Medical English
advertisement

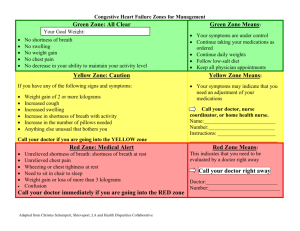
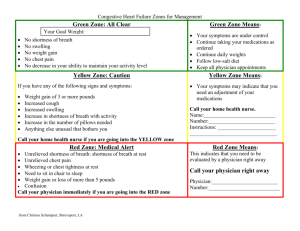
Factors which make difference to the way we communicate with somebody. 1. Ego 2. age 3. education level 4. culture 5. mental state/mood 6. emergency situation 7. level of consciousness 8. gender What a doctor might use instead of word “cardiac arrest”? Chest pain, shortness of breath, heart palpitations (racing heart) and flu like symptoms. Why do we need to have good communication skills? ● humanistic work environment ● competency in professional skills ● satisfaction at workplace ● patient satisfaction ● healthcare quality and as a result a healthy community The words you use matter as much as your voice management. Nonverbal communication is important too. Non verbal communication: ● facial expression ● tone of voice ● movement ● appearance ● eye contact ● gestures ● posture Doctor Patient Interview: 1. Step: Establishing Rapport/ Initial Contact ● 4 objectives: ○ Objective 1: Great the patient and ask her preferred form of address. (Good morning Mr. Hanks, isn't it? We have not meet before) ○ Objective 2: Introduce yourself and clarify your role ○ Objective 3: Explain the purpose of the interview (I’d like to have a little chat with you to ask some questions if it’s OK?) ○ Objective 4: Obtain permission for special circumstances (Taking notes/presence of student doctor/ listening her heart) ○ ○ Plus showing that you care about them such as bringing a cup of water for the patients or helping them to change clothes and asking them “how are you feeling today?” The communication should be as private as possible. Involvement of members of family should be avoided as much as possible. Talking with lying and sitting patient is different and prefer to talk patients while they are sitting to maximise the involvement of interview. 2. Step: Opening Questions ● What would you like to discuss today? ● What brings you here today? ● What kind of problems/issues would you like to share with me? ● A follow up visit can start with “Am I right in thinking you have come about your routine check up?” + “Is there anything else you would like to discuss today?” ● Use facilitation techniques to encourage patient to talk ○ Silence is key ○ Repeating the last sentence in questioning tone ○ Make observational statements such as “you have stop few min ago while talking…… can you tell me what you are thinking about?” ○ Occasional nods of head + Yes? Then? Huh,huh? Hospital round: bedside visits by physicians 3. Step: Opening Statement 4. Step: Setting The Agenda ● Anything else? ● Do you have any other problem? ● Which of these problems concerns you the most? ● Which of your problems did you hope I could help you with today? ● Physician ranks the problems in order of importance? ● Shall we start with…? ● we’ll come back to …….. later. ● If that’s all right? 5. Step: History of Present Illness (HPI) ● Patients past history ● family history ● social history ● Seven dimensions to describe a symptom ○ chronology ○ location ○ quality (Pain can feel sharp, hot, and achy) ○ quantity (intensity of pain, number of times) ○ asking of pain specially ■ nature of pain (dull, sharp) ○ ○ ○ 6. 7. 8. 9. ■ onset of pain (sudden, gradual) ■ severity of pain ■ duration of pain ■ progress (constant, intermittent) ■ aggravating and relieving factors ■ previous occurrence ■ associated symptoms ■ patients notion of what might cause the pain setting (who was with you, where do you get the pain aggravating and alleviating factors manifestation associated Step: Past Medical History Step: Social History Step: Review of Systems Step: Closing the interview ENT: ear nose throat GUS: genitourinary system Depression: sort of mood have you been in cardiac failure:shortness of breath asthma:getting wheezy prostate: problem with waterworks coronary thrombosis: chest pain lung cancer: coughing blood Paresthesia: pins and needles anesthesia: numbness retrosternal chest: pain behind breastbone orthopnea: inability to breath when lying dysmenorrhea: painful periods dyspepsia: indigestion Intermittent Claudication: cramp in leg which comes and goes dyspnea: breathlessness stress incontinence: trouble holding water m: male f:female b:black w:white l: left r:right reg: regular yo:years old ETOH: ethyl Alcohol ICU: Intensive care unit NAD: nothing abnormal detected Abd: abdomen Hb: Haemoglobin ℅: complain of ?:possible A&W: Alive and well P: Pulse HTN: hypertension TURP:Transurethral resection of the prostate FH: family history CXR: chest X ray PMH: past med history HPC: history of past complain LFTS:liver function test MSU: mid stream unit CCF: congestive cardiac failure HS: Heart sound MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging EUA: Examination Under Anaesthetic AIDS: acquired immune deficiency syndrome BPD: borderline personality syndrome ECT: electroconvulsive therapy N/V: nausea and vomiting a.c: before meals cap.: capsule ggt:drops ADH: antidiuretic hormone CBC:complete blood count I&D: Incision and drainage LOC:loss of consciousness ARDS: acute respiratory distress syndrome CT: chemotherapy OA: Osteoarthritis b.i.d: twice a day OGTT: Overall glucose tolerance test fuo: fever of unknown origin SOBOE:Shortness of breath on exertion HS1. Hematopoietic-Specific Protein 1 D&C: Dilation and curettage O/E : On examination JVP:jugular venous pressure