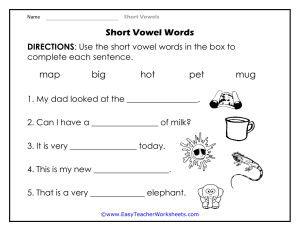
GROUP 15 OUTLINE REPORT LADY JANE LEANO DATU JUDEL SAMBOAWAN ELYSSA CASTANARES LINGUISTIC 121: LANGUAGE IN CULTURE AND SOCIETY INSTRUCTOR: MA’AM, NEPTHALIE GUAZO TITLE: CHANGES IN THE ENGLISH LANGUAGE INTRODUCTION: Language change refers to the process by which a language evolves over time, resulting in differences in its pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar. Language change is the phenomenon by which permanent alterations are made in the features and the use of a language over time. All natural languages change, and language change affects all areas of language use. Language is a constantly changing system. In each century, new words appear constantly, old words, their spelling and meaning, assimilated words from different language change, they become stronger in a particular language over time. Indeed language does not stand still in one place, because inventions and innovations appear every day, and accordingly they lead to a change in language. People move from one country to another, bringing with them new words and phrases for another country or culture. GRIMM’S LAW Grimm’s law shows the systematic relationship between consonant in Germanic languages and consonants in other Indo-European languages, stating what phonetic changes took place. It also shows that changes in a language and in groups of languages come about gradually and not as a result of random word changes. GREAT VOWEL SHIFT: Great vowel shift was a series of changes in the pronunciation of the English Language that took place primarily between 1400 and 1700, beginning in southern England and today having influenced effectively all dialects of English. A series of changes in the quality of the long vowels between Middle and Modern English as a result of which all were raised. It refers to the 15th century change in pronunciation of long vowels that occurred in England. CONCLUSION: A. English continues to develop, changes and emerge with thousands of new words being developed every year. But even the borrowing from many other languages the heart of English language remains the Anglo- Saxon of Old English. The grammar of English is also distinctly Germanic- three genders (he, she and it) and a simple set of verb tense. B. To conclude , the developments of language depends on several factors and one of the major elements has been vocabulary from old English to modern English.