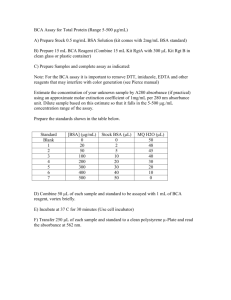
Introduction Proteins are large biomolecules consisting of one or more long Chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Protein is also a macronutrient that is essential to building muscle mass (Szalay, J.2019). Proteins in particular are a biochemical compound that need to be measured often. Due to the presence of amino acids such as tyrosine and tryptophan, proteins and peptides containing the aromatic amino acids absorb UV light at a wavelength of 280 Nm (protein Man, T.2019). Spectrophotometry is a technique used to measure the amount of light absorbed by a substance at specific wavelengths. It is a powerful analytical technique used to measure the amount of light absorbed by a sample. This technique is commonly used in the field of biochemistry and molecular biology to determine the concentration of proteins and other biomolecules in a sample. In this lab, the biuret method was used to determine the total protein concentration in a given sample. The biuret method is a commonly used analytical method for protein determination. This method relies on the formation of a complex between peptide bonds in the protein and copper ions in an alkaline solution. The intensity of the color produced is directly proportional to the concentration of protein present in the sample. The focus was on the biuret method for protein determination. This reaction results in the formation of a complex between the copper ions and the peptide bonds, which absorbs light at a specific wavelength. By measuring the absorbance of this complex using a spectrophotometer, the concentration of protein in a sample can be determined. The objectives of this lab exercise were to gain hands-on experience with the biuret method and spectrophotometry, to understand the principles behind the method, and to learn how to accurately determine protein concentration in biological samples using a standard curve. By the end of the lab exercise, a solid understanding of the biuret method and how it can be used to quantitatively measure protein concentration was acquired. Methodology 1, 0.8, 0.6, 0.4 and 0.2 ml of NaCl was pipetted into test tubes labelled 1 – 6 respectively. 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1 ml of BSA were then added to the each of the labelled test tubes. This made up the final volume 1 ml in all the test tubes. In two separate test tubes labelled test 1 and test 2, 0.8ml and 0.6ml of NaCl were added and 0.2 ml and 0.4ml of serum was added respectively to make 1ml in each test tube. 2ml Biuret reagent was added in all 8 test tubes. The reagents were mixed properly and incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes. The absorbance was then measured using a spectrophotometer. A standard curve of concentration of BSA vs. Optical Density (O.D.) was then drawn. DISCUSSION The experiment`s objective was successfully fulfilled by measuring the absorbance of light that was transmitted thought the tube in the spectrophotometry device, and the results show which wavelength of light are absorbed or transmitted by each color sample. According to the results the solution with 0 NaCl and 1.0 BSA absorbed the highest light, it shows that the sample with BSA 1 and 0 NaCl had had the highest absorbance in table 1.1, and had the greatest absorbance of light to pass though the sample easily. And the sample with 0 BSA but 1.0 NaCl had the least absorbance of light, hence it shows that a sample with more BSA has a high absorbance of light than that of high NaCl. Table 1.2, had test 1 and 2 which show the adding of blood serum to normal saline, it was observed that test 1 had a greater absorbance than test two, reason being that test 1 had more normal saline then test 2 had, and higher absorbance of light compared to test 2. Test 2 had less serum which was only about 0.2(ml), meaning a solution with more normal saline will have a good absorbance of light that that with more serum. CONCLUSION In conclusion, this laboratory showed that the Bradford assay and biuret method is a colorimetric technique specific for proteins and peptides. Copper salts in alkaline solution form a purple complex with substances containing more than two or more peptide bonds. The absorbance produced is proportional to the number of peptide bonds that are reacting and therefore to the number of protein present in the reaction system. Thus different concentrations of sample lead to different absorbance at 520nM. Therefore this lab experiment has demonstrated that the biuret reaction with proteins is suitable for the determination of protein solution by spectrophotometry at around 520 to 560Nm. The use of bovine or human serum albumin standardized the biuret method, Biuret is a good general protein assay for a lot of materials, and however the Bradford assay is faster and sensitive. RECOMMENDATIONS For accuracy results, it is recommended that the known controls are run for each assay that is being used. For this laboratory Bradford assay was used. It is important that the errors such as gross and systemic errors are avoided. For gross errors, proper measurements of solutions should be considered when using the metered pipette so that you don’t pour more or less as required. It is recommended that the reading and recording of data and the calculations are accurately done. It’s also important that the instruments or the glassware such as the test tubes are dry and clean and clearly labeled to minimize the errors. Systemic errors can be reduced by making sure that the instruments used for measuring are well calibrated. In this experiment a spectrophotometer was used and it is recommended that it is warmed for at least 15 minutes prior to use and it should be adjusted to zero (0) on the transmittance scale. Readjustment and recalibration is necessary for running the next sample to avoid systemic errors.