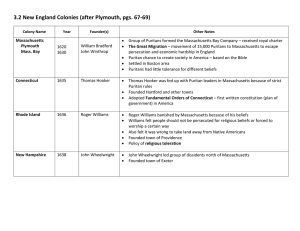
2.4 The New England Way The Rise of Puritanism: ● Church of England retained too many elements of Catholicism ● Rejected Catholic structure of authority from pope or king ○ Congregationalists: Independent local congregations should choose ● Reading bible and listening to sermons > devotion to sacraments administered by priests ● Followed ideas of John Calvin (Swiss theologian) ○ Idleness and immoral behavior were signs of damnation ○ No guarantees of salvation Moral Liberty: ● Minority became separatists: abandoned Church of England ● Searched for liberty in colonies ● Freedom: ability to obey God’s will through self-government1 ● 1645 speech: John Wintrop distinguished “natural” (native) and “moral” (Christian) liberty ● Elect had right to establish churches and govern society The Pilgrims at Plymouth: ● First Puritans to emigrate to America ● 1608 - fled to Netherlands ● Financed by English investors ● September 1620 - Mayflower embarked ○ Blown off course to Cape Cod, native population decimated by smallpox ○ Plymouth Colony ● Mayflower Compact: men agreed to obey laws enacted by chosen representatives ● Arrived without food or farm animals six weeks before winter ○ Half died ○ Survived with help of local Indians (Squanto) ● 1614 - Thomas Hunt kidnaped Squanto ● 1619 - Squanto returned, discovers his people (Patuxet) died from disease ○ Interpreter, taught how to fish, plant corn ○ Helped forge alliance with Massasoit (local chief) ● 1621 - invited Indians to Thanksgiving ● 1627 - common land divided to settlers ● 1691 - overshadowed by Massachusetts The Great Migration: ● 1629 - London merchants create Massachusetts Bay Company ○ Further Puritan cause, profit with Indian trade ● 1630s - Great Migration: established stable basis for society ● Most came in families ○ Desire to escape religious persecution, anxiety about future of England, prospect of economy betterment ○ Older + more prosperous ○ Equal gender ratio ○ Healthy climate ○ = population growth The Puritan Family: ● Male authority, limited women rights ● Women were spiritual equals to men + allowed to become full church members ● Ideal marriage: reciprocal, legal divorce ○ Men had absolute authority at home ■ Physical “correction” was appropriate ● 1465 John Wintrop speech: women achieved freedom through subjection to husband’s authority ● More children survived infancy, woman’s adult life devoted to children Government and Society in Massachusetts: ● Puritans feared excessive individualism and lack of social unity ● Organized self-governed towns ● Land remained in commons: collective use or to be divided later ● Congregational Church for each town ● 1647 law: must establish a school ● 1636: Harvard College ● Shareholders of Massachusetts Bay Company emigrated to America ● Freemen elected governor ● Voluntary agreement to make church decisions ● Church membership - restrictive prestige ○ Smaller % of population had control Church and State in Puritan Massachusetts: ● 1641 General Court - Body of Liberties ○ Interpreted as privileges ● Inequality = expression of God’s will ● Separate rights for freemen, women, children, and slaves ● Law required towns to establish churches and taxes to support ministers ● Death penalty for worshipping other gods ● Religious uniformity = necessary for social order ● Religious liberty = liberty to practice the truth