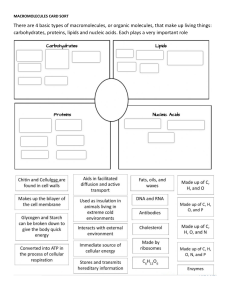
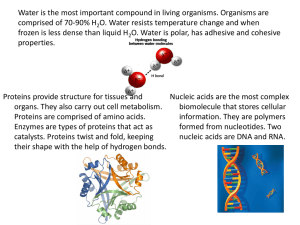
School Daily Lesson Log I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards Teacher Teaching Dates and Time Alaminos Integrated National High School Maureen D. Tolentino March 6 - 9, 2023 First day (ABM, EIM 1 & 2) Second day(ABM, EIM 1 & 2) At the end of the lesson, the learners are expected to: 1. Distinguish between carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids; 2. Summarize the general characteristics of each biomolecule; and 3. Relate the structures of the biomolecules with their properties. Grade Level Grade 11 Learning Area Quarter Physical Science Third Quarter Third day (ABM, EIM 1 & 2) Fourth day (ABM, EIM 1 & 2) The learners demonstrate an understanding of: 1. The relationship between the function and structure of biological macromolecules 1. Make a creative representation of the historical development of the atom or the chemical element in a timeline A. Performance Standards 2. Learning The Learners: Competencies/ 1. Explain how the structures of biological macromolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acid, and proteins determine their properties and functions. S11/12PS-IIIe-22 Objectives Write LC code for each II. CONTENT Biological Macromolecules III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide pages 2. Learner’s Materials pages 3. Textbook pages Teacher’s Guide for SHS LM – Physical Science Module 7 Teacher’s Guide for SHS Teacher’s Guide for SHS Teacher’s Guide for SHS Quarter 3 – LM – Physical Science - Quarter 3 – Module LM – Physical Science - Quarter 3 – Module 7 LM – Physical Science 7 Module 7 Quarter 3 – Video Clips from youtube, laptop, LED Video Clips from youtube, laptop, LED TV, Video Clips from youtube, laptop, LED TV, Video Clips from youtube, laptop, LED TV, speaker speaker speaker TV, speaker 4. Additional Materials from Learning K to 12 Curriculum Guide Physical Science K to 12 Curriculum Guide Physical Science K to 12 Curriculum Guide Physical Science K to 12 Curriculum Guide Physical Science Resource (LR) portal pages 534 - 538 pages 534 - 538 pages 534 - 538 pages 534 - 538 https://www.studocu.com/ph/ https://www.studocu.com/ph/ https://www.studocu.com/ph/ https://www.studocu.com/ph/ Other Learning Teacher’s Guide for SHS Resources I. PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or Begin with classroom routine: presenting the new lesson a. Prayer Teacher’s Guide for SHS Teacher’s Guide for SHS Teacher’s Guide for SHS b. Checking of Attendance Begin with classroom routine: a. Prayer b. Checking of Attendance Begin with classroom routine: a. Prayer b. Checking of Attendance Begin with classroom routine: a. Prayer b. Checking of Attendance Review of the previous lesson Review of the previous lesson Review of the previous lesson Review of the previous lesson/Motivation 1.What are the importance of carbohydrates in living organism Process Questions: Answering the pre-test in module 7 pages 2, 1-15 items. (5 mins) 1. What are Biological Macromolecules? 1. What is the importance of protein in living organism? 2. What is the importance of Fats and lipids in living organism? B. Establishing purpose for lesson a the Discussion on biological macromolecules Biological macromolecules are large, organic molecule such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Most of them are organic compounds and the functional group determines their chemical properties. Biomolecules have a huge variety of functions, such as storing energy, protection, etc. Now be ready with your journey to the different biomolecules, their structures, and functions found in your food. Analyze the Nutritional Facts of a food product given on the module and rank the nutrients needed by the following patients based on importance. Discussion about carbohydrates Discussion about lipids and fats 1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids or fats The word carbohydrate may be broken down to carbon and hydrate. Another term for carbohydrate is saccharide. Carbohydrates are classified either as simple or complex. Simple sugars are monosaccharide and disaccharides. Complex sugars are polysaccharides. Carbohydrates are the primary energy source of the human body. The different saccharides that humans eat are converted to glucose which can be readily used by the body. The excessive consumption of carbohydrates is converted to Lipids or fats are important nutrients in your body but eating too many especially unhealthy fats such as saturated fats and trans fats can lead to heart disease, cancer, and obesity. Lipids also serve other functions such as material for cell membrane, insulation to maintain body temperature, aid in digestion, and as signal molecules. Discussion about Nucleic Acids 4.Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids play an essential role in the storage, transfer, and expression of genetic information. Nucleic acid was discovered by a 24-year old Swiss physician named Friedrich Miescher in 1868. He was puzzled that an unknown substance in white blood cells did not resemble carbohydrates, proteins, or lipids. He was able to isolate the substance from the nucleus and initially called it nuclein. He eventually was able to break down nuclein into protein and nucleic acids. He found out that nucleic acids contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. glycogen which is stored in the liver and in muscles. Glycogen is a slowreleasing carbohydrate A. a patient with hypertension B. a patient renal failure C. a patient with diabetes mellitus C. Presenting examples/ Instances of new lesson the D. Food is a source of molecules that are needed for life. These are biological molecules. What you eat belongs to biomolecules. There are four biological molecules that make up all of life. Now, I have here a word hunt for your warm up. Look for the words and write your answer: biomolecule, carbohydrate, lipid, protein, and nucleic acid. - Discussion about the different types - Discussion about classifications of lipids. of carbohydrates. the different There are different classifications of lipids: triglyceride, phospholipid, wax, and steroid. The lipid family is one of the most varied in terms of structure but they share the common property of being insoluble in water. - Discussion about the Examples of Nucleic acid The most common examples of nucleic acids are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA(ribonucleic acid). DNA is a nucleic acid that carries the genetic code of organisms. It is fondly termed as the blueprint of life. RNA, on another hand, carries the information from the DNA to the cellular factories for the synthesis Giving examples of Lipids and fats of proteins. If carbohydrates are composed of saccharide units, proteins of amino acids, and Fat and oil are the most common lipids of fatty acids, nucleic acids are examples of lipids. They are under composed of nucleotides. Nucleic acids are triglycerides because they are composed of also known as polynucleotides. glycerol and three fatty acids. Fat refers to solid triglyceride usually from Three parts of nucleotide: animal sources such as meat, milk, butter, 1. Nitrogenous base margarine, eggs, and cheese. Oil refers to 2. Five-carbon carbohydrate or sugar liquid triglycerides from plant sources. 3. Phosphate group Examples are olive oil, corn oil, sunflower oil, and soybean oil. Animal fats contain high percentages of saturated fatty acids while plant oils are mostly unsaturated fatty acids. Did you know that? Marathon runners, tri-athletes, and other runners eat carbohydrates for weeks leading up to a big event. They call it “carbo-loading”. What’s the point? As the athletes consume massive amounts of starch and pasta, the energy begins to store up in their body, saving itself for use during the event Lipids They are made from carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen They are soluble (dissolve) in oil but are insoluble (don’t dissolve) in water. Examples: fats and oils Function: long-term storage of energy in the body Monomer: fatty acid E. Discussing concepts practicing skills new and new - Discussion of answers in the previous activity - Ask the students to Give Examples of carbohydrates - Ask the students about the examples of the sources of proteins. - Discussion on the composition of Nucleic Acids They are made from carbon, hydrogen, They are made from carbon, hydrogen, and Proteins are composed of four oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. oxygen. elements, namely: carbon, hydrogen, Monomer: nucleotide oxygen, and nitrogen. Sulfur and other Examples: DNA and RNA Monomer: saccharides metals are sometimes also found in Examples: rice, cereal, potatoes, fruits, proteins. If carbohydrates are made up Function: involves the genetic materials, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and pastas of saccharides, proteins are made up of Ribonucleic Acid (RNA). DNA is the Function: main energy source of the body. amino acids. blueprint of life because it contains instructions on how to make proteins in the - Discussion of answers Examples of proteins and their functions body. are: - Group activity 1. Keratin is a structural protein found in hair, skin, and nails. 2. Fibroin / Silk protein - Fibroin is found in silk. Silk has a smooth and soft texture. It is one of the strongest natural fibers that have high resistance to deformation. It is also a good insulating material. 3. Collagen is a major insoluble fibrous protein found in connective tissues such as tendons, ligaments, skin, cartilage and the cornea of the eye. It comprises as much as 30% of proteins in animals. 4. Enzymes function to catalyze chemical reactions. They either speed up a reaction, Carbohydrates lower the needed energy for a reaction to take place, or bind substances to their specific partners. Examples of enzymes a. Lipase - help in digestion of fats b. Pepsin - help in breaking down proteins into peptides (smaller units) c. Sucrase - also called invertase; help in the digestion of sugars and starches 5. Myoglobin is a polypeptide that stores oxygen in muscles. It contains a heme group which has an iron where the oxygen is stored. F. Discussing concepts practicing skills new Activity 1.1 Macromolecule Plates and Glass and new -Discussion about the common uses pof Proteins carbohydrates and how it is important to living organisms. They are made from carbon, hydrogen, 1.Write inside the first plate an example of oxygen, and nitrogen Proteins are made up of amino acids food rich in carbohydrates that you have eaten combined through a dehydration link called a peptide bond. a while ago and tell us what you feel after Monomer: amino acid Two classes: eating it. 1. Saturated fats have two carbons attached to each carbon (except the one at the end). Saturated fats are unhealthy fats like butter. 2. Unsaturated fats are missing at least one hydrogen and are curl in shape. The unsaturated fats are healthy, and include oils. What did you feel after eating the food rich in carbohydrates? ____________________________________ ___________________________ Structures of the Different Biomolecules Remember this mnemonic device of biomolecules: CHO CHO CHON CHONP C stands for the element Carbon N stands for the element Nitrogen H stands for the element Hydrogen P stands for the element Phosphorus O stands for the element Oxygen 2.Write inside the second plate an example of food rich in lipids that you have eaten a while ago. What did you feel after eating the food rich in lipids? ____________________________________ ________________________ 3.Write inside the third plate an example of food rich in protein that you have eaten a while ago and tell us what you feel about what you have eaten. What did you feel after eating the protein - rich food? ____________________________________ _________________________ 4.Write inside the glass the function of nucleic acids. G. Developing mastery - Discussion of the answers above Process Questions: 1. What are the uses of carbohydrates? Discussion of the Terms and 2. What are the types of Definitions: carbohydrates? Monosaccharide – simplest form of carbohydrates Monomer – a molecule that can react with other molecule to form very large molecules orpolymers Peptide – short chain of amino acid monomer link by peptide bonds Hormones – special chemical messengers that are created in the endocrine gland Amino acids – organic compounds that combined to form proteins Enzymes – proteins which make the bio chemical reaction fast Nucleotide – made up of three components: nitrogen-containing base, five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group Phospholipids - contain glycerol, twofatty acids, and a phosphate group - Group Activity for the different types of proteins. - Answer What’s more on page 13 G. Finding Practical applications of concepts are Practical applications of concepts are Practical applications of concepts are Practical applications of concepts are practical applications of incorporated in the examples incorporated in the examples incorporated in the examples incorporated in the examples concepts and skills in daily living H. Making Process Questions: Process Questions: Process Questions: generalization and - Answer What I have Learned Activity abstractions about 1. What are the different Biological 1. What are the benefits of 1. What is the importance lipids in 1.3 - Maze Runner page 14 the lesson Macromolecules? carbohydrates in living organisms? living organisms? 2. What are the different sources of carbohydrates? 2. What are the types of lipids? 3. What is the importance of protein in living organisms? 4. What are the types of proteins? - Answer What I can do on page Activity 1.4 – on page 16 A. Evaluating learning For a better understanding of what the learners For a better understanding of what the For a better understanding of what the For a better understanding of what the learners have learned, the learners will do the learning learners have learned, the learners will do learners have learned, the learners will do have learned, the learners will do the learning tasks provided by the teacher. the learning tasks provided by the teacher. the learning tasks provided by the teacher. tasks provided by the teacher. B. Additional activities application remediation Short Quiz - Short Quiz - Short Quiz - Answer Assessment on page 17 - 19 Answer additional activities on page 20 for or C. REMARKS IV. REFLECTION V. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation A. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% B. Did the remedial lessons work> No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson A. No. of learners who continue to require remediation Activity 1.5 Biomolecule Poem Summarize the topics and creatively translate them into a poem describing what you have learned about biomolecules. Write your answer on a separate answer sheet. Which of my teaching strategies worked well? Why did these work? B. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? D. What innovation or localized materials did I use/ discover which to share with other teachers? C. Prepared by: Checked by: Noted by: MAUREEN D. TOLENTINO SEVILLA C. MANALILI AIDA M. BEJO, EDD Teacher III Head Teacher III Principal III