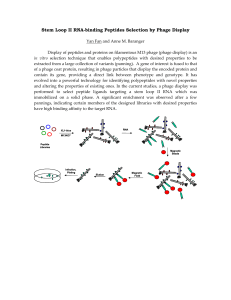
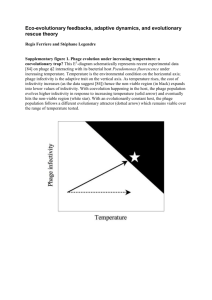
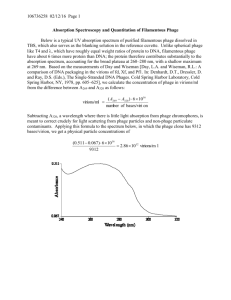
Prophages encode phage-defense systems with cognate self-immunity Siân V. Owen, Nicolas Wenner, Charles L. Dulberger, Ella V. Rodwell, Arthur Bowers-Barnard, Natalia Quinones-Olvera, Daniel J. Rigden, Eric J. Rubin, Ethan C. Garner, Michael Baym, Jay C.D. Hinton Cell Host & Microbe DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.09.002 Figure 1 The bstA gene of prophage BTP1 confers phage defense Cell Host & Microbe DOI: (10.1016/j.chom.2021.09.002) Figure 1 The bstA gene of prophage BTP1 confers phage defense Cell Host & Microbe DOI: (10.1016/j.chom.2021.09.002) BstA homologs are foundFigure in 2diverse bacterial taxa and are frequently associated with prophages Cell Host & Microbe DOI: (10.1016/j.chom.2021.09.002) Figure 3 BstA homologs from Salmonella, E. coli, and K. pneumoniae confer phage defense Cell Host & Microbe DOI: (10.1016/j.chom.2021.09.002) Figure 4 BstA mediates population-level phage defense through abortive infection BstA protein does not protect individual cells from phage infection Figure 4 BstA mediates population-level phage defense through abortive infection 5 BstA systems include cognate Figure self-immunity elements, aba, which are required for successful prophage induction Figure 6 BstA protein does not affect phage lysogeny but inhibits phage DNA replication in the absence of aba Figure 6 BstA protein does not affect phage lysogeny but inhibits phage DNA replication in the absence of aba Summary Figure 6 •BstA is an abortive infection protein found in prophages of Gram-negative bacteria •aba, a short DNA sequence within the bstA locus, acts as a self-immunity element •aba gives BstA-encoding prophages immunity to BstA-driven abortive infection •Variant BstA proteins have distinct and cognate aba elements •8/10