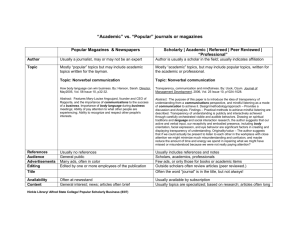
ASSESSMENT REPORT DPL30043 DATA TRANSPARENCY SESSION: I 2022/2023 PREPARED BY : NO NAME MATRICS NO. 1 WAN FATIN AFRINA BINTI WAN ABD RAHMAN 10DLS21F1052 2 DENNIS S/O PITHER 10DLS21F1057 3 HOMISHWARRY D/O MUTHUKUMARAN 10DLS21F1059 CLASS : DLS3B PREPARED FOR : PUAN MARIATI BINTI BAHARUN Page | 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS NUM CONTENTS PAGE NUMBER 1 Definiton of data transparency 3 2 Main aspects of data transparency 3 3 Benefits of data transparency 4 4 Risk without data transparency 5 5 Data transparency checklist 6 6 Conclusion 6 7 Suggestion to improve data transparency in 7-8 companies 8 Example of companies used data transparency 9 9 Refferences 10 Page | 2 1. DEFINITON OF DATA TRANSPARENCY • Data transparency is where companies collect the personal and business data and data insights of their customers, or outside their organization. • Supply chain transparency requires companies to know what is happening upstream in the supply chain and to communicate this knowledge both internally and externally. • A company is held legally responsible for the statements they write in their privacy policy. That means they could face legal repercussions if they share or sell data without the knowledge or consent of their prospects, clients, or customers. • Transparency can be measured along two dimensions: supply chain scope (the depth of interaction in the supply chain) and milestones on the path to complete transparency. 2. MAIN ASPECTS OF DATA TRANSPARENCY • There are two main aspects to data transparency. • The first is transparency within the communication system through which the data flows. • This means that data should be easily accessible and manageable regardless of the application that originally received it and how it was collected, transmitted, and stored. • The second aspect of data transparency concerns the origin of data and its accuracy, consent, and use. Page | 3 3. BENEFITS OF DATA TRANSPARENCY I. Consumers • • By giving them confidence in the system they entrust with their data. Ensures customer expectations are met accordingly, thus boosting the firm's customer retention. • Building customer loyalty is by the simple acts that businesses and employees portray. • Honesty allows clients to comfortably view and consume your products, support your brand and other business practices. II. Marketers • They are confident in the accuracy of the data. • Makes trust possible, and trust is an essential foundation for any long-lasting relationship. III. Platforms • Confirm that the data collection method is reliable. • To give greater insight into procurement spending by opening access to key procurement information and providing it in a user-friendly format. • Allows monitoring of procurement expenditure and acts as a deterrent for corrupt practices. Page | 4 4. RISK WITHOUT DATA TRANSPARENCY • You could face lawsuits Affected customers may choose to sue your business, costing thousands or millions in legal fees and reimbursements. You could also face penalties from local authorities for not being transparent about your data or not implementing proper security measures. • You can be held for ransom Businesses can be hit with ransomware and have their data hijacked, whether from a competitor or from hackers looking to extort money or proprietary information about your products or services. • Your reputation can be destroyed Customers want to trust the companies they buy from; data breaches can damage your reputation and public image. It tells you that you have no security measures in place to protect your information. • Your business operations can be disrupted Data breaches require cybersecurity experts to conduct internal investigations to locate the source of the attack, understand the extent of the breach, develop mitigation strategies, and eliminate key threats. Operations can be greatly reduced before further attacks occur. Page | 5 5. DATA TRANSPARENCY CHECKLIST • Protect your website with antivirus software and a secure sockets layer (SSL). This method of encryption ensures that all data your customers enter through forms on your website is encrypted and cannot be used by hackers. • Get data breach and cyber security training for leaders of your company to stay on top of the latest software and strategies to protect data and know-how to train and prepare their staff. • Train your employees on safety procedures, including not sharing files, passwords, or sensitive information outside the company. • Carefully read any third parties’ privacy policies such as tech subscription services, and financial services, research the company, and ask if they have had any data breaches before you decide to work with them. • Hire cybersecurity specialists to provide yearly check-ups across your website, databases, software, and servers to find any weaknesses hackers may find to steal your data. 6. CONCLUSION Therefore, Data transparency and traceability are essential for protecting our privacy and safeguarding our planet. Companies that don't adhere to these standards will find themselves at a disadvantage in the increasingly competitive global marketplace.As highlighted in this report, transparency reporting has emerged as a valuable practice for companies and organizations across a number of industries. These reports enable the public and policymakers to hold these organizations accountable for their policies and practices and provide important qualitative and quantitative insights to stakeholders. Although transparency reporting does come with some challenges, related to for example, risks and standardization, the practice has significantly transformed what meaningful transparency and accountability looks like in numerous sectors. Going forward, we hope to see more companies across more sectors adopt this practice. Page | 6 7. SUGGESTION TO IMPROVE DATA TRANSPARENCY IN COMPANIES I. Only collect necessary data One of the easiest ways to improve data transparency is to reduce the amount being collected. It can be tempting for software developers to collect a broad range of information with the reasoning that it’s better to have and not need. However, this creates a couple of issues for software developers. Unnecessary data takes up valuable storage space in servers, which quickly gets expensive. Additionally, software developers are responsible for ensuring the security of the information their program collects, and unnecessary data adds complexity to that task. Finally, a major component of data transparency is communicating how and why it’s collected with users. Anything not needed will make this much more challenging and leave people wary or confused. II. Understand regulations In addition to internal data transparency policies, developers must be aware of regional legal regulations. Many areas have adopted strict information protection legislation over recent years, which may impact how developers approach transparency. One of the most well-known regulations is the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). GDPR includes strict developer guidelines for collecting and processing personal information. Under these regulations, developers must provide clear legal reasoning for collecting user data and follow processing rules such as storage limits and confidentiality. Page | 7 III. Establish a data transparency policy More businesses are adopting formal companywide data transparency policies. Software developers should consider adding these to their teams as well. This policy ensures accountability for developers and clients, which helps build trust with users. A data transparency policy often includes details such as required communication with users, standards for the internal handling of data, and restrictions on what data is permitted to be collected. For example, a client might need users to be informed about any personal information being saved by a piece of software. A data transparency policy may also address whether or not people can opt-in or out of collection. IV. Map out how data is collected and used Optimizing and improving data transparency relies on maintaining a clear understanding of exactly where information goes once it is collected. This includes where it's stored, how it's moved to another location, and who has access to it. Mapping out all these elements can reveal areas for improvement. For example, industry experts have pointed out that permissions for user data should be restricted to only those who need access. This helps reduce the risk of a leak and makes it easier to track how it’s being handled, improving transparency communication. Page | 8 8. EXAMPLE Page | 9 9. REFFERENCES https://globalmarketingprofessor.com/the-importance-of-transparency-in-socialmedia-marketing/ https://dzone.com/articles/how-to-ensure-data-transparency-and-why-its-import https://sustainlab.co/blog/why-data-transparency-and-traceability-matter-insustainability TEXT BOOK DPL 30043 (POLITEKNIK SEBERANG PERAI) Page | 10 -END OF REPORT-