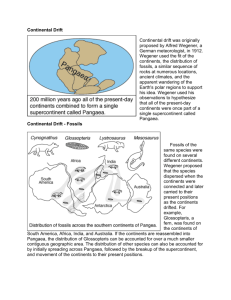
10 Science Quarter 1 Self Learning Module 7 Continental Drift 1 Science - Grade 10 Quarter 1 Self Learning Module 7 – Continental Drift Second Edition, 2021 Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things, impose as a condition the payment of royalties. Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors do not represent nor claim ownership over them. Published by the Department of Education Schools Division Superintendent: Gladys Amylaine D. Sales CESO VI Assistant Schools Division Superintendent: Peter J. Galimba PhD Development Team of the Self Learning Module Writer: Jean P. Baladhay Editor: Christy Ann G. Banguanga Reviewer: Edna Rose P. Gueco Illustrator: Roma Christi A. Ambrocio Layout Artist: Jean P. Baladhay Management Team: Janalyn B. Navarro Edna Rose P. Gueco Ellen G. Dela Cruz Printed in the Philippines by Department of Education – Region VI – Division of Bacolod City Office Address: Telefax: E-mail Address: Rosario-San Juan Sts., Bacolod City 6100 (034) 704-2585 bacolod.city@deped.gov.ph 2 I Need to Know This module was designed and written with you in mind. It is here to help you enumerate the lines of evidence that support plate movement (S10ES –Ia-j-36.6) The scope of this module allows you to use it in many different learning situations. The language used recognizes the diverse vocabulary level of students. The lessons are arranged to follow the standard sequence of the course. But the order in which you read them can be changed to correspond with the textbook you are now using. This module will discuss lesson on Continental Drift. After going through this module, you are expected to 1. enumerate the lines of evidence that support the continental drift, and 2. discuss the evidences that supports the continental drift theory. Lesson Continental Drift Lesson Overview Today, most people know that landmasses on Earth move around, but people haven’t always believed this. It wasn’t until the early 20th century that German scientist Alfred Wegener put forth the idea that the Earth’s continents were drifting. He called this movement Continental Drift. In this module you are going to learn one of Wegener’s greatest observations on continental drift hypothesis. Wegener said that continents move around on Earth’s surface and that they were once joined together as a single supercontinent. While Wegener was alive, scientists did not believe that the continents could move. He proposed that the continents were once united into a single supercontinent named Pangaea, meaning all earth in ancient Greek. He suggested that Pangaea broke up long ago and that the continents then moved to their current positions. He called his hypothesis continental drift. 3 Figure 1. The Break up of Pangaea Besides the way the continents fit together, Wegener and his supporters collected a great deal of evidence for the continental drift hypothesis. For one, identical rocks of the same type and age are found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Wegener said the rocks had formed side-by-side and that the land had since moved apart. Mountain ranges with the same rock types, structures, and ages are now on opposite sides of the Atlantic Ocean. The Appalachians of the eastern United States and Canada, for example, are just like mountain ranges in eastern Greenland, Ireland, Great Britain, and Norway. Wegener concluded that they formed as a single mountain range that was separated as the continents drifted. Ancient fossils of the same species of extinct plants and animals are found in rocks of the same age but are on continents that are now widely separated. Wegener proposed that the organisms had lived side by side, but that the lands had moved apart after they were dead and fossilized. He suggested that the organisms would not have been able to travel across the oceans. For example, the fossils of the seed fern Glossopteris were too heavy to be carried so far by wind. The reptile Mesosaurus could only swim in fresh water. Cynognathus and Lystrosaurus were land reptiles and were unable to swim. 4 Figure 2. Fossils of Ancient Plants and Animals Grooves and rock deposits left by ancient glaciers are found today on different continents very close to the equator. This would indicate that the glaciers either formed in the middle of the ocean and/or covered most of the Earth. Today glaciers only form on land and nearer the poles. Wegener thought that the glaciers were centered over the southern land mass close to the South Pole and the continents moved to their present positions later on. Coral reefs and coal-forming swamps are found in tropical and subtropical environments, but ancient coal seams and coral reefs are found in locations where it is much too cold today. Wegener suggested that these creatures were alive in warm climate zones and that the fossils and coal later had drifted to new locations on the continents. Although Wegener’s evidence was sound, most geologists at the time rejected his hypothesis of continental drift. Scientists argued that there was no way to explain how solid continents could plow through solid oceanic crust. Wegener’s idea was nearly forgotten until technological advances presented even more evidence that the continents moved and gave scientists the tools to develop a mechanism for Wegener’s drifting continents. Activity 1 would allow you to investigate the presented study of Wegener and enumerate the lines of evidence that support the continental drift theory. Let’s get to know them. 5 I Will Do Activity 1: Connect the Continents! Study the illustration of Gondwanaland and read the selection below. Figure 3. Gondwanaland Gondwanaland or “Gondwana” is the name for the southern half of the Pangean supercontinent that existed some 300 million years ago. Gondwanaland is composed of the major continental blocks of South America, Africa, Arabia, Madagascar, Sri Lanka, India, Antartica and Australia. The name “Gondwana” is derived from a tribe in India (Gonds) and “wana” meaning “land of.” It is superficially divided into a western half (Africa and South America) and an eastern half (India, Sri Lanka, Madagascar, Antartica and Australia). How did the continents move apart? Scientists believe that North America drifted toward the northwest. Eurasia turned 20º clockwise as it moved northward. Africa and South America broke apart, forming the Atlantic Ocean. Africa turned counter clockwise and moved eastward, while South America moved westward. India separated from Antarctica and Africa, and then moved northeastward. Then India collided with Asia. Australia, once joined to Antarctica, broke off and drifted eastward. The lines of evidence that support this idea are as follows: The facing coastlines of Africa and South America reasonably match; The fossils found along the matching coastline are similar; 6 Geologic features such as mountain ranges and faults from separate continents line up along the matching coastlines; The type and age of rocks along the matching coastlines are similar; Layers of coal in Antarctica indicate that it was once closer to the tropics; Deposits of glaciers match along the continental coastlines; the direction of ice movement is also consistent. Materials Gondwanaland scissors World Map Puzzle map glue or paste old folder/ card board coloring materials Procedures 1. In your Gondwanaland Puzzle Map, identify and label the continents as South America, Antarctica, Australia, Africa and India. 2. Cut out the continent shapes and try to paste them together in the folder/ card board and match up the fossil evidence to form the Gondwanaland. Note: Be careful in using the scissors. 3. Color the mountain belt and fossil evidence based from the legend provided. Legend: European Flora - Green Glossopteris - Yellow Mesosaurus - Blue Cynognathus - Orange Lystrosauros - Brown Mountain Belt - Black Analysis Questions 1. What is the name of the continent formed by combining all the continents in the puzzle? A. continental drift B. glacier scaring C. Gondwanaland D. plate tectonics 2. What have you noticed with the shape of the continents? A. The continents look like a maze that is connected. B. The continents look like a house with different rooms. 7 C. The continents look like a pie that is cut into equal sizes. D. The continents look like a jigsaw puzzle that seems to fit each other. 3. Which two (2) continents have the most obvious fit of the coastlines? A. Antarctica and Africa B. Africa and North America C. Africa and South America D. South America and Europe 4. How the fossil evidence helped you connect the continents together? A. Different fossils are found along continental margins that appear to join together, that give us clue to separate the continents easily. B. Similar fossils are found along continental margins that appear to join together, that give us clue to separates the continents easily. C. Similar fossils are found along continental margins that appear to join together, that give us clue to connect the continents easily. D. Variety of fossils are found along continental margins that appear to join together, that give us clue to connect the continents easily 5. Which fossil occurs on the most landmasses? A. Cynognathus B. Glossopteris C. Lystrosaurus D. Mesosaurus I Will Practice Unscramble the letters to form the correct terms related to continental drift. Write your answer on a separate sheet. 1. an extinct mammal-like reptile whose fossils are only found in South Africa and South America 2. the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia 3. a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. 4. the southern half of the Pangaean supercontinent 5. any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age I Will Apply 8 SNOGTHUANYC RAUSERIA NEAGAAP GANANDNDALOW LISSOF The figure shows Earth’s ancient supercontinent as it appeared about 300 million years ago, according to Alfred Wegener. Write the letter that represents each of the following present-day continents. A B D C F E _____ Africa _____Antarctica _____ Europe and Asia _____ North America _____Australia _____ India _____ South America References 9 Alumaga, M. et al. 2014. Science and Technology 10. Quezon City: Vibal Group, Inc. pages 20-21 Decella, C. 2009. High School Science Today. Marikina City: Diwa Learning Systems Inc. pages 199-200 https://letstalkscience.ca/educational-resources/backgrounders/continental-drift-andplate-tectonics (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) http://www.phschool.com/itext/sci_exp/iText/products/0-13-1812432/ch1/ch1_s3_3.html (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/historical.html (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://wps.prenhall.com/esm_tarbuck_escience_11/32/8321/2130415.cw/content/in dex.html (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://www.google.com/search?q=pangaea&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2a hUKEwjg_qbubfpAhXG62EKHW58CUYQ_AUoAXoECBQQAw&biw=1366&bih=629 #imgrc=6tv18SWaPZIGIM (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://www.yourdictionary.com/pangaea (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://www.npsd.k12.nj.us/cms/lib04/NJ01001216/Centricity/Domain/221/Pangaea %20lab%20activity%202016.pdf (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pangaea_colors.svg (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://www.countries-ofthe-world.com/continents-of-the-world.html (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pangaea_to_present.gif (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Laurasia-Gondwana.svg (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/vsc/file_mngr/file-139/This_Dynamic_PlanetTeaching_Companion_Packet.pdf (Accessed Date: June 10, 2020) https://www.npsd.k12.nj.us/cms/lib04/NJ01001216/Centricity/Domain/221/Pangaea %20lab%20activity%202016.pdf (Accessed Date: June 10, 2020) https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Pangaea_continents.svg (Accessed Date: August 14, 2021) Answer Key 11 I Will Do 1. C- Gondwanaland 2. D- The continents look like jigsaw puzzle that seems to fit each other. 3. C - Africa and South America 4. C -Similar fossils are found along continental margins that appear to join together, that give us clue to connect the continents easily. 5. B -Glossopteris I Will Practice 1. Cynognathus 2. Eurasia 3. Pangaea 4. Gondwanaland 5. Fossil Gondwanaland Puzzle Map 12 I Will Apply D Africa E Antarctica G Australia A Europe & Asia F India B North America C South America Template No. 1- Gondwanaland Puzzle Map 13 Written Assessment No. 7 Worksheet Concept Check Name: _______________________________ Grade & Section: ___________ Part I. Multiple Choice. Read each item carefully. Select the letter of the best answer 1. Which evidence did Wegener NOT use to support his idea of continental drift? A. The thickness in the layers of ice in Antarctic. B. Rock strata on different continents lined up when coastlines were matched up. C. Mountain ranges on different continents lined up when coastlines were matched up. D. Fossils of plants and animals in climates where their survival would have been impossible. 2. Which is the supercontinent landmass that formed million years ago? A. Australia B. Eurasia C. Pantallasa D. Pangaea 3. How do the mountain ranges located on both side of Atlantic Ocean supports the continental drift theory? A. They have the same height and width. B. They are just separate mountain ranges. C. They both have ancient fossil and coal seams. D. They both have the same rock types, structures and ages. 4. Which is the greatest contribution of Alfred Wegener in science that paved way in the study of plate movement? A. Cell Theory B. Big bang Theory C. Geocentric Theory D. Continental Drift Theory 5. According to Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift, A. The continents do not move. B. Earth is slowly cooling and shrinking. C. Earth’s surface is made up of seven major landmasses. D. The continents were once joined together in a single landmass. 6. Most geologists rejected Alfred Wegener’s idea of continental drift because A. The geologists were afraid of a new idea. B. Wegener used different evidences to support his hypothesis. C. Wegener was interested in Earth was like millions of years ago. D. Wegener could not identify a force that could move the continents. 14 7. In order to support his hypothesis, Alfred Wegener provided evidence from _____________, traces of ancient organisms in rock. A. climate B. fossils C. landmasses D. rocks 8. Which is the fern-like fossil used by Wegener to prove that the continents used to be part of a supercontinent? A. Cynognathus B. Glossopteris C. Lystrosaurus D. Mesosaurus 9. Which glacier scars were found in Africa that proved the hypothesis of Wegener correct? A. The continents have not moved. B. Africa has always been near the equator. C. Africa had experience sea floor spreading. D. Africa was once in an area of the Earth that had a very cold climate. 10. Which was Wegener's continental drift idea? A. The continents have been increasing over time. B. The continents have moved slowly apart to their current locations. C. The continents have always been located at their current locations. D. The continents are moving slowly together from their current locations. Part II. Enumeration. The following are the lines of evidence that support plate movement: 1 2 3 4 5 6 Reflection Question: Since the continents are still drifting apart, what do we expect to happen million years from now? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 15 Answer Key to Concept Check FOR TEACHER’S USE ONLY. Do not attach this portion to the SLM for students. I. Multiple Choice 1. A 2. D 3. B 4. D 5. D 6. D 7. B 8. B 9. D 10. B II. Enumeration 1. The facing coastlines of Africa and South America reasonably match 2. The fossils found along the matching coastlines are similar 3. Geologic features from separate continents line up along the matching coastlines 4. The type and age of rocks along the matching coastlines are similar 5. Layers of coal in Antarctica indicate that it was once closer to the tropics 6. Deposits of glaciers match along continental coastlines; the direction of ice movement is also consistent. Reflection A million years from now, we would expect that the position of the continents will change. For inquiries or feedback, please write or call: Department of Education – SDO-Bacolod City (Office Address): Rosario-San Juan Sts., Brgy. 14, 6100, Bacolod City Telefax: Email Address: bacolod.city@deped.gov.ph 16