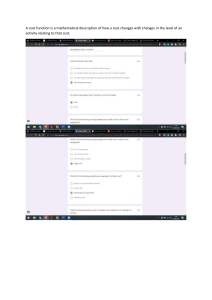
Assessed curriculum Mathematics assessment criteria: Year 5 Criterion A: Knowing and understanding Maximum: 8 At the end of year 5, students should be able to: i. select appropriate mathematics when solving problems in both familiar and unfamiliar situations ii. apply the selected mathematics successfully when solving problems iii. solve problems correctly in a variety of contexts. Achievement level 0 Level descriptor The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors below. The student is able to: i. select appropriate mathematics when solving simple problems in familiar situations ii. apply the selected mathematics successfully when solving these problems iii. generally solve these problems correctly in a variety of contexts. 1–2 The student is able to: i. select appropriate mathematics when solving more complex problems in familiar situations ii. apply the selected mathematics successfully when solving these problems iii. generally solve these problems correctly in a variety of contexts. 3–4 The student is able to: i. select appropriate mathematics when solving challenging problems in familiar situations ii. apply the selected mathematics successfully when solving these problems iii. generally solve these problems correctly in a variety of contexts. 5–6 The student is able to: i. select appropriate mathematics when solving challenging problems in both familiar and unfamiliar situations ii. apply the selected mathematics successfully when solving these problems iii. generally solve these problems correctly in a variety of contexts. 7–8 Mathematics guide 45 Mathematics assessment criteria: Year 5 Criterion B: Investigating patterns Maximum: 8 At the end of year 5, students should be able to: i. select and apply mathematical problem-solving techniques to discover complex patterns ii. describe patterns as general rules consistent with findings iii. prove, or verify and justify, general rules. Achievement level 0 Level descriptor The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors below. The student is able to: 1–2 i. apply, with teacher support, mathematical problem-solving techniques to discover simple patterns ii. state predictions consistent with patterns. The student is able to: 3–4 i. apply mathematical problem-solving techniques to discover simple patterns ii. suggest general rules consistent with findings. The student is able to: i. select and apply mathematical problem-solving techniques to discover complex patterns ii. describe patterns as general rules consistent with findings iii. verify the validity of these general rules. 5–6 The student is able to: i. select and apply mathematical problem-solving techniques to discover complex patterns ii. describe patterns as general rules consistent with correct findings iii. prove, or verify and justify, these general rules. 7–8 Note: A task that does not allow students to select a problem-solving technique is too guided and should result in students earning a maximum achievement level of 4 in year 5. However, teachers should give enough direction to ensure that all students can begin the investigation. For year 5, a student who describes a general rule consistent with incorrect findings will be able to achieve a maximum achievement level of 6, provided that the rule is of an equivalent level of complexity. 46 Mathematics guide Mathematics assessment criteria: Year 5 Criterion C: Communicating Maximum: 8 At the end of year 5, students should be able to: i. use appropriate mathematical language (notation, symbols and terminology) in both oral and written explanations ii. use appropriate forms of mathematical representation to present information iii. move between different forms of mathematical representation iv. communicate complete, coherent and concise mathematical lines of reasoning v. organize information using a logical structure. Achievement level 0 Level descriptor The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors below. The student is able to: 1–2 i. use limited mathematical language ii. use limited forms of mathematical representation to present information iii. communicate through lines of reasoning that are difficult to interpret. The student is able to: 3–4 i. use some appropriate mathematical language ii. use appropriate forms of mathematical representation to present information adequately iii. communicate through lines of reasoning that are complete iv. adequately organize information using a logical structure. The student is able to: i. usually use appropriate mathematical language ii. usually use appropriate forms of mathematical representation to present information correctly iii. usually move between different forms of mathematical representation iv. communicate through lines of reasoning that are complete and coherent v. present work that is usually organized using a logical structure. 5–6 The student is able to: 7–8 Mathematics guide i. consistently use appropriate mathematical language ii. use appropriate forms of mathematical representation to consistently present information correctly iii. move effectively between different forms of mathematical representation iv. communicate through lines of reasoning that are complete, coherent and concise v. present work that is consistently organized using a logical structure. 47 Mathematics assessment criteria: Year 5 Criterion D: Applying mathematics in real-life contexts Maximum: 8 At the end of year 5, students should be able to: i. identify relevant elements of authentic real-life situations ii. select appropriate mathematical strategies when solving authentic real-life situations iii. apply the selected mathematical strategies successfully to reach a solution iv. justify the degree of accuracy of a solution v. justify whether a solution makes sense in the context of the authentic real-life situation. Achievement level 0 Level descriptor The student does not reach a standard described by any of the descriptors below. The student is able to: 1–2 i. identify some of the elements of the authentic real-life situation ii. apply mathematical strategies to find a solution to the authentic real-life situation, with limited success. The student is able to: i. identify the relevant elements of the authentic real-life situation ii. select, with some success, adequate mathematical strategies to model the authentic real-life situation iii. apply mathematical strategies to reach a solution to the authentic real-life situation iv. discuss whether the solution makes sense in the context of the authentic real-life situation. 3–4 The student is able to: 5–6 i. identify the relevant elements of the authentic real-life situation ii. select adequate mathematical strategies to model the authentic reallife situation iii. apply the selected mathematical strategies to reach a valid solution to the authentic real-life situation iv. explain the degree of accuracy of the solution v. explain whether the solution makes sense in the context of the authentic real-life situation. The student is able to: 7–8 48 i. identify the relevant elements of the authentic real-life situation ii. select appropriate mathematical strategies to model the authentic real-life situation iii. apply the selected mathematical strategies to reach a correct solution to the authentic real-life situation iv. justify the degree of accuracy of the solution v. justify whether the solution makes sense in the context of the authentic real-life situation. Mathematics guide