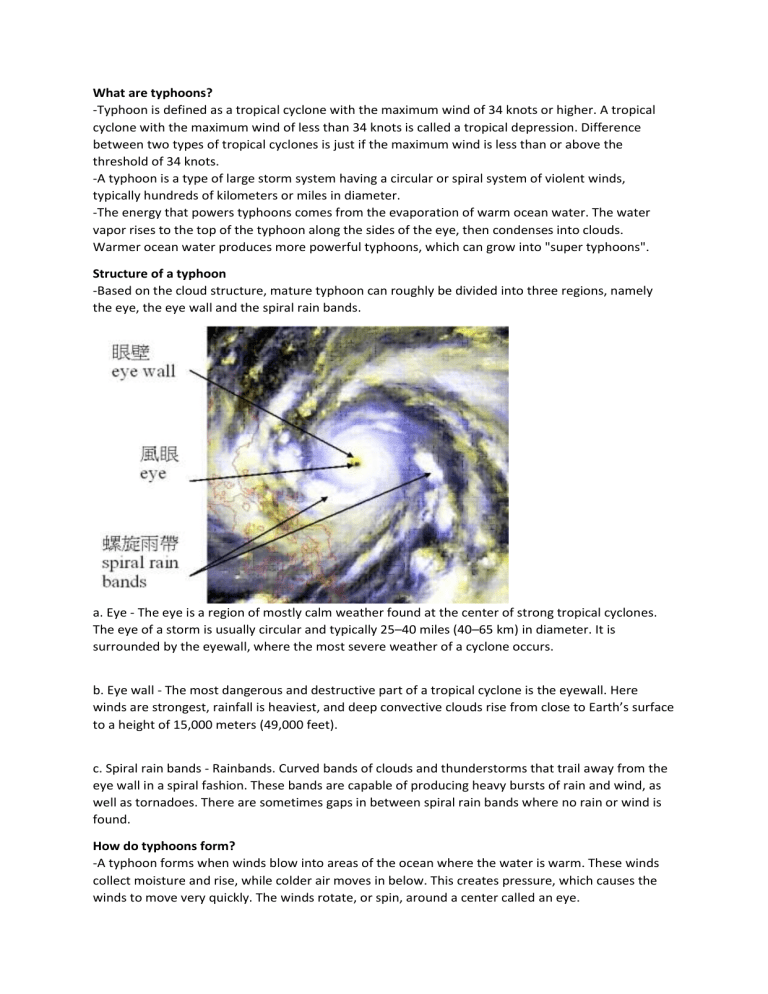
What are typhoons? -Typhoon is defined as a tropical cyclone with the maximum wind of 34 knots or higher. A tropical cyclone with the maximum wind of less than 34 knots is called a tropical depression. Difference between two types of tropical cyclones is just if the maximum wind is less than or above the threshold of 34 knots. -A typhoon is a type of large storm system having a circular or spiral system of violent winds, typically hundreds of kilometers or miles in diameter. -The energy that powers typhoons comes from the evaporation of warm ocean water. The water vapor rises to the top of the typhoon along the sides of the eye, then condenses into clouds. Warmer ocean water produces more powerful typhoons, which can grow into "super typhoons". Structure of a typhoon -Based on the cloud structure, mature typhoon can roughly be divided into three regions, namely the eye, the eye wall and the spiral rain bands. a. Eye - The eye is a region of mostly calm weather found at the center of strong tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is usually circular and typically 25–40 miles (40–65 km) in diameter. It is surrounded by the eyewall, where the most severe weather of a cyclone occurs. b. Eye wall - The most dangerous and destructive part of a tropical cyclone is the eyewall. Here winds are strongest, rainfall is heaviest, and deep convective clouds rise from close to Earth’s surface to a height of 15,000 meters (49,000 feet). c. Spiral rain bands - Rainbands. Curved bands of clouds and thunderstorms that trail away from the eye wall in a spiral fashion. These bands are capable of producing heavy bursts of rain and wind, as well as tornadoes. There are sometimes gaps in between spiral rain bands where no rain or wind is found. How do typhoons form? -A typhoon forms when winds blow into areas of the ocean where the water is warm. These winds collect moisture and rise, while colder air moves in below. This creates pressure, which causes the winds to move very quickly. The winds rotate, or spin, around a center called an eye.