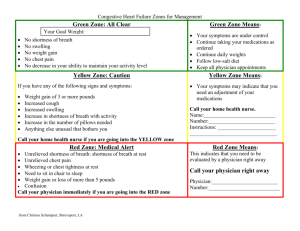
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, which is an anatomical pump, with its intricate conduits (arteries, veins, and capillaries) that traverse the whole human body carrying blood. The blood contains oxygen, nutrients, wastes, and immune and other functional cells that help provide for homeostasis and basic functions of human cells and organs. Heart valve disease is when any valve in the heart has damage or is diseased. In some cases, one or more of the valves don't open or close properly. This can cause the blood flow through your heart to your body to be disrupted. Signs and symptoms Chest pain or palpitations (rapid rhythms or skips) Shortness of breath, difficulty catching your breath, fatigue, weakness, or inability to maintain regular activity level. Lightheadedness or fainting An aortic aneurysm is a balloon-like bulge in the aorta, the large artery that carries blood from the heart through the chest and torso. The aneurysm can burst completely, causing bleeding inside the body. This is called a rupture. Signs and symptoms that aortic aneurysm might be suspected include: Chest tenderness or chest pain, dizziness or light-headedness, back pain, and loss of consciousness due to the ruptures. Coronary artery disease, also called CAD, is a condition that affects your heart. It is the most common heart disease in the United States. CAD happens when coronary arteries struggle to supply the heart with enough blood, oxygen and nutrients. Cholesterol deposits, or plaques, are almost always responsible for this condition. Signs or symptoms. Chest pain or also called(Angina). You may feel pressure or tightness in your chest, as if someone were standing on your chest. This pain, called angina, usually occurs on the middle or left side of the chest. Shortness of breath. If your heart can't pump enough blood to meet your body's needs, you may develop shortness of breath or extreme fatigue with activity. Heart attack. A completely blocked coronary artery will cause a heart attack. Signs and symptoms of arrhythmias may include: A fluttering in the chest. A racing heartbeat (tachycardia) A slow heartbeat (bradycardia) Chest pain. Shortness of breath Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Heart failure does not mean that your heart has stopped or is about to stop working. It means that your heart is not able to pump blood the way it should. It can affect one or both sides of the heart. The weakening of the heart's pumping ability causes: Blood and fluid to back up into the lungs The buildup of fluid in the feet, ankles and legs - called edema, tiredness and shortness of breath Heart failure signs and symptoms may include: Shortness of breath with activity or when lying down. Fatigue and weakness. Swelling in the legs, ankles and feet. Rapid or irregular heartbeat. Cardiomyopathy refers to conditions that affect the myocardium (heart muscle). Cardiomyopathy can make your heart stiffen, enlarged or thickened and can cause scar tissue scar . As a result, your heart can’t pump blood effectively to the rest of your body. Cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure. Signs and symptoms. Fatigue. Heart palpitations (rapid heartbeat). Shortness of breath (dyspnea). Swelling (edema) in the legs, calves or ankles. Syncope (fainting). Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium. The pericardium is a thin sac that surrounds your heart. It protects and lubricates your heart and keeps it in place within your chest. Pericarditis causes can include: Immune system response after heart damage due to a heart attack or heart surgery Sign and symptoms be felt in the middle or left side of the chest, Worsen while lying down and breathing deep, Resemble chest pain from a heart attack An arterial blood gases (ABG) test measures the acidity (pH) and the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood from an artery. This test is used to find out how well your lungs are able to move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. Its used to check hypoxia and COPD. An aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test measures the amount of this enzyme in the blood. AST is normally found in red blood cells, liver, heart, muscle tissue, pancreas, and kidneys. A high AST level may also indicate any of the following conditions that aren’t directly related to your liver: Hemochromatosis (having too much iron in your body, which damages your heart, liver and pancreas). Heart attack (myocardial infarction). A B-type natriuretic peptide or brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), is a commonly performed blood test that is used to diagnose or rule out heart failure. Specifically, the test measures levels of the protein BNP that is made in the heart and blood vessels. BNP levels are higher than normal when you have heart failure. A Creatine Kinase (CK) test measures the amount of this protein in the blood. It is mostly found in your skeletal muscles and heart. The test can be used to help diagnose a heart attack, though not very often. CK testing used to be a common test for heart attacks. But another test, called troponin, has been found to be better at detecting heart damage. A troponin test measures the level of troponin in your blood. Troponin is a type of protein found in the muscles of your heart. Troponin isn't normally found in the blood. When heart muscles become damaged, troponin is sent into the bloodstream. As heart damage increases, greater amounts of troponin are released in the blood. High levels of troponin in the blood may mean you are having or recently had a heart attack. A blood lipid profile measures the levels of each type of fat in your blood: total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. These fats are important for cell health, but they can be harmful when they build up in the blood. Sometimes they can lead to clogged, inflamed arteries, a condition call atherosclerosis. This may keep your heart from working normally if the arteries of your heart muscle are affected. https://www.google.com/search?q=Goole+im ages&rlz=1C1CHBF_enUS802US802&oq=Gool e+images&aqs=chrome..69i57j0i10i131i433l2j0i 10j0i10i131i433j0i10l3j46i10j0i10.5131j0j7&sourc eid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 https://medlineplus.gov/ https://www.mayoclinic.org/ Booth, K. A., & Mundt, L. A. (2019). Phlebotomy: A competency-based approach. McGraw-Hill Education.