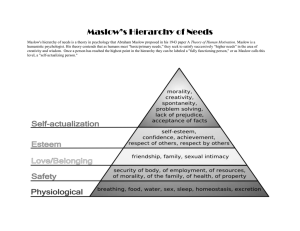
Chapter 9 Abraham Maslow: Needs-Hierarchy Theory Abraham Maslow Work Cited • At a time when most psychologists focused aspects of human nature that were considered abnormal, Maslow shifted to focus to look at the positive sides of mental health • His interest in human potential, seeking peak experiences and improving mental health by seeking personal growth had a lasting influence on psychology • He wrote many books including two of his most famous, Motivation and Personality and Toward a Psychology of Being • Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a theory that describes the pattern that human motivations traditionally go through. • The hierarchy of needs is portrayed in a pyramid with 5 levels of human needs. • These human needs are, in order, physiological needs, safety needs, social belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. • The base of the pyramid is the largest and describes the most fundamental needs. The most fundamental and basic layers of the pyramid are “deficiency needs”. Deficiency needs must be met first before moving up the pyramid or else an individual may feel anxious and tense, not necessarily experience physical indications. • Maslow’s theory also suggests that the most basic level of needs must be met before the individual will strongly desire the secondary needs. • • • • • • • STRENGTHS Provides a basic framework for human motivation. Easy to understand. Can be used in many different settings. Paved the way for many other motivational theories. WEAKNESSES Theory assumes that all people experience these needs in the same order, failing to recognize cultural and individual differences. • Low generalization across individuals. • Difficult to test empirically. • Many contradictions.