – PROCESS COSTING SYSTEM Ex. 7-1. Cost of Production Report. WA The following information is available for Department A of Siena Manufacturing Company for the month of July: Work in process, 7/1, 30% complete Costs: Materials Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Started in production during July Costs added: Materials Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Work in process, 7/31, 20% complete 5,000 units P12,000 6,000 8,000 20,000 units P36,000 16,000 20,200 2,000 units Materials are added at the beginning of the process and Siena Company uses the weighted average method to account for cost. Required: Prepare a cost of production report and give all entries required to record the above information. Units to account Beginning inventory Started 5,000 units 20,000 units 25,000 units Costs to account Beginning inventory Added 26,000 72,200 98,200 Units as accounted Completed Ending Inventory Cost Accounted WAM Completed 93,610 Ending Inventory 4,700 98,310 23,000 units 2,000 units 25,000 units FIFO 93,875 4,260 98,135 EUP (WAM) Materials 23,000 2,000 25,000 Completed Ending Inventory EUP Cost per EUP 48,000 M= =1.9 2 25,000 CC= 50,200 =2.1 5 23,400 Conversion Costs 23,000 400 23,400 M CC Cost of Completed 23,000 x 1.92 23,000 x 2.15 M CC Cost of Ending Inventory 2,000 x 1.92 400 x 2.15 WIP – Department A RMI FP FOH 72,200 WIP – Department B WIP- Department A EUP (FIFO) 93,610 36,000 16,000 20,200 93,610 44,160 49,450 93,610 3,840 860 4,700 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions Materials 0 18,000 2,000 20,000 Beginning Inventory Completed Ending Inventory EUP Cost per EUP Cost of Completed Cost Beg. Inv. Cost to complete - CC 3,500 x 1.65 Cost of B.I. completed S&C 18,000 x 3.45 36,000 M= =1.8 20,000 CC= Conversion Costs 3,500 18,000 400 21,900 36,200 =1.65 21,900 M CC 26,000 5,775 31,775 62,100 93,875 Cost of Ending Inventory 2,000 x 1.8 400 x 1.65 3,600 660 4,260 Ex. 7-2. Cost of Production Report with lost units using FIFO Palmolive Asia manufactures gel in three departments and accounts costs using the FIFO method. The Finishing Department is the last step before the product is transferred to storage vats for bottling. In this department, all materials are added at the beginning of the process and any lost units which are inherent in production process are discovered at this point. The following data are available for the Finishing Department for the month of September of the current year. In process, Sept. 1 – 10,000 units (75% complete) Costs from Preceding Department Costs this Department Materials Labor Overhead P76,000 P43,000 78,000 84,000 Received from preceding dept. – 40,000 units Costs added this period: Materials Labor Overhead Costs from preceding dept. Finished and transferred to storage – 35,000 units In process, Sept. 30, ½ complete – 10,000 units P140,000 324,000 260,000 280,000 Required: Prepare a cost of production report and give all entries required to record the above information. Units to account Beginning inventory Started 10,000 units 40,000 units 50,000 units Units as accounted Completed Ending Inventory Uncounted (loss) 35,000 units 10,000 units 45,000 units 5,000 units 50,000 units Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions Beginning Inventory (10,000) Started and Completed (25,000) Ending Inventory (10,000) Normal Loss – Continuous (5,000) EUP Cost per EUP 140,000 M= =4 35,000 CC= TI = 584,000 =17.97 32,500 280,000 =8 35,000 Materials 0 25,000 10,000 0 35,000 Conversion Costs 2,500 25,000 5,000 0 32,500 Cost of Completed Beginning Inventory Cost to Complete: CC 2,500 x 17.97 Cost of B.I. completed Started and Completed 25,000 x 29.97 M CC TI Cost of Ending Inventory 10,000 x 4 5,000 x 17.97 10,000 x 8 Transferred In 0 25,000 10,000 0 35,000 281,000 44,925 325,925 749,250 1,075,175 40,000 89,850 80,000 209,850 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions Ex. 7-4. Cost of Production report using FIFO FRC Corporation operates two departments in its operations, namely Process 1 and Process 2. Below are information gathered from the production department during the six months ended June 30, 2019: Units Work in process, Jan 1 Started in process Transferred out Process 1 12,000 88,000 80,000 Process 2 10,000 74,000 Costs: Work in process, Jan. 1 Added this period: Materials Labor Overhead P10,400 P21,370 P39,600 28,400 5,200 P69,598 54,940 36,900 The work in process on Jan. 1 is 2/3 complete in Process 1 and 3/5 complete in Process 2 while the work in process on June 30 is 3/5 complete in Process 1 and 7/8 complete in Process 2. Materials are applied 100% at the start of the process in Process 1 while in Process 2, 30% are applied at the start of the process, 40% when the process is one halfcompleted and 30% at the end of the process. Conversion costs are applied evenly in all the departments. Required: 1. Determine the EUP for materials and conversion cost in Process 1 & Process 2. 2. Allocate the total costs to account to completed and transferred and to work in process end. Process 1 Beginning Inventory: 2/3 complete Ending Inventory: 3/5 complete Materials Application: Start – 100% Process 2 Beginning Inventory: 3/5 complete Ending Inventory: 7/8 complete Materials Application: Start – 30%; ½ complete – 40%; End – 30% PROCESS 1 Materials 0 68,000 20,000 88,000 Beginning Inventory (12,000) Started and Completed (68,000) Ending Inventory (20,000) EUP Cost per EUP M= 39,600 =0.45 88,000 CC= Cost of Completed Beginning Inventory Cost to Complete – CC 4,000 x 0.4 Started and Completed 68,000 x 0.85 33,600 =0.4 84,000 M CC Cost of Ending Inventory 20,000 x 0.45 12,000 x 0.4 Conversion Costs 4,000 68,000 12,000 84,000 10,400 1,600 57,800 69,800 9,000 4,800 13,800 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions PROCESS 2 Beginning Inventory (10,000) Started and Completed (64,000) Ending Inventory (16,000) EUP Cost per EUP M= 69,598 =0.89 78,200 CC= TI = 91,840 =1.12 82,000 69,800 =0.8725 80,000 Materials 3,000 64,000 11,200 78,200 Conversion Costs 4,000 64,000 14,000 82,000 Cost of Completed Beginning Inventory Cost to Complete: M 3,000 x 0.89 CC 4,000 x 1.12 Cost of B.I. completed Started and Completed 64,000 x 2.8825 Cost of Ending Inventory 11,200 x 0.89 14,000 x 1.12 16,000 x 0.8725 M CC TI Transferred In 0 64,000 16,000 80,000 21,370 2,670 4,480 28,520 184,480 213,000 9,968 15,680 13,960 39,608 Ex. 7-5. Two types of materials, uneven application The cost accountants of Sonnex Company provides you with the following data from their 2 nd Production Department. Opening Inventory, 3/8 completed Received from preceding dept. Transferred to next dept. Ending inventory: 30% is 30% complete 30% is 50% complete 40% is 80% complete 12,000 30,000 27,000 15,000 Sonnex Company uses two types of materials in the production. Type 1 is added at the start of the process while Type 2 is added as follows: 20% at the start of the process, 25% when the process is 40% complete, 25% when the process is 75% complete and the balance at the end of the process. Required: Determine the equivalent units of production for Materials: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 Start/Beginning Type 2 20% - start of the process 25% - @40% complete 25% - @75% complete 30% - end EUP (WAM) Completed (27,000) Ending Inventory: 4,500 (30% complete) 4,500 (50% complete) 6,000 (80% complete) EUP (WAM) Type 1 27,000 Type 2 27,000 15,000 42,000 900 2,025 4,200 34,125 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions EUP (FIFO) Type 1 0 15,000 15.000 30,000 Beginning Inventory (12,000) Started and Completed (15,000) Ending Inventory EUP Type 2 9,600 15,000 7,125 31,725 Problem 7-3. Process costing with lost units: WA Starlight Manufacturing Company uses two types of materials in its processing operation and adds these materials as follows: 4 pounds of Materials X at the start of the process and two pounds of Material Y when the process is 50% complete. Conversion costs are incurred uniformly throughout the process. At 50% stage of completion, inspection occurs and any spoiled units are scrapped. 5% of the units processed up to inspection point are considered normal. The following data pertains to August operation of Starlight Company. In process, Aug 1 In process, Aug 31 Units completed & transferred Units started Unit costs: Material X Materials Y Conversion costs per EUP 18,000 units, 75% complete 6,000 units, 25% complete 73,800 units 65,000 P6.00 per pound P4.00 per pound P8.00 Required: Prepare a cost of production report Material x 73,800 6,000 3,200 83,000 Completed (73,800) Ending Inventory (6,000) Normal Loss (3,200) Abnormal Loss (0) Total: (83,000) Cost per EUP MX=6 x 4=24 Materials Conversion Costs MY =4 x 2=8 Material Y 73,800 0 0 73,800 Cost of Completed 73,800 x 32 73,800 x 8 Normal Loss CC=8 M CC Normal Loss 3,200 x 24 1,600 x 8 76,800 12,800 89,600 M CC Cost of Ending Inventory 6,000 x 24 1,500 x 8 Conversion Costs 73,800 1,500 1,600 76,900 2,361,600 590,400 2,952,000 89,600 3,041,600 144,000 12,000 156,000 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions TEST MATERIAL 2. (No spoilage) PRC Manufacturing Company computed its equivalent unit costs under FIFO process costing as follows: Last Period This period Direct materials P34.00 P35.00 Packaging 4.00 5.00 Direct labor 13.00 12.50 Overhead 15.60 15.00 Direct materials and packaging are added at the start and end of the process, respectively. The EUP of IP, beginning under FIFO method is as follows: Direct materials, 54,000 Direct labor costs, 16,200 Overhead costs, 18,000 PRC Manufacturing Company transferred a total of 400,000 units to finished goods warehouse during August and had 25,000 units in ending IP inventory. The ending inventory units were 40 percent complete as to direct labor and 30 percent complete as to overhead. 1. How much is the cost of work in process, beginning? a. P3,596,400 b. P2,362,500 c. P2,327,400 d. P3,380,400 Completed portion of Beginning Inventory: Direct Materials Packaging Direct Labor Overhead 2. The EUP for the period was: Materials Direct Materials Packaging a. 371,000 400,000 b. 400,000 346,000 c. 425,000 346,000 d. 425,000 400,000 Beginning Inventory (54,000) Started & Completed (346,000) Ending Inventory (25,000) EUP Cost per EUP Current Cost Units to account Beginning inventory Started Cost of Beginning Inventory Cost to Complete Started & Completed Total (54,000 x 34) (0) (16,200 x 13) (18,000 x 15.60) 1,836,000 0 210,600 280,800 2,327,400 Conversion Costs Direct Labor Overhead 393,800 389,500 356,000 353,500 393,800 395,800 372,200 371,500 DM 0 346,000 25,000 371,000 35 12,985,000 54,000 units 371,000 units 425,000 units DM 1,836,000 0 12,110,000 13,946,000 PC 54,000 346,000 0 400,000 5 2,000,000 DL 37,800 346,000 10,000 393,800 12.50 4,922,500 Units as accounted Completed Ending Inventory PC 0 270,000 1,730,000 2,000,000 DL 210,600 472,500 4,325,000 5,008,100 OH 36,000 346,000 7,500 389,500 15 5,842,000 400,000 units 25,000 units 425,000 units OH 230,800 540,000 5,190,000 6,010,800 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions Uniqlo Company adds materials when the process is 50% complete and conversion costs are added uniformly throughout the process. The following Cost of Production Report was prepared by an inexperience cost accountant that uses FIFO method in accumulating costs. Physical units: In process, beg (60% complete) Started in process Total units to account Accounted as follows: Completed and transferred In process, end (45% complete) 30,000 200,000 230,000 190,000 40,000 Costs: In process, beg. Costs (Mat. P67,800; CC, P29,300) Added during the month (Mat, P579,000; P248,900) Total costs to account Accounted as follows: Costs transferred to next department In Process, costs As accounted P97,100 827,900 P925,000 P805,600 119,400 P295,000 3. The EUP for materials & conversion costs is: Materials Conversion costs a. 190,000 200,000 b. 180,000 190,000 c. 160,000 190,000 d. 200,000 190,000 4. The correct amount of costs transferred to next department amounted to: a. P904,820 b. P901,620 c. P815,960 d. P785,620 5. What is the balance of the WIP account at the end of the period? a. P139,580 b. P29,880 c. P26,280 d. P23,580 EUP (FIFO) Materials 0 160,000 0 160,000 Beginning Inventory (30,000) Completed (160,000) Ending Inventory (40,000) EUP Cost per EUP 579,000 M= =3.62 160,000 CC= Conversion Costs 12,000 160,000 18,000 190,000 Cost of Completed Cost Beg. Inv. Cost to complete - CC 12,000 x 1.31 S&C 160,000 x 4.93 248,900 =1.31 190,000 M CC Cost of Ending Inventory 0 18,000 x 1.31 91,100 15,720 788,800 901,620 0 23,580 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions 23,580 TEST MATERIAL 3 (with spoilage) Specialty Store makes Christmas décor in two departments, Forming and Decorating. On December 1, forming had 2,500 in process that were 80% complete as to materials and 60% converted. During December, 15,000 units were started and 500 were in process at the end of the month, 75% incomplete as to materials and conversion costs. The following are available for the Forming Department under FIFO method. Beginning costs P20/EUP P18/EUP Materials Labor & OH Current costs P10/EUP P12/EUP 1. The cost of the 2,500 units in the Forming Department on Dec. 1 is a. P28,000 b. P50,000 c. P67,000 d. P95,000 2. The total cost of materials added during December is a. P151,250 b. P187,500 c. P204,000 d. P210,000 Cost of Beginning Inventory Materials Conversion Cost (2,000 x 20) 1,500 x 18 40,000 27,000 67,000 Cost Added: Beginning Inventory Started & Completed Ending Inventory 500 14,500 1250 15,125 x 10 P151,250 Toby Company, a manufacturer of baseball bats, buy wood as a direct material for baseball bats. The forming department processes the baseball bats and the bats are then transferred to the Finishing department where additional work is applied. The Forming department began manufacturing 10,000 bats during the month of November. There was no beginning inventory. Costs for the Forming department for November were as follows: Direct materials Conversion costs Total P33,000 17,000 P50,00 A total of 8,000 bats were completed and transferred to the Finishing Department; the remaining 2,000 bats were still in the Forming process at the end of month. All of the Forming department’s direct materials were placed in process, but on average only 25% of the conversion cost was applied to the ending work in process inventory. 3. The cost allocated to (1) units transferred to the Finishing and (2) the work in process at the end of November is a. (1) P50,000 and (2) P10,000 b. (1) P40,000 and (2) P2,500 c. (1) P53,000 and (2) P50,000 d. (1) P42,400 and (2) P7,600 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions Materials 8,000 2,000 10,000 Completed (8,000) Ending Inventory (2,000) EUP Cost per EUP 33,000 M= =3.3 10,000 CC= M & CC Conversion Costs 8,000 500 8,500 Cost of Completed 23,000 x 5.3 42,400 17,000 =2 8,500 M CC Cost of Ending Inventory 2,000 x 3.3 500 x 2 6,600 1,000 7,600 The cost department of BGC Corp. operates a process cost system using the average method. Production records showed the following data for one of the three production departments. Received from preceding dept. Completed & transferred to next dept. Completed & on hand In process, end 100,000 kilos 71,840 kilos 4,160 kilos 24,000 kilos In this department additional material is added to the units from the preceding department. Three distinctly different types of materials are used at three separate stages of production in this department. Material A is added at the start of the process Material B is added when the process is one-fourth completed Material C is added when the process is three-fourth completed Labor and overhead incurred at a uniform rate throughout the process in this department. Examination of the unfinished work discloses that: ¼ was 7/8 complete; ½ was ½ completed; and ¼ was 1/6 completed. 4. Calculate the EUP for material A, B and C a. 100,000, 100,000, 100,000 b. 100,000, 100,000 82,000 c. 100,000, 94,000, 94,000 d. Not given Venux Textiles Company manufactures a variety of natural fabrics for the clothing industry. The following data pertains to the Weaving Department for the month of September: Completed (76,000) Ending: 6,000, 7/8 completed 12,000, ½ completed 6,000, 1/6 complete Material A 76,000 Material B 76,000 Material C 76,000 16,000 12,000 6,000 100,000 6,000 12,000 94,000 6,000 82,000 Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions WA 60,000 52,000 50,000 EUP for Direct materials EUP for conversion costs Completed & transferred out Work in process, Sept. 1 20,000 units Costs: Direct materials Conversion costs Costs added in September: Direct materials Conversion costs FIFO 40,000 44,000 50,000 P94,000 44,400 P164,000 272,800 5. The work in process beginning is a. 100% converted b. 60% converted c. 40% converted d. 0% converted WAM Completed (50,000) Ending Inventory (10,000) EUP Materials 50,000 10,000 60,000 Conversion Costs 50,000 2,000 52,000 Materials 0 30,000 10,000 40,000 Conversion Costs 12,000 30,000 2,000 44,000 FIFO Beginning Inventory (20,000) S & C (30,000) Ending Inventory (10,000) EUP 12,000 / 20,000 = 60% incomplete; 40% completed/converted Cost Accounting and Control 2019 Edition Problem and Solutions TEST MATERIAL 4. (with spoilage) Splenda Company has the following information for October of the current year: Units: Started WIP beginning, 65% incomplete Normal spoilage (discrete) Abnormal spoilage WIP, ending, 70% complete 100,000 20,000 3,500 5,000 14,500 Costs: Work in process, beginning Materials Conversion costs P15,000 10,000 All materials are added at the start of the production process. Splenda Company inspects goods at 75% completion as to conversion. The costs per EUP for materials and conversion are P1 and P1.5, respectively, under FIFO method. 1. The cost assigned to work in process, end is a. P21,025 b. P25,375 c. P29,725 d. P36,250 2. The cost assigned to completed units is: a. P237,000 b. P244,437.50 c. P242,500 d. P267,500 BI (20,000) S/C (77,000) EI (14,500) NL (3,500) AL (5,000) EUP M 0 77,000 14,500 3,500 5,000 100,000 CC 13,000 77,000 10,150 2,625 3,750 106,525 Cost of Completed BI CTC (CC) S/C (13,000 x 1.5) (77,000 x 2.5) NL M CC Normal Loss 3,500 x 1 2,625 x 1.5 25,000 19,500 192,500 237,000 7,437.5 244,437.50 M CC Cost of Ending Inventory 14,500 x 1 10,150 x 1.50 3,500 3,937.5 7,437.5 M CC Abnormal Loss 5,000 x 1 3,750 x 8 14,500 15,225 29,725 5,000 5,625 10,625