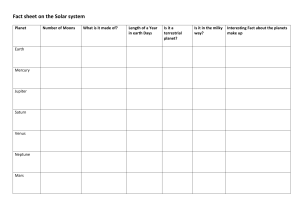
Matter States & Properties: 8th Grade Science Presentation
advertisement

CLASSROOM RULES 1. BE CONSISTENT TOWARDS WEARING ID AND PROPER UNIFORM. WEAR THEM EVERY SCHOOL DAYS UNLESS YOU ARE READY WITH THE CONSEQUENCES. 2. ALWAYS WEAR YOUR NAME TAG DURING SCIENCE SUBJECT. 3. DO NOT USE YOUR CELLPHONE DURING THE DISCUSSION, CELLPHONE WILL BE CONFISCATED. 4. ENTER TO THE CLASS ON TIME. 5. IF I ASK QUESTION ANSWER IT, IF YOU DON’T KNOW THE ANSWER SAY “CALL A FRIEND”. 6. DO NOT ANSWER IN CHORUS RESPECT! RAISE YOUR HAND IF YOU HAVE QUESTION. 7. IF YOU WANT TO GO OUTSIDE GET THE PASS KEY AND ALWAYS ONE AT TIME. 8TH GRADE HELLO SCIENCE 8! GOOD MORNING! TABLE OF CONTENTS 01 02 MATTER STATES PROPERTIES OF MATTER 03 ACTIVITY RAMBO WORD DETERMINE THE RAMBLED LETTERS 2. RAISE YOUR HAND IF YOU KNOW THE ANSWER 1. TMATRE MATTER IOSDL SOLID UIIDQL LIQUID AGS GAS TICLESPAR PARTICLES MATTER MATTER ANYTHING THAT OCCUPIES SPACE AND HAS MASS. ANYTHING THAT WE SAW, FEEL, AND TOUCH ARE MATTER. 01 3 STATES OF MATTER SOLID, LIQUID, AND GAS. DEFINING MATTER DEMOCRITUS JOHN DALTON Simple experiment. Questions 1. What happens to the sugar? 2. Where does the sugar go? 3. How would you know that the sugar is still on the solution? Answers 1. Dissolve 2. Attached to water or the solution 3. Taste the water itself Principle of particulate matter 1. All matter is made of tiny particles. 2. There is empty space in between the particles. 3. The particles are in constant motion. 4. There are forces that act between the particles. Properties of Solid 1. 2. 3. Definite shape – the particles of solid are close to each other in orderly arrangement, and maintain the shape of the solid. Definite volume – particles have strong attraction between each other. Then, the volume is maintained even when transferred to other container. Low compressibility – because of the closeness of the particles to each other, and the lack of space for the particles to move. Properties of Solid 4. High density – completely occupy space. 5. Does not flow easily – particles are packed together and found fixed positions. Properties of Liquid 1. 2. No Definite shape – the particles of liquid are close to each other in but not orderly arranged, Definite volume – particles have strong attraction between each other. Then, the volume is maintained even when transferred to other container. Properties of Liquid 1. 2. 3. Low compressibility – because of the closeness of the particles to each other, and there is little space for the particles to move. Lower density – this is because of the absence of an orderly arrangement between particles even if they are close together. Flow easily – can slide past one another easily. SOLID LIQUID SOLID LIQUID NON-NEWTONIAN LIQUID SOLID Properties of Gas 1. 2. No Definite shape – the particles of gas are far apart from each other. Since its particles can move to any apace available. No Definite volume – the large space in between the particles allows gases to move completely and occupy the given space. Properties of Gas 1. 2. 3. High compressibility – the large spaces between gas particles allows these particles to be easily pushed to come closer to each other. Very Low density – the weak interaction between gas particles results in large spaces in between. Flow easily – can slide past one another easily. SOLID LIQUID GAS PROPERTIES SHAPE DEFINITE NO DEFINITE NO DEFINITE VOLUME DEFINITE DEFINITE DEFINITE COMPRESSIBILITY LOW LOW HIGH DENSITY HIGH LOW VERY LOW FLOW OF PARTICLES DOES NOT FLOW EASILY FLOW EASILY FLOW EASILY Application TITLE: Matter is Matters 1. This is a group activity. 2. Group 1: Solid: ONION 3. Group 2: Liquid: COOKING OIL 4. Group 3: Gas: LPG TITLE: Matter is Matters 1. 2. 3. Describe the properties of your chosen topic. What are the effects of this things to ourselves and to our family? What is the relationship of these things to our topic? Generalization: 1. what term used when we say “anything that occupies space and has mass”. A. mass B. volume C. compatibility D. matter 2. These are three states matter EXCEPT. A. solid B. viscosity C. liquid D. gas Generalization: Solid Liquid Gas Evaluation: Bring out ¼ sheet of paper. ASSIGNMENT #1 : MYtter Day Chart 1. 2. 3. 4. Create chart of matter that mosltly found in your home. Cathegorize them if it is solid, liquid, or gas. Define the three states of matter base on your own undertanding. Your assignment will be passed tomorrow. ASSIGNMENT #1 : MYtter Day Chart 1. Expect everyone to comply. 2. Remeber you are students with the purpose. ASSIGNMENT #1 : MYtter Day Chart MATTER SOLID LIQUID GAS DEFINITION DEFINITION DEFINITION Rubrics for Mytter Day Activity. Ratings Description 10 points the thought is clearly stated, complete details, has accurate work which is catchy and very commendable presentation. 8 points the accuracy of the work is good, the ideas of a solid, liquid, and gas are stated, presentation is good. 6 points the tangency of the information is not quite good, the presentation is not really connected to the topic. 4 points did attain the proper expectation of typical organization of matter as well as the information is not clearly stated. 0 point did not make or comply. 8TH GRADE THANK YOU GRADE 8! CHANGING STATES OF MATTER FUSION VAPORIZATION SOLID LIQUID GAS Mercury is the smallest planet Venus has very high temperatures Saturn is the planet with rings SOLIDIFICATION CONDENSATION TEMPERATURE AND MATTER FUSION Solid SOLIDIFICATION Liquid VAPORIZATION Liquid Liquid Solid CONDENSATION Gaseous Gaseous Liquid 150,000 Big numbers catch your audience’s attention 9H 55M 23S Jupiter's rotation period 333,000 The Sun’s mass compared to Earth’s 386,000 KM Distance between Earth and the Moon WHAT IS ENERGY? VENUS JUPITER Venus is the second planet from the Sun It’s the biggest planet in the Solar System MARS SATURN Despite being red, Mars is a cold place Saturn is a gas giant and has several rings THE HISTORY OF ENERGY MERCURY VENUS MARS JUPITER SATURN Mercury is a small planet Venus is a hot planet Mars is a very cold place Jupiter is the biggest planet It’s composed of hydrogen 1750 1839 1935 1980 2019 1769 NEPTUNE 1887 EARTH 1960 SUN 1991 PLUTO 2050 CERES It’s composed of hydrogen Earth is where we all live It’s the star we all orbit Pluto is a dwarf planet It’s a nice asteroid FORMS OF ENERGY MERCURY VENUS MARS It’s the closest planet to the Sun Venus is the second planet from the Sun Mars is actually a very cold place JUPITER SATURN NEPTUNE Jupiter is the biggest planet of them all It’s composed of hydrogen and helium It’s the farthest planet from the Sun ENERGY TYPES 01 MECHANICAL Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun 02 CHEMICAL Venus is the second planet from the Sun 03 GRAVITATIONAL Mars is actually a very cold place ELECTRIC 04 Jupiter is the biggest planet of them all KINETIC 05 Saturn is composed of hydrogen and helium POTENTIAL 06 Neptune is the farthest planet from the Sun ENERGY CONVERSION LIGHT CHEMICAL CHEMICAL MECHANICAL ELECTRICAL LIGHT ELECTRICAL LIGHT