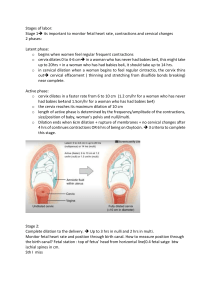
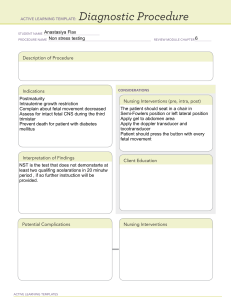
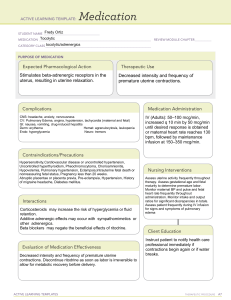
Mariana Mora 1 Pre-Term Labor (PTL) Pre-Term Labour (PTL o Labor which begins between 20 and 36.9 weeks resulting in cervical change o PTL is a description of fetal age – not maturity or size. Physiology of labor o Progesterone- from placenta, relaxes smooth muscles (uterus), tightens the cervix with ropes of collagen Production ↓s as body prepares for labor o Estrogen excites the uterine muscle Production ↑ @ end of pregnancy labour prompts the production of fatty acid hormones: prostaglandins o Prostaglandins – soften the cervix by digesting the collagen fibers A soft cervix will dilate faster Tocolytics o Rx’s that relax muscles & prevent softening of the cervix Assessment: PTL Risk Factors Physiologic o Infection o PPROM/PROM o Incompetent cervix o STI’s o Smoking o Substance abuse o cocaine o Domestic violence/trauma o Multiple gestation o polyhydramnios o Maternal Dehydration o Late, no prenatal care o Cervical problems o Placental problems o Stress o Maternal illness o Maternal Age o Previous PTL or PTB o Fetal Abnormalities o Race Mariana Mora 2 Incompetent Cervix o Painless dilatation of cervix s contractions, during 2nd trimester o Presents with bulging or ruptured membranes & inevitable abortion of an immature fetus o Repeat in subsequent pregnancies if tx not initiatedHx of losses o Weekly Transvaginal Ultrasound to monitor cervical length. o Seen on ultrasound as funneling. Acquired o Inflammation o Infection o Cervical trauma o ↑ uterine volume o Hormonal-Relaxin Congenital o Short cervix o DES exposure o (Diethylstilbestrol) o Bicornuate uterus (a uterus that is shaped irregularly. Heart shaped, appearing to have 2 sides instead of being one hollow cavity) TX: Cerclage (procedure in which cervical opening is closed w stitches to prevent/delay preterm birth) o 14-16wks o Purse-string suture o cervix is sewn closed during pregnancy, removed at 36-37 wks or o left in for future pregnancies and a C/S is performed o TEACH S&S OF LABOUR Cerclage o McDonald’s suture (FYI) o Shirodkar procedure (FYI) o The risks for both include: Infection (if rescue cerclage) Damage to cervix during sx. Excessive blood loss PPROM PTL Permanent narrowing and stiffening of cervix. Tearing of cervix – “chopped meat” effect. o Teach to monitor for contractions and report immediately to HCP to prevent tearing of the cervix during labor. o The cerclage must be removed if labor occurs prematurely. Elective cerclage o Outpatient can go home same day. o Teach: to refrain from Coitus Mariana Mora 3 to report any contractions to HCP. Rescue cerclage o Hospitalized o Placed when dilation and effacement have already occurred o 1/3 PPROM (↑↑↑ infection rate) Fetal Heart Rate in a Premie o a preterm fetus may have a higher baseline fetal heart rate with apparent reduction of baseline variability o fetal baseline heart rate is higher, averaging at 155 between 20–24 weeks (compared to a term fetus where average baseline fetal heart rate is 140). A premie will have a higher baseline fetal heart rate o Before 30 weeks of gestational age, the frequency and amplitude of accelerations are reduced. o Pre-term fetus may exhibit accelerations with a peak of only 10 beats per minute lasting for 10 seconds. o A premie will have an apparent reduction of baseline variability. PTL Risk Factors: Microbiological o UTI o Cervical infection o Uterine infection o How do you get the infection? o PPROM!!!!!! PTL: Clinical Manifestations o Cervical Change- critical criteria o frequent regular uterine contractions -painful or not painful. o Change or increase in vaginal discharge (PROM, PPROM) o Backache, pelvic pressure, thigh pain o Fetal presenting part engaged Assessment of PTL Dx Tests o Monitor uterine contractions: Toco 6 ctxs. or more per hour Q10min) o Vaginal exam to determine dilation, effacement o Dilation greater than 1 cm. o Effacement greater than 80% o 4cm or more cant stop labor o Monitor for ROM o Fetal fibronectin (fFN) 20-34 weeks Fetal Fibronectin (fFN) a protein found in fetal membranes that is described as the “glue” that binds the membranes to the uterus it is found in the cervicovaginal fluid before 20th week and rarely after. If present between 20 & 34 6/7 weeks (in cervical canal) possible PTD Better predictor of who WILL NOT go into labour. Mariana Mora 4 Swab test of the vaginal canal Expensive ($200) Planning and Intervention: PTL o Assess maternal and fetal well being o Encourage bedrest o Provide fluids for hydration o Dehydration stimulates pituitary gland to increase ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) and oxytocin- this causes contractions which stimulates labor. o Administer Rx: tocolytics o Monitor effectiveness of Rx o Patient teaching RT discharge planning Tocolytics: Used off label to suppress uterine activity o Usual criteria used to determine potential use of Tocolytics: Cervix less than 4cm. dilated Membranes intact Less than 37 weeks gestation o Contraindications to Tocolytic Therapy: Severe PIH Bleeding Chorioamniotis Fetal demise ROM o May be used until prenatal steroids become effective (48°) Beta Adrenergic Agonists o Ritodrine (Yutopar) – not used anymore o Terbutaline (Brethine) – used for treatment of Asthma, bronchial dilator, relaxes smooth muscle tissue of the airways, GI, various blood vessels & uterus –used off label mimics the action of epinephrine: increases pulse rate & heart muscle contractions o IV pump (continuous infusion SQ pump) o PO – 2.5 – 5.0mg. Q2-6 hours o SQ – 0.25mg. Q 20min. x3 or Q 1-3 hours o Side effects: o Main side effects involve cardiopulmonary system Maternal and fetal tachycardia Palpitations, chest pressure Pulmonary edema Hypotension Hyperglycemia Hypokalemia arrhythmias Tremors, jitteriness, apprehension Headache N/V Neonate – may exhibit hypoglycemia & hypocalcemia after delivery o D/C for: Mariana Mora 5 HR >120 BP < 90/60 FHR>180 Maternal Pulmonary Edema Calcium Channel Blockers o Blocks the flow of Ca+ in the myometrium – relaxes smooth muscles, Off label use : inhibits uterine activity to stop PTL o Nifedipine (Procardia) Cardiac drug to regulate contractility and lower BP o Side effects: Maternal Hypotension (BP must be assessed prior to administration) Maternal Tachycardia Palpitations H/A Dizziness Flushing of Skin Peripheral Edema ↓Uteroplacental blood flow Fetal Hypoxia & Fetal Bradycardia NSAIDs Prostaglandin Synthesis Inhibitors o Indomethacin (Indocin) Indomethacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is indicated for the ↓ of inflammation in the tx of rheumatoid arthritis. It also is a Prostaglandin Synthesis Inhibitors o Side Effects: o GI problems (usually given with Maalox) o Can cause the ductus arteriosus, to close prematurely NOT to be used after 34 weeks of pregnancy. CNS Depressant o Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO4) o Primary use as CNS depressant is seizure prophylaxis. It’s main action is to block neuromuscular transmission o Used for tx of seizures in eclampsia and preeclampsia. o Secondary use MgSO4 acts directly as a Ca+ antagonist and is use to regulate cardiac contractility, relax smooth muscle, vasodilation (↓BP) o Off label use: relaxes the uterus and ↓ uterine irritability, thus used to delay delivery in PTL o Constant infusion of 2gm/hr after bolus of 4gm over 30 min o Assess blood levels – therapeutic blood level 4-7mg/dL Under 4 mag isnt doing anything o Action: Depresses CNS (respirations, LOC, DTRs) o Side Effects RISK for Pulmonary edema Hypotension Flush feeling Mariana Mora 6 N/V H/A Lethargy o Neonatal lethargy, poor suck reflex, delayed motility of GI tract o CONTRAINDICATED: Myasthenia Gravis or Neuromuscular Disorders exist o Toxicity: Respirations <12 Hyporeflexia- diminished +1 or absent DTRs 0 B/P <90/60 Oliguria urine output <30ml/hr Pulmonary Edema (Crackles or Rales) Confusion Serum MgSO4 >7.0 o Antidote: Calcium Guconate Evaluation: PTL o Risk of preterm delivery decreased o Contractions will be <6/hour with no cervical changes o Discuss cause, ID & tx of PTL o ID adaptations of PTL o Describe appropriate self-care measures o Pregnancy is maintained o Birth to healthy infant