Isotopes: Definition, Uses, and Atomic Mass Calculations
advertisement
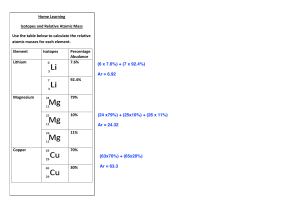
ISOTOPES OBJECTIVES At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: K : identify common isotopes and their uses. S : write the isotopic symbol of an isotope. A : appreciate the role played by isotopes in human lives. LEARNING COMPETENCY determine the relationship between atomic mass and relative abundance of isotopes. solve for the average atomic mass of elements. recognize common isotopes and their uses. (STEM_GC11AMIc-e-19) HISTORY OF ISOTOPES The history of isotopes begins with the discovery of radioactivity by Antoine Becquerel in 1896. This discovery led to the discovery of the first isotopes, which were radioactive forms of elements that had the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei but different numbers of neutrons. In 1913, Frederick Soddy coined the term "isotope" to describe these different forms of elements. He also proposed that isotopes could be used to track chemical reactions and processes in living organisms. In the following years, many isotopes were discovered, and their properties and applications were studied. In 1932, James Chadwick discovered the neutron, which helped to explain the properties of isotopes and led to the discovery of many more isotopes. During World War II, isotopes played a crucial role in the development of nuclear weapons. After the war, isotopes were used in many other areas, including medicine, agriculture, and industry. Today, isotopes are used in a wide range of applications, including radiometric dating, medical imaging, cancer treatment, and environmental monitoring. The study of isotopes and their properties continues to be an active area of research in many fields of science. ISOTOPES Isotopes are variants of an element that have the same number of protons in their atomic nucleus, but different numbers of neutrons. This means that isotopes of the same element have the same atomic number (which determines the element's chemical properties), but different atomic masses (which determine the isotope's physical properties). Isotopes can be either stable or radioactive. Stable isotopes do not decay over time and have a constant ratio of isotopes in natural materials, while radioactive isotopes undergo radioactive decay and have a changing ratio over time. The properties of isotopes, both stable and radioactive, make them useful for a wide range of applications in science, industry, and medicine. Consider the illustration below showing a neutral hydrogen atom, which consists of only one proton and one electron, has three different isotopes—protium, deuterium, and tritium respectively. Another way of representing isotopes is by writing the element name or symbol followed by a hyphen and then the mass number. Thus, protium, deuterium, and tritium may be written as hydrogen-1 (H-1), hydrogen-2 (H-2), and hydrogen-3 (H-3),respectively. COMMON ISOTOPES AND THEIR USES Many isotopes are used in different industries. Naturally occurring uranium consists of 99.3% uranium238, 0.711% uranium-235 and 0.006% uranium-234. These percentages are referred to as isotopic abundances. Uranium isotopes are principal fuels for nuclear reactors. Uranium-238 is also used to determine the age of sediments from marine environments. Carbon has several known isotopes however naturally occurring carbon consists of 98.93% of carbon-12 and 1.07% of carbon-13. Its other isotopes are short-lived and are present in very small amounts. An example is carbon-14 which is used in the carbon dating of archaeological materials. Isotopes are also utilized in medicine. In radioisotope therapy, iodine-131 is taken orally to help treat thyroid cancer. Radiation from technetium-99 is used to produce images of specific organs in the body for medical diagnosis and treatment. ACTIVITY1 Use your Modern Periodic Table as guide. ACTIVITY 2 1. Californium – 252 is used to determine the moisture content in soil important for road construction and building industries, while Sodium – 24 is utilized to locate leaks in pipe lines. How Many protons and neutrons does each atom have? 2. A radioisotope contains 27 protons and 33 neutrons. Identify what element and write its isotopic symbol using method A and method B. The atomic mass value of elements as given in the Modern Periodic Table is the weighted average of all isotopes found naturally occurring in the earths’ crust. That is, even though all given elements do not have exactly the same mass, any naturally occurring isotope sample will contain the same percentage. Atomic mass is calculated as the sum of the products of the atomic mass (isotopic mass) and the percentage abundance of each isotope of the element naturally occur in nature. Mathematically expressed as: SAMPLE PROBLEM 1. Carbon occurs naturally in the earth’s crust as two isotopes. Given the mass and natural abundance, calculate the atomic mass of carbon. ACTIVITY 3 Solve for the average atomic mass of the following isotopes. 1. Silicon the second most abundant element in the earth’s crust is used extensively as semi-conductors in the electronics industry. Solve for the average atomic mass of silicon given the following information below. 2. Potassium has three stable isotopes that naturally occurs in the earth’s crust namely, potassium – 39 (38.9637 amu), potassium – 40 (39.9640) and potassium -41(40.9618). The percentage abundance of each isotopes is 93.2581%, 0.0117% and 6.73302% respectively. Solve for the average atomic mass of potassium.