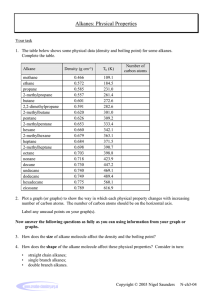
11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Alkanes Alkanes are everywhere. Take a quick look around - you are sure to find many produc alkanes. The surface of that road outside your house was made from long-chain alkan you put in your car is made from alkanes too. The plastic in your toothbrush is a type o alkanes, and alkanes form the base of many chemicals, such as your toothpaste and s Overview This article is about alkanes in organic chemistry. We'll define alkane before looking at their functional group and general formula We'll then explore alkane nomenclature and isomerism. After that, we'll learn about their geometry, then look at both how alkanes are m properties. To finish, we'll compare alkanes and alkenes. Alkane definition First of all, let's look at the basic definition of an alkane. Definition An alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon. What do those terms actually mean? A hydrocarbon is an organic molecule that contains only hydrogen Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 1/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Saturated molecules contain only carbon-carbon (C-C) and carbon bonds. In contrast, unsaturated hydrocarbons contain at least one carbon=carbon (C=C) doub hydrocarbons are known as alkenes, and we’ll take a quick look at them later. Alkane functional group You should know from "Organic Compounds" and "Functional Groups" that organic mo groups. These are atoms, or groups of atoms, that make them react in a certain way. T alkane is the C-C single bond. However, this bond is found in almost every organic co don't consider it to be a functional group. Instead, they say that alkanes are organic m group. Alkane general formula Alkanes form a homologous series with the general formula CnH2n+2. Remember that molecules that share the same chemical characteristics and general formula. In fact, th and arrangement. For example, ethane (C2H6 ) and propane (C3H8 ) are two of the sim shown below. You can see that propane is very similar to ethane - it simply contains an two end carbons. Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 2/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Ethane, left, and propane, right. StudySmarter Originals Example The alkane butane has four carbon atoms. Calculate its number of hydrogen ato Alkanes are represented by the general formula CnH2n+2. The question tells us th and so here, n = 4. We can see from the formula that alkanes h (2n + 2) hydrogen into this expression, we find that butane has (2(4) + 2) = 10 hydrogen atoms. Alkane nomenclature Alkanes are probably the simplest type of organic molecule to name. They follow all th including those involving root names and side chains (see Organic Compounds for a q is indicated by the suffix -ane. The following alkane is a good example - see if you can Example Name the following alkane: Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 3/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes An unknown alkane. StudySmarter Originals First, identify the longest carbon chain in the molecule. Sometimes this chain is ha what looks like a side branch. Here, the longest chain is 5 carbon atoms long. If w names, shown below, we know that this molecule must be based on pent-. Becau ane. Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 4/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Number of carbons in longest chain Root name 1 meth- 2 eth- 3 prop- 4 but- 5 pent- Next look at the side chains. There are 2 methyl groups (-CH3) attached to 2 of the dimethyl- will be used. But which carbons are they joined to? To find out, number chain. We've shown this down below. Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 5/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes The unknown alkane with its carbon chain numbered. StudySmarter Originals The methyl groups are either attached to carbons 3 and 4 if you count from the rig left. However, as you know from Organic Compounds, the numbers of the carbon functional groups must add up to the lowest total possible. Therefore, in this mole the left. This gives us the overall name of 2,3-dimethylpentane. Alkane isomerism Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 6/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Look at the alkane C4H10. This could represent multiple different molecules. For exam methylpropane: Butane, left, and 2-methylpropane, right. StudySmarter Originals Count the carbons and hydrogens to be sure. Both molecules have 4 carbon and 10 h are known as isomers. Definition Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangemen Alkanes can show a type of structural isomerism called chain isomerism, as explored Chain isomerism Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 7/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Definition Structural isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ chain isomers differ in their arrangement of the carbon chain. For example, pentane and 2-methylbutane both have the same number of carbon and pentane has a single long chain that is 5 carbons in length, 2-methylbutane has a 4-ca side chain. Therefore, these molecules are chain isomers. Pentane, left, and 2-methylbutane, right. StudySmarter Originals To find out more about the other types of isomerism, take a look at "Isomerism". Molecular Shape of Alkanes Alkanes are based on a tetrahedral shape. We've used methane as an example. It look Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 8/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes The tetrahedral shape of methane. StudySmarter Originals The molecule is a triangular pyramid, with a hydrogen atom at each corner of the pyra centre. The angle between each of the bonds is 109.5o. The shape of alkanes is all thanks to VSEPR theory (valence shell electron pair repulsi electron pairs repel each other, and the strength of the repulsion depends on the type whether it is a lone pair or a bonded pair. All of the electron pairs around methane's ce identical single covalent bonds, and this means that they repel each other equally. Du electron pairs align themselves in a tetrahedral geometry, as this geometry keeps all o each other. Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 9/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes How are alkanes made? We'll now consider the sources of alkanes: We get many alkanes from crude oil. We turn some of these into shorter-chain alkanes through cracking We can also synthesise alkanes by hydrogenating alkenes. Crude oil Alkanes are formed from dead plant and animal matter that has been squashed unde over a long, long period of time. Cast your mind back 400 million years or so, to a wor we know it. The first vertebrates were only just starting to emerge on land, giant mush common sight, and oceans covered the vast majority of the planet. When creatures liv remains fell to the ocean floor and were buried in layers of silt and sand. Over millions and higher, creating a high-pressure, high-temperature anaerobic environment. This remains to slowly start turning into a substance called crude oil. The process is known Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 10/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Crude oil formation. StudySmarter Originals Deep dive When mined from the sea bed, crude oil is our primary source of alkanes. Howev so long, crude oil is seen as an unsustainable resource, and it is linked to many e at Combustion for more. Cracking The alkanes found in crude oil are usually long-chain hydrocarbons, with chains made These long-chain molecules aren't very useful. Instead, we break them down into sma process called cracking. Large alkane molecules are heated up to around 500°C in th Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 11/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes (Al2O3) or silicon dioxide (SiO2) catalyst. This breaks some of the covalent bonds withi hydrocarbons. Alkene hydrogenation Another way of synthesising alkanes is by hydrogenating alkenes. This involves heati presence of a nickel catalyst. Deep dive Hydrogenating certain alkenes produces trans fats, found in margarines and lots health organisations associate these molecules with an increased risk of corona trans fats are banned in some nations - including the US. Check out Reactions of hydrogenation, or head over to Cardiovascular Disease to learn more about othe your heart. Properties of alkanes Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, consisting of C-C and C-H bonds only. These bo because carbon and hydrogen have similar electronegativities, the bonds are also no information). This means that the only forces between alkane molecules are van der W as temporary or induced dipole forces. Electrons in a molecule are constantly moving randomly, and at any one point could b might be clustered together, and some might be further apart. This creates a small dip location and strength. Dipoles in one molecule then attract or repel neighbouring mo as well, and this attraction holds the molecules together. Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 12/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes However, the attraction is relatively weak, giving alkanes the following properties: Solubility Alkanes are insoluble in water. This is because their non-polar C-C and C-H bonds ca molecules. However, alkanes are soluble in other non-polar solvents and are good so Combustibility Alkanes are readily combustible and have high negative enthalpies of combustion, w them as fuels such as petrol. They burn in excess oxygen to produce carbon dioxide a Volatility If you ever fill up your car at a petrol station, you’ll notice the stark warning signs: no li because short-chain alkanes are highly volatile and the surrounding air is likely to be small spark could cause a devastating explosion. Their volatility decreases as they inc Reactivity Alkanes are generally unreactive due to the strength of their non-polar C-H and C-C b energy to overcome, and most reactions simply can’t provide that. However, they can UV light; this reaction is further explored in Chlorination. They can also be cracked to this in more detail in Cracking (Chemistry). Melting and boiling points Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 13/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Alkanes have relatively low melting and boiling points. This is because the only force weak van der Waal forces, due to their C-C and C-H bonds being non-polar. As the chain length of alkanes increases, their boiling points increase. A larger molecu any one time, its temporary dipole could be larger. It will therefore experience greater smaller molecule. However, as the number of branches increases, an alkane’s boiling the molecules can’t pack together as tightly. Imagine packing strands of spaghetti in a rows in the same orientation. Now imagine if the spaghetti is branched, like twigs. The large gaps between the strands, forcing them further apart from each other and wastin between molecules are not very strong over long distances, and so the attraction betw See Intermolecular Forces for a further explanation on van der Waal forces. Alkanes and alkenes We know that alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. They contain just C-C and C-H sin into unsaturated hydrocarbons. For example, consider propene. Take off one hydroge the two free electrons to form another bond between these two carbons, and you sho following: Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 14/15 11/7/22, 2:19 PM Alkanes Propane, left, and propene, right. StudySmarter Originals This molecule is known as propene and is a type of alkene. We’ll explore alkenes in a know that they are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain a C=C double bond. This b them more reactive than alkanes. Alkanes - Key takeaways Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. They have the C-Cfunctional group and the general formula CnH2n+2. They are named using standard nomenclature rules and the suffix -ane. Long-chain alkanes are found in crude oil. We can produce short-chain alkanes b molecules, and also synthesise alkanes by hydrogenating alkenes. The bonds within alkanes are relatively strong and non-polar, making alkanes in combustible, and giving them low melting and boiling points. Alkenes differ from alkanes by having one or more C=C double bond. Create the best notes with StudySmarter.de https://app.studysmarter.de/studyset/3783423/summary/25194311 15/15