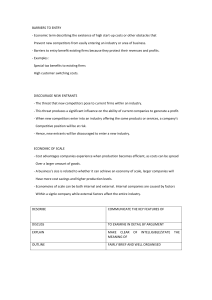
Page 201 CHRISTIANA CHRISTOFI BA & MA ECONOMICS CHAPTER 23 MARKET STRUCTURE LEARNING OBJECTIVES 01 02 03 analyse the effect of having a high number of firms on price, quantity, choice, profit describe the characteristics of a monopoly discuss the advantages and disadvantages of monopoly MARKET STRUCTURE Refers to those characteristics of a market that influence the behaviour of buyers and sellers and the outcome they achieve in terms of product, quality and price. These characteristics include: number and size of firms in the market the degree and intensity of price and non price competition the nature of barriers to entry COMPETITIVE MARKETS Firms compete in the market to increase their customer base, sales, market share and profits. Price Competition Non-Price Competition involves competing to offer consumers the lowest or best possible prices of a product competing on all other features of the product other than price Money is all that matters Quality, Quick shipping, Warranty Elasticities Product placements in trade fairs, promotional campaigns, after sale care Discount Store 99 cents, Primark Metro grocery market, Zara PRICE COMPETITION VS NON-PRICE COMPETITION PERSUASIVE ADVERTISING IS DESIGNED TO CREAT E A CONSUMER WANT AND PERSUADE THEM TO BUY THE PRODUCT IN ORDER TO BOOST SALES. Competitive advantage – by improving the products, respond immediately PRICE SKIMMING: SETTING A HIGH P R I C E F O R A N E W P R O D U C T T H AT I S UNIQUE OR VERY DIFFERENT FROM O T H E R P R O D U C T S O N T H E M A R K E T. P E N E T R AT I O N P R I C I N G : S E T T I N G A V E R Y L O W P R I C E T O AT T R A C T C U S T O M E R S T O BUY A NEW PRODUCT COMPETITIVE PRICING: SETTING A PRICE S I M I L A R T O T H AT O F COMPETITORS’ PRODUCTS WHICH ARE A L R E A D Y AVA I L A B L E I N T H E M A R K E T COST PLUS PRICING: SETTING PRICE BY ADDING A FIXED AMOUNT TO THE COST OF MAKING THE PRODUCT D E S T R U C T I O N P R I C I N G ( P R E D AT O R Y PRICING): • Prices are kept very low (lower than the cost of production per unit) in order to ‘destroy’ the sales of existing products, as consumers will turn to the lowest priced products. Once the product is successful, it can raise prices and cover costs. PRICE WARS: A PRICE WAR IS WHEN TWO OR M O R E R I VA L C O M PA N I E S L O W E R P R I C E S O F C O M PA R A B L E P R O D U C T S O R S E RV I C E S W I T H THE GOAL OF STEALING CUSTOMERS FROM THEIR COMPETITORS—OR GAINING MARKET SHARE. PROMOTIONAL PRICING: SETTING T H E P R I C E O F A F E W P R O D U C T S AT B E L O W C O S T T O AT T R A C T CUSTOMERS INTO THE SHOP IN THE H O P E T H AT T H E Y W I L L B U Y O T H E R PRODUCTS AS WELL PERFECT COMPETITION In a perfectly competitive market, there will be many sellers and many buyers – a lot of different firms compete to supply an identical product. As there is fierce competition, neither producers nor consumers can influence market price – they are all price takers. If any firm did try to sell at a high price, it would lose customers to competitors. If the price is too low, they may incur a loss. There will also be a huge amount of output in the market. PROFITS IN COMPETITIVE MARKETS • In the short run, they may earn mote, or less, than this level of profit which is referred to as normal profit. • If demand for the product rises, the firms in the industry will make higher than normal profit. This level of profit, called supernormal profit or abnormal profit, will attract new firms into the industry. M O N O P O LY MARKETS Scale of production: the size of production units and the methods of production used. Sunk costs: cost that cannot be recovered if the firm leaves the industry. GROUP ACTIVITY 2 In each case, consider what type of barriers to entry and exit may exist in the following markets: a) Airlines b) Film production c) Steel production d) Window cleaning services All Multiple Choice Questions Page 206 HOMEWORK Four-part questions a,b, d Page 206 Christiana Christofi - BA & MA Economics