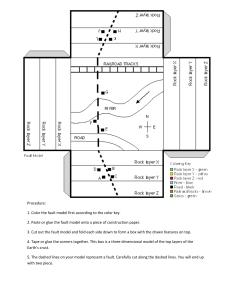
Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Division of Negros Oriental Mabinay District I Cansal-ing Provincial Community High School Senior High School Name: ___________________________ Grade/Section: _______________ Score: ______ Date: ________________ Time started: _______ Time finished: ________ Structure of the Earth Activity 1: Identifying the Earth’s Layers Duration: 1 hour A. Directions: Use the words below to label the Earth’s layers. Using crayons, color each layer with colors matching the labels. asthenosphere oceanic crust continental crust mantle inner core outer core B. Write the layer of the Earth that is being described. 1. Upper part of mantle; partially molten or deforms liquidly like “plastic under pressure” - _________________ 2. Consists mostly of iron and nickel; under intense pressure, which keeps it solid despite high temperatures. - ____________________ 3. Thickest layer; composed of dark and dense rock - ___________________ 4. Outermost layer composed of silica-rich rocks - _____________________ 5. Thinner part; made of dark, silica-poor rocks like basalt - ___________________ 6. Consists mostly of iron and nickel; not under enough pressure to be solid, so it is liquid - ____________________ Prepared by : Andre Ariel B. Cadivida Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Division of Negros Oriental Mabinay District I Cansal-ing Provincial Community High School Senior High School Name: ___________________________ Grade/Section: _______________ Score: ______ Date: ________________ Time started: _______ Time finished: ________ Movement of the Earth’s Crust Directions: Draw and label correctly the three main types of faults. NORMAL FAULT REVERSE FAULT STRIKE-SLIP FAULT Prepared by : Andre Ariel B. Cadivida Republic of the Philippines Department of Education Division of Negros Oriental Mabinay District I Cansal-ing Provincial Community High School Senior High School Directions: Complete the chart below to distinguish between each of the three main types of faults. Write your answers in the table below. Type of Fault Type of Force (compression, tension or shearing) Normal Reverse Strike-slip Prepared by : Andre Ariel B. Cadivida Vertical or horizontal motion Type of plate boundary Types of Earthquakes (shallow, intermediate, deep or all)