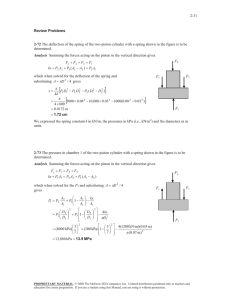
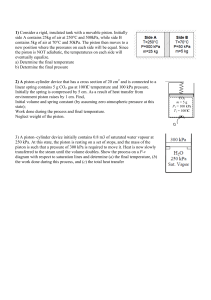
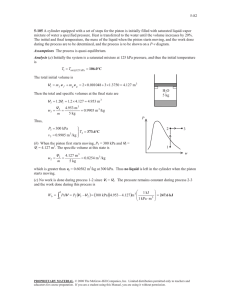
1) Consider a rigid, insulated tank with a movable piston. Initially side A contains 25kg of air at 250°C and 500kPa, while side B contains 5kg of air at 70°C and 50kPa. The piston then moves to a new position where the pressures on each side will be equal. Since the piston is NOT adiabatic, the temperatures on each side will eventually equalize. a) Determine the final temperature b) Determine the final pressure 2) A piston-cylinder device that has a cross section of 20 cm2 and is connected to a linear spring contains 5 g CO2 gas at 100°C temperature and 100 kPa pressure. Initially the spring is compressed by 5 cm. As a result of heat transfer from environment piston raises by 1 cm. Find, Initial volume and spring constant (by assuming zero atmospheric pressure at this state); Work done during the process and final temperature. Neglect weight of the piston. CO2 m=5g P1 = 100 kPa T1 = 100°C CO2 m = 4.748 g Q 3) A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.8 m3 of saturated water vapour at 250 kPa. At this state, the piston is resting on a set of stops, and the mass of the piston is such that a pressure of 300 kPa is required to move it. Heat is now slowly transferred to the steam until the volume doubles. Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines and determine (a) the final temperature, (b) the work done during this process, and (c) the total heat transfer Solution 1 Solution 2 : CO2 can be assumed to be an ideal gas, as P<<Pcr and T>>Tcr. a) V1 = mR T1 0.005 × 0.1889 × 373 = = 0.00352 m3 P1 100 Fyay = 100 × 0.002 = 0.2 kN k= b) F 0 .2 = = 4 kN / m x1 0.05 P2 = P1 + k ∆x 4 × 0.01 = 100 + = 120 kPa Ap 0.002 V2 = V1 + ∆V = V1 + Ap ⋅ ∆x = 0.00352 + 0.002 × 0.01 = 0.00354 m 3 W12 = 120 + 100 P2 + P1 × ∆V = × 0.00002 = 0.0022 kJ 2 2 Solution 3 : 3. A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.8 m3 of saturated water vapour at 250 kPa. At this state, the piston is resting on a set of stops, and the mass of the piston is such that a pressure of 300 kPa is required to move it. Heat is now slowly transferred to the steam until the volume doubles. Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines and determine (a) the final temperature, (b) the work done during this process, and (c) the total heat transfer