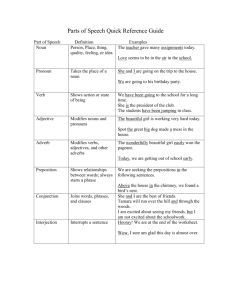
Parts of Speech English Language Afeisha Leshmore There are eight Parts of Speech Nouns Naming word Pronouns Replaces a noun Adjectives Describes something Adverbs Describes a verb Prepositions Show a relationship Conjunctions Joins words or clauses Interjections Expresses emotions Nouns Nouns A noun is a naming word. A noun is used to name Person Thing Animal Place Ideas Nouns Abstract nouns expresses ideas such as love happiness anger justice freedom Pronouns Pronouns A pronoun is used in place of a noun or noun phrase to avoid repetition Examples I, you, it, we, us, them, those, Mary is tired. She wants to sleep Mart is tired. Mary wants to sleep I want her to dance with me. Possessive pronouns Mine, yours, hers, This bike is my bike This bike is mine. Adjectives Adjectives An adjective is a word that describes a noun or noun phrase. Example Sonic has blue fur and red and white boots. NP* The adjectives are placed before the noun Verbs Verbs Verbs show an action or a state of being. It can show what someone or something is doing. Examples The girl is skipping. The boy is running. Examples Verbs Verbs can also show a state of being or existence. Example I am happy I feel sick Verbs Verbs and tenses Verbs have different tenses which tell us WHEN an action happens or happened. Past tense:- I lived in Arima last year Present tense:- I lives in Port of Spain right now. Future tense:- I will live in Chaguanas next year. Types of verbs Auxiliary verbs Regular verbs Stative verbs Linking verbs Transitive verbs Intransitive verbs …..and many more Adverbs Adverbs Adverbs describes or modifies a verb, an adjective or another adverb. I tell us how (often), where, when or to what extent Many adverbs end in “ly” Example Slowly, happily, quickly very, always well Example I am speaking softly. Yesterday I ate my cake Adverbs Adverbs of manner Adverbs of Frequency They answer the question HOW? Answers the question HOW OFTEN? Slowly, loudly, easily, Always, usually, never Adverbs of Time Adverbs of degree. Answers the question WHEN? This answers the question TO WHAT EXTENT? Yesterday, now, soon, Very, really, too, so, quite Adverbs of Place. Answer the question WHERE? Here, there, outside, above Preposition Prepositions Prepositions shows the relationship of a noun, or pronoun to another word. Types of Prepositions Time Examples Place At, on, from, with, about, between. Relationship I left my keys on the table for you. I left my keys on the table for you. My birthday is in May Conjunctions Conjunctions Conjunctions join words, ideas, phrases or clauses together and show how they are connected. Examples and, or but, because, until, if I was hot and tired but I still finished my work. I listened to music while I was running. Interjections Interjections Interjections is a word that expresses a string feeling or emotion. It is a short exclamations Examples Ouch! Hey! Wow! Ugh! Example 1. Ouch! I just hit my foot. 2. Wow, Did she really win the race! Some time a word can be in more than one part of speech depending on its function. For example Prices increased last year. There is an increase in the number of followers. Articles Articles Articles are used to help define nouns Examples Example I need a dictionary an, a, the 1. “A/an” are used to talk about nouns in The dictionary needs to be in English. general. 2. “The” is used to talk about a specific noun Article can function as an Adjective or Determiner. Determiners Determiners A determiner is a word or phrase that appears before a noun. A determiner helps to identify things. 1. Articles: a, an, the. 2. Possessives. My, your, his. 3. Demonstratives: this, that, these, those. 4. Numbers : one, two, three, first, second, third. 5. Quantifiers: some, many, few, others. 6. Interrogatives: what, which, where.